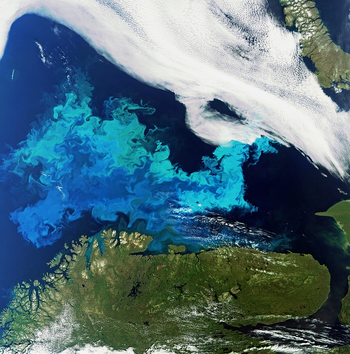
Plankton bloom
In this article, the term 'plankton' is used indiscriminately for 'phytoplankton' and focuses on small photosynthesizing organisms, especially microalgae and cyanobacteria (see Marine Plankton). Plankton bloom is a short-lasting strong increase of a plankton population. The concentration of plankton multiplies a thousand or even a million fold and collapses shortly after. A quantitative definition of plankton blooms in terms of cell, biomass, or chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) concentration depends on the plankton species and environmental conditions. Plankton blooms are a worldwide phenomenon that occurs when the water temperature is favorable and light and nutrients are sufficiently available. Due to eutrophication of the coastal waters, plankton blooms have become more frequent. Global warming may also play a role. This article introduces some elementary notions that provide insight into the phenomenon of plankton blooms. A simplified model of plankton bloom dynamics is presented in Appendix A.
Contents
Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton are aquatic organisms that grow through photosynthesis. Many thousands of different phytoplankton species are known (Sournia et al., 1991[1]; Andersen, 1992[2]). The most common phytoplankton species in seawater are diatoms, flagellates and cyanobacteria. The smallest species (picophytoplankton, size < 2 micron, consisting mostly of cyanobacteria) have the highest nutrient-uptake efficiency and are therefore most abundant in nutrient-poor ocean waters, whereas the larger diatoms tend to dominate the phytoplanktonic biomass in nutrient-rich waters (Edwards et al., 2011[3]; Burson et al., 2018[4]). Blooms of large phytoplankton species (diatoms) only occur when the temperature does not exceed a critical limit of about 15oC (Cloern, 2018[5]). Plankton blooms can extend over large areas, as illustrated in Fig. 1.
All phytoplankton species grow by absorbing dissolved CO2 under the influence of light and thereby emit oxygen. The chemical equation representing primary production by photosynthesis, derived empirically from the average composition of oceanic phytoplankton, can be written as (Redfield, 1958[6])
[math]106 \, CO_2 + 16 \, HNO_3 + H_3PO_4 + 122 \, H_2 O + \mathrm{trace} \; \mathrm{elements} \; \mathrm{and} \; \mathrm{vitamins} + \mathrm{light} \rightarrow C_{106}H_{263}O_{110}N_{16} P + 138 \, O_2 . \qquad (1) [/math]
Marine phytoplankton contributes almost half to the total oxygen production on Earth (Behrenfeld et al., 1998[7]). Phytoplankton species are called 'autotrophs' or 'primary producers', because they are able to feed and produce organic material from mineral substances. They are a food source for other marine organisms, zooplankton in the first place. However, the distinction between phytoplankton and zooplankton is often not clear, as many species belonging to these plankton groups are 'mixotrophs': they are phototrophic but can also ingest particulate or dissolved organic matter (Flynn et al., 2013[8]). For more details about the different plankton species, see the article Marine Plankton.
The size of a plankton bloom is generally expressed in terms of organic carbon weight, [math]g \, C[/math]. The value can be obtained by taking samples and measuring the ash-free dry biomass content (see In situ monitoring of eutrophication, Sampling tools for the marine environment). However, it is most usual to estimate phytoplankton biomass by quantifying chlorophyll a, the photosynthetic pigment common to all types of phytoplankton. It can be determined by various optical techniques due to its fluorescence properties. Techniques are described in the articles Plankton remote sensing, Differentiation of major algal groups by optical absorption signatures. A limitation of remote sensing is that only surface blooms are observed whereas below-surface blooms my also occur (Blondeau-Patissier et al., 2014[9]).
Conditions for growth: light, temperature and nutrients
Besides CO2 and sunlight, phytoplankton needs certain nutrients for growth. These are primarily the minerals nitrogen N, phosphorus P and silicon Si (mainly in the form of dissolved salts, nitrate, ammonium, phosphate and silicate, see Nutrient conversion in the marine environment). Small amounts of trace metals (Fe, Mn, Zn, Cu, Ni, ..) and certain vitamins are also required. Lack of any of these nutrients limits the growth of phytoplankton. Nutrient concentrations in the ocean are generally so low that phytoplankton species in the ocean are in fierce competition to exploit these scarce resources. The ratio in which the primary nutrients are needed has been determined in the past at 106 C: 16 N: 1 P, the so-called Redfield ratio, according to Eq. (1). However, the ratio varies by species (Davidson et al., 2012[10]), allowing some species to grow better or less well than others under certain conditions. Growth further depends critically on light and temperature (Bissinger et al., 2008[11]; Boyd et al., 2013[12]). Here too, the optimum values are specific to each plankton species.
Phytoplankton can grow under favorable conditions unrestrained as long as there is no restriction in the availability of the necessary nutrients and light. Population growth occurs through division of the parent cell, with the formation of two or more offspring. The cell division frequency for each species is different and depends on temperature and light; it can happen every few hours, but also every few days. Since this applies to each individual in the population, growth has an exponential character. Huge population growth is therefore possible in a short time.
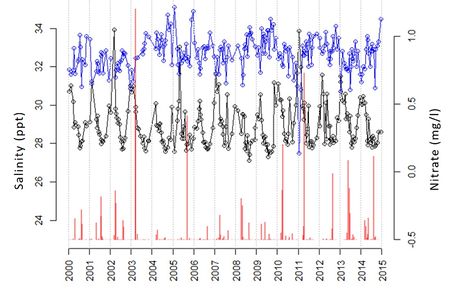
An example of the explosive short-lived nature of plankton blooms is illustrated in Fig. 2, showing a multi-year observation record of the diatom Chaetoceros socialis at a measuring station in the North Sea 10 km north of the Dutch Wadden island of Terschelling. The figure also shows observations of the nitrogen concentration (dissolved nitrate) and the salinity at the measuring point.
The conditions for plankton blooms vary with the seasons. This is not only due to temperature and light. In the winter, nutrient-rich organic material is stirred from the seabed. Therefore, nutrient concentrations are often highest in early spring. With increasing light and temperature, the conditions for plankton bloom become optimal; the largest plankton blooms therefore occur in general during springtime. The strongest plankton growth takes place in the upper water layer where light penetrates best, the so-called euphotic zone. Vigorous mixing over the water column is less favorable because it moves part of the phytoplankton into deeper water layers, where growth is limited due to a lack of light. In the oceans, plankton blooms generally start after the winter at the time that the downward surface layer mixing comes to an end[14]. Vertical mixing is counteracted by density stratification, whereby water with a higher temperature and/or lower salinity floats on top of colder/saltier seawater. Organic detritus, because of its specific density, tends to be collected at the interface zone (picnocline), where nutrients are released after mineralization of the detritus. This creates ideal conditions for the development of strong plankton blooms, especially blooms of mixotrophic plankton that feed both on nutrients and organic material (Berdalet et al., 2014[15]; Sigman and Hain, 2012[16]). In the open ocean, chlorophyll concentrations are typically highest at the bottom of photic layer, called subsurface chlorophyll maximum, around 100 m below the surface, see Open ocean habitat.
The expected future changes in ocean conditions (increase in temperature, stratification, eutrophication and acidity) can be beneficial for mixotrophic phytoplankton and unfavorable to diatoms (Glibert, 2020[17]). Measurements further show that when the seawater temperature increases, the biomass and productivity of phytoplankton decreases, while a shift takes place from larger phytoplankton species (haptophytes) to smaller species (cyanobacteria) (Van de Poll, 2013[18]).
Other factors that condition plankton blooms
Inter-species competition
The resources for optimal growth (nutrients, light, temperature) are not the same for different plankton species. As these resources are highly variable (in space, in time), myriad species with different adaptations have evolved (Hutchinson, 1961[19]). The species that uses the instantly available resources with the highest efficiency will experience the strongest growth and dominate other phytoplankton species. Therefore, the dynamics of plankton blooms cannot be estimated from the average reproduction rate of the various plankton species. A common assumption is that the composition of the plankton population adapts rapidly, so that optimal use is made of the growth potential provided by the available resources (Glibert, 2017[17]). For example, field observations by Philippart et al. (2007[20]) in the eutrophic Wadden Sea show that the composition of the plankton population changes according to the ratio between different nutrients. In this study, as well as in the tropical Godavari estuary (Bharathia et al. 2018[21]), it was observed that large phytoplankton species (diatoms) are favored in waters when the N:P ratio is relatively low, while high N:P ratios favor small species (flagellates, cyanobacteria).
The composition of phytoplankton populations depends on many other factors. For example, diatoms require sufficient dissolved Si and have a growth optimum at lower temperatures than many cyanobacterial and flagellate species (Anderson, 2000[22]). The form in which N is present (nitrate or ammonium) also plays a role[17]; diatoms and dinoflagellates prefer nitrate (NO3-) while small flagellates and picocyanobacteria grow on ammonium (NH4+). Diatoms have a high growth rate in nutrient-rich waters, while small species (e.g. cyanobacteria) are strong competitors when nutrients and light are deficient. Coccolithophores (e.g. Emiliana huxleyi) are often dominant in the sunlit oligotrophic upper layer of the stratified subtropical ocean, where their disadvantage of high energy requirements for the production of calcium carbonate scales (coccoliths) is compensated by very efficient nutrient uptake[23].
Another adaptation influencing the competition between phytoplankton species for light and nutrients is the ability of certain plankton species to migrate towards zones that offer the best growth conditions. For example, dinoflagellates can move up and down for nutrient uptake in nutrient-rich deeper water and for photosynthesis in sunlit surface water. In low-turbulence environments, small mobile plankton (e.g. flagellates) can outcompete large nonmotile species (e.g. diatoms), that would sink out of the photic zone in the absence of turbulence. In stratified water where turbulence is suppressed, flagellates typically constitute the bulk of the population (Margalef, 1978[24], Klausmeier and Litchman, 2001[25]). Flagella and efficient nitrogen uptake are special adaptations that enable dinoflagellates to dominate in nutrient-poor, low-turbulence waters, as 'specialist' or 'K-strategy' species. This contrasts with fast-growing ('r-strategy') diatoms that strive in nutrient-rich turbulent waters (Glibert, 2016[23], see also r/K selection theory). In nutrient-poor, sunlit surface waters, typical for the subtropical ocean, some microbial species (e.g. the cyanobacterium Trichodesmium) are capable of fixing dissolved nitrogen gas N2. This crucial adaptation, called diazotrophy, is a major driver of the primary productivity in oligotrophic oceans.
In one modeling approach, the composition of the phytoplankton community is determined by maximizing net primary production at each time step, depending on the use of available nutrients and light at a given temperature by the different plankton species. The use of these resources during this time step influences the new available light (self-shading effect) and nutrients for which the composition of the phytoplankton population is optimized at the next time step. These models assume that the population at each time step is always tuned to optimal resource use, compatible with maximal growth rates. Numerical simulations by Los and Wijsman (2007[26]) of plankton blooms based on this assumption generally show fair similarity to field observations.
A complicating factor is that phytoplankton can adjust the rate at which different resources are used. For example, by spending more energy on capturing light at the expense of less efficient nutrient uptake, or vice versa. This allows optimal growth to be achieved in depth zones with the most favorable trade-off between light and nutrients. The theory of Pahlow (2005[27]) explains the aforementioned subsurface chlorophyll maximum in the open ocean with this mechanism.
Predation
The size of plankton populations is limited not only by shortage of nutrients, but also by mortality and predation. Phytoplankton are an essential food source for many organisms in the sea. The main phytoplankton grazers are zooplankton and mixotrophic species, which come in different shapes and sizes. The smallest zooplankton (micro-zooplankton, mainly flagellates, ciliates and mixotrophic phytoplankton), while grazing on the smallest phytoplankton species, can adapt quickly to changes in the prey population and thus largely controls the size of picophytoplankton blooms. This is less the case for the larger zooplankton, that consists mainly of herbivore copepods in the oceans and of filter feeding benthos and benthic larvae in estuarine environments. Blooms of larger phytoplankton species (diatoms, dinoflagellates), that dominate in eutrophic and nitrogen-controlled conditions[20], are therefore less sensitive to grazer dynamics. The lesser grazing sensitivity of dinoflagellates and some other swimming phytoplankton can also be due to flight behavior (Harvey and Mende-Deuer, 2012[28]) or a lower nutrient content of larger phytoplankton (Branco et al., 2020[29]). Digestion of phytoplankton by large zooplankton species leads to excretion of organic material in the form of fecal pellets. In the deep ocean, fecal pellets sink to the bottom. In this way CO2 and nutrients are removed from the marine ecosystem - actually just the small part that is not mineralized during sinking. In shallow coastal waters, fecal pellets are mineralized on the bottom where the released nutrients are exploited by the benthic ecosystem. Organic bottom material that is stirred up by waves and currents provides nutrients to the pelagic phytoplankton. Organic matter and nutrients are stored in the soil in areas where net sedimentation occurs, but otherwise the recycling of nutrients in coastal waters is faster than in the ocean.
Mortality
Phytoplankton mortality is largely due to viral infections (Baudoux, 2007[30]). In the (sub)tropical ocean, the contribution of viruses to the decay of plankton blooms is similar or even superior to the impact of grazing, whereas grazing dominates at higher latitudes (Mojica et al., 2016[31]). The mortality rate of phytoplankton exceeds in some cases the growth rate, but is generally lower. Most dead plankton are too small to sink to the bottom. Part of the dead plankton is broken down by bacteria in the euphotic zone, where the released nutrients fuel new blooms. Another part aggregates with other organic and inorganic particles until reaching a mass that makes the aggregates sink to the bottom. In the oceans, these sinking aggregates (called 'marine snow') are sequestered in deep water layers, see Ocean carbon sink. In addition to gravitational sinking, downward transport of organic matter in the ocean also occurs in downwelling regions (see the article Shelf sea exchange with the ocean) and through episodic localized subduction currents (Llort et al., 2018[32]). The total ocean carbon sink due to these different processes is in the order of ¼ of the total global carbon emissions (De Vries et al., 2019[33]).
Consequences of plankton blooms
Increased fishery yields
There is ample evidence that eutrophication of coastal waters has led to an increase in primary production and an increase in the food supply for higher trophic species. Although there is no one-one correspondence between the biomasses of different trophic levels, a strong increase in fishing yields in eutrophicated coastal waters can be attributed to this increased primary production (Nixon, 1988[34]; Nixon and Buckley, 2002[35]).
Oxygen depletion
Plankton blooms operate by photosynthesis and therefore produce a lot of oxygen. The reverse happens when the bloom decays; oxygen is extracted from the water when the organic material is mineralized (the work of bacteria). The oxygen demand of a collapsing plankton bloom can be very high - see Possible consequences of eutrophication. Dissolved oxygen will be depleted if the water is not flushed or aerated fast enough, a situation called anoxia. This is a common phenomenon in lakes and microtidal seas, but it can also occur in lagoons and estuaries. In cases where differences in temperature or salinity between upper and lower water layers stratify the water column, anoxia can easily arise in the lower water layer (see Estuarine turbidity maximum). This is on the one hand due to mineralization of sinking organic material, and on the other hand due to suppression of turbulent mixing with water of the more aerated and oxygen-rich top layer. Most organisms cannot live in anoxic water and die, and thus aggravate anoxia. Oxygen depletion is often an indirect result of eutrophication, that stimulates the formation of plankton blooms in the upper water layer.
Harmful algae
Numerous algae species (a few hundred of the many thousands of species) produce toxic substances and are therefore called harmful algae. Many aquatic (and non-aquatic) organisms are poisoned when they ingest large amounts of these toxic algae. This can happen when a bloom of harmful algae develops. Marine aquaculture is particularly affected by toxic algal blooms; consumers are poisoned by toxins that are bio-concentrated in exposed fish and shellfish (which are not affected themselves). Harmful algal blooms (HABs) are a natural and frequent phenomenon, similar to non-harmful plankton blooms (Smayda, 1997[36]). The chemicals produced by harmful algae (e.g. certain species of diatoms and dinoflagellates) are thought to be a defence mechanism against predators, either through toxin production or feeding deterrence, see Chemical ecology and phytoplankton and Functional metabolites in phytoplankton. However, some doubts exist about the effectiveness of these defence mechanisms to reduce grazing pressure by zooplankton (Zigone and Wyatt, 2004[37]). There is some evidence that the size and frequency of harmful algal blooms are increasing (Hallegraeff, 1993[38]). Some theories relate the increase in toxic algal blooms to eutrophication, in particular in situations where the natural nutrient ratio is disturbed; other theories point to enhanced stratification, acidity and global warming (Glibert, 2020[17]). However, a clear explanation of the causes is still lacking (Anderson, 2012[39]; Berdalet et al., 2016[40]; Wells et al., 2020[41]).
Occurrence of plankton blooms
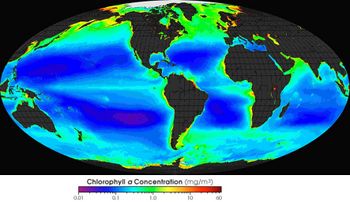
Plankton blooms require light and nutrient-rich water. Nutrient-rich surface waters occur naturally in the so-called upwelling zones, areas where deep ocean water rises up (see the articles Ekman transport and Shelf sea exchange with the ocean). Major upwelling zones are located along the Atlantic coast of Africa and the Pacific coasts of California and south America, where ocean surface currents are bent off the coast by the effect of Earth's rotation. Net primary productivity NPP (gross production minus respiration) can exceed 1000 [math]g \, C m^{-2} y^{-1}[/math], which is much more than the ocean average of about 150 [math]g \, C m^{-2} y^{-1}[/math][42].
However, the highest nutrient concentrations are not found in the oceans, but in coastal waters, especially in estuaries and lagoons (Howarth, 1988[43]), mainly due to release of nutrients by human activities (see e.g. Eutrophication in coastal environments). Most of the primary production occurs during seasonal or episodic plankton blooms. However, the annual NPP in coastal systems is not exceptionally high; values range typically from 50 to 400 [math]g \, C m^{-2} y^{-1}[/math]. Large spatial differences occur within estuaries as well as strong interannual fluctuations, but on average the NPP seldom exceeds 500 [math]g \, C m^{-2} y^{-1}[/math] (Cloern et al., 2014[44]). A major reason is the greater importance of light as a limiting factor for plankton growth than nutrient deficiency, especially in deep (often dredged) estuaries. This is due to the turbidity of the water in estuaries and lagoons and along the adjacent coast (see the articles Estuarine turbidity maximum and Which resource limits coastal phytoplankton growth/ abundance: underwater light or nutrients?). A model study by Liu et al. (2018[45]) shows that in well-mixed turbid estuaries, plankton blooms are restricted to the zone downstream from the estuarine turbidity maximum.
The role of river discharge on plankton blooms in estuaries is ambiguous. High discharges supply nutrients, but they also flush plankton out of the estuary. Observations by McSweeney et al. (2016[46]) in the Delaware show that high river discharges generate stratification with favorable light conditions for plankton blooms in the surface layer. In estuaries with large intertidal flats, pelagic plankton have to compete for nutrients with benthic plankton (De Jonge and van Beusekom, 1992[47]). Comparing observations from many estuaries, it appears that the total annual decay of organic matter in most estuaries is larger than the gross primary production. This means that, unlike other marine systems, these estuaries are net producers of CO2 (Caffrey, 2004[48]; Gattuso et al., 1998[49]).
Appendix A: Simplified plankton bloom model
The occurrence of plankton blooms, with rapid emergence and equally rapid disappearance, is a prominent feature of eutrophication. This appendix provides a qualitative explanation of plankton bloom dynamics, following the paper by Huppert et al. (2002[50]). The explanation is based on a simple model in which an plankton bloom is related to the available amount of a certain nutrient. This nutrient is assumed to be essential for the growth of the plankton population, but to be present in such a low concentration that it limits the growth of the population. Because the uptake of the nutrient by the plankton decreases the nutrient concentration, the population growth and the nutrient concentration form together a self-regulating feedback system. The different processes that play a role are set out below. The model is meant to enable a better understanding of the plankton bloom process; it is too simple for application to real field situations because many of the processes discussed previously are ignored. A particularly important missing feature is the coupled dynamics of grazing zooplankton that curbs phytoplankton growth and thus delays nutrient depletion.
We call [math]P(t)[/math] the biomass, representing the size of the plankton population at time [math]t[/math] in a certain volume [math]V[/math] of the sea, and [math]N(t)[/math] the average nutrient concentration in this volume. The temporal variation of the plankton biomass, [math]dP/dt[/math] and the nutrient concentration, [math]dN/dt[/math], are regulated according to the following assumptions and approximations:
- Nutrient uptake [math]B[/math]. The uptake depends on the plankton biomass [math]P[/math] and on the nutrient concentration [math]N[/math]. If the nutrient concentration is low (limiting), linearity of the dependence in both [math]P[/math] and [math]N[/math] is a reasonable assumption, [math]B=\beta (t) \, P \, N[/math]. The uptake efficiency [math]\beta(t)[/math] depends on other environmental conditions for plankton growth, in particular temperature and light. Nutrient uptake increases the plankton biomass by [math]B_P=\beta_P(t) \, P \, N[/math] and decreases the nutrient concentration by [math]B_N=-\beta_N(t) \, P \, N[/math]. The ratio [math]\rho=\beta_N(t)/\beta_P(t)[/math] is constant. Saturation of the nutrient uptake (i.e. [math]B[/math] independent of [math]N[/math] when [math]N[/math] is abundant) is ignored.
- Biomass decay with nutrient restitution [math]G[/math]. The plankton biomass decreases by respiration, mortality and mineralization of plankton detritus, [math]G_P = - \gamma (t) \, P[/math], while the nutrient concentration increases with restitution of nutrient by [math]G_N=\rho \gamma (t) \, P[/math]. It is assumed that respiration and mineralization are quasi-instantaneous processes; their efficiency for nutrient restitution is expressed by the rate factor [math]\gamma(t)[/math].
- Nutrient loss [math]S[/math] related to the loss of plankton biomass by predation, sinking to the bottom and export, and therefore assumed proportional to the plankton biomass: [math]S=- \sigma (t) \, P[/math]. Predation by zooplankton depends not only on the plankton biomass but also on the biomass of zooplankton. The zooplankton population itself depends on the plankton biomass and increases when the plankton biomass is high. However, zooplankton dynamics is ignored in the model.
- Nutrient loss [math]A=-\alpha (t) \, N[/math], as a result of biogeochemical processes that limit the availability of nutrients for uptake by plankton.
- Nutrient supply from external sources, [math]Q[/math]. Major external nutrient supplies (partly in the form of organic material) are coming from rivers, atmospheric deposition and stirring up of organic bed material.
We focus on the period in which the plankton population experiences rapid growth and rapid decline. This period is assumed so short that the factors [math]\alpha, \beta, \gamma, \sigma[/math] can be considered approximately constant. Collecting the expressions of the factors influencing the temporal variation of plankton population, [math]dP/dt[/math] and the nutrient concentration, [math]dN/dt[/math], we arrive at the equations:
[math]dP/dt = B_P+G_P+S_P = (\beta \, N - \gamma - \sigma ) \, P , \qquad (A1)[/math]
[math]dN/dt = B_N +G_N + A + Q = \rho (\gamma - \beta \, N) \, P - \alpha \, N + Q . \qquad (A2)[/math]
These coupled nonlinear equations are known as the Lotka-Volterra equations. The solution is not straightforward. It depends not only on the coefficients appearing in the equations but also on the initial conditions [math]P=P_0, \, N=N_0[/math] at time [math]t=0[/math]. Different types of long-term behavior of [math]P[/math] and [math]N[/math] may result: convergence to a static equilibrium state, to a cyclic state or to a state of chaotic fluctuations around certain attractors. We will not consider the long-term behavior, especially because the assumption of constant coefficients does not hold. For a qualitative understanding of the short-term behavior we will first consider the equilibrium solution of the Eqs. (A1) and (A2) corresponding to [math]dP/dt=0[/math] and [math]dN/dt[/math]. The equilibrium solution is given by the curves
[math]N_{eq}=\large\frac{\gamma + \sigma}{\beta}\normalsize, \quad P_{eq}=\large\frac{Q -\alpha N}{\rho (\beta N - \gamma)}\normalsize. \qquad (A3)[/math]
These curves are drawn in Fig. A1. The curves cut the [math]P,N[/math] phase plane in 4 phase sectors:
- Green phase: [math]P[/math] and [math]N[/math] both increase;
- Yellow phase: [math]P[/math] increases, [math]N[/math] decreases;
- Red phase: [math]P[/math] and [math]N[/math] both decrease;
- Blue phase: [math]P[/math] decreases and [math]N[/math] increases.
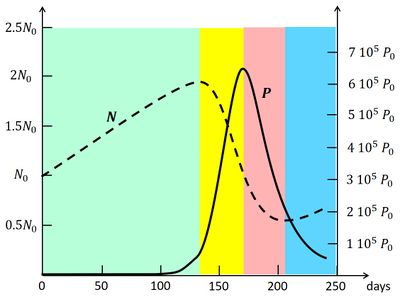
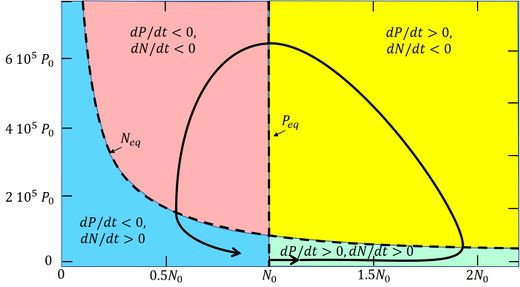 Fig. A1. Solution of the Lotka-Volterra equations (A1, A2), showing the coupled evolution of [math]P(t)[/math] and[math]N(t)[/math] in the [math]N-P[/math] phase plane (solid line). The model parameters are set as follows: [math]\alpha=0, \, \beta=0.1/N_0/day, \, \rho=10^{-3}, \, \gamma=0, \, \sigma=0.1/day, \, Q=7.5 \, 10^{-3} N_0/day, [/math] [math]N_0=0.1 g/m^3, P_0=6.10^{-5} g/m^3[/math]. From Huppert et al. (2002)[50]. |
Now consider the evolution graph in Fig. A1, which is obtained by numerical integration of the Eqs. (A1) and (A2) [50]. The bloom starts in the green phase sector, where initially the plankton biomass [math] P [/math] is very small. The environmental conditions (temperature, light) have just become favorable for nutrient uptake, i.e. the uptake efficiency factor [math]\beta [/math] has increased significantly. Shortly before (not shown in the figure), [math]\beta [/math] was much smaller and [math]N_ {eq} [/math] much larger, so that the plankton population was still in the blue phase (i.e. decreasing in size). Due to the increased uptake efficiency, the biomass [math]P[/math] is now increasing, but the increase is slow because the rate of increase is proportional to [math]P[/math] (cf. A1). Nutrient uptake is still quite low and the nutrient concentration is still increasing due to the supply [math]Q[/math]. However, with increasing population size [math]P[/math] the nutrient uptake also increases and at some moment the nutrient concentration [math]N[/math] changes from increasing to decreasing. The [math]P-N[/math] system enters the yellow phase, where [math]P[/math] will grow rapidly, because the rate of change [math](\beta \, N - \gamma - \sigma ) \, P [/math] (Eq. A1) is large and initially still increasing in spite of the decrease of [math]N[/math] (Eq. A2). The plankton bloom essentially takes place at the end of the green phase and the beginning of the yellow phase. The nutrient concentration decreases in the yellow phase and finally becomes so small that further growth of the plankton biomass is no longer possible. At that time the plankton biomass has reached its maximum and the [math]P-N[/math] system enters the red phase, where the plankton biomass decreases. The nutrient concentration continues its rapid decrease (cf. A2) because the uptake of nutrients by the plankton population is still high. However, the plankton population also declines at a fast rate because [math](\beta \, N - \gamma - \sigma) \, P [/math] (cf. A1) is large and negative. The collapse of the plankton population mainly takes place in the red sector. The decrease of the nutrient concentration ends when the uptake of nutrients has become very small, because of the small size of the plankton population. The [math]P-N[/math] system then enters the blue phase where [math]P[/math] decreases further, while [math]N[/math] increases, but both at a slow rate. The plankton bloom as a function of time, corresponding to the trajectory in the [math]P-N[/math] phase plane, is shown in Fig. A2. It illustrates the dramatic increase and collapse of the plankton biomass (5 orders of magnitude) in a short time. The peak of the bloom coincides with the strongest decrease of the nutrient concentration. The same coincidence is visible in the observation record of the plankton bloom and nutrient concentration in Fig. 2. It also appears, both in the model and the data, that the variation of the nutrient concentration is much less pronounced than the variation in the plankton biomass.
The nonlinearity of the plankton bloom equations has implications that may appear surprising at first sight. One may notice, for instance, that complete nutrient depletion is not a necessary condition for the crash of the plankton population. The point is that below a certain level, which is not necessarily very small, the nutrient concentration is insufficient to sustain a very large plankton population.
The maximum plankton population size that can be reached during the bloom is not linearly related to the initial nutrient concentration [math]N_0[/math] and the initial population size [math]P_0[/math]. Depending on the values of [math]N_0, P_0[/math], it can happen that an increase of either [math]N_0[/math] or [math]P_0[/math] leads to a smaller bloom size, instead of a larger size[50]. According to the model, the nutrient concentration that is reached when the population enters the yellow phase determines to a large degree the maximum population size that can be reached during the yellow phase. This feature is not visible in the observations presented in Fig. 2. In fact, other factors such as sunlight and temperature also play a role. In the case of Fig. 2, it appears that the largest blooms are correlated with low salinity values. This points to a change in the type of water masses present at the measuring site. Stratification effects (suppression of vertical mixing) may also play a role in triggering plankton blooms (Berdalet et al., 2014[15]).
When all the factors influencing the plankton bloom dynamics remain constant in time, the bloom model predicts that the system will tend to the equilibrium state [math]N_{eq}, P_{eq}[/math] (eq. A3), which is stable if the nutrient loss rate [math]\alpha[/math] is sufficiently small. In practice, however, the temporal variation of the factors influencing the bloom dynamics prevents the establishment of an equilibrium state. When time dependency of the factors in the model equations (A1, A2) is taken into account, the multi-annual behavior of model simulations can exhibit unpredictable chaotic fluctuations (Huppert et al., 2005[51]). In case of a seasonally fluctuating uptake efficiency [math]\beta(t)[/math], the model produces chaotic behavior if the nutrient influx [math]Q[/math] is low and the mortality rate [math]\sigma[/math] is large.
Related articles
- Marine Plankton
- Green Ocean modelling
- Nutrient conversion in the marine environment
- Which resource limits coastal phytoplankton growth/ abundance: underwater light or nutrients?
- Possible consequences of eutrophication
- Eutrophication in coastal environments
- Open ocean habitat
- Shelf sea exchange with the ocean
- Threats to the coastal zone
- Estuarine turbidity maximum
- Plankton remote sensing
- Plankton remote sensing North Sea
- Differentiation of major algal groups by optical absorption signatures
- Remote sensing of zooplankton
- Light fields and optics in coastal waters
- The Continuous Plankton Recorder (CPR)
- Diversity and classification of marine benthic algae
- Functional metabolites in phytoplankton
External sources
References
- ↑ Sournia, A., Chretiennot-Dinet, M.-J. and Ricard M. 1991. Marine phytoplankton: how many species in the world ocean? Journal of Plankton Research 13: 1093–1099
- ↑ Andersen, R.A. 1992. Diversity of eukaryotic algae. Biodiversity and Conservation 1: 267-292
- ↑ Edwards, K. F., Klausmeier, C. A. and Litchman, E. 2011. Evidence for a three-way trade-off between nitrogen and phosphorus competitive abilities and cell size in phytoplankton. Ecology 92: 2085–2095
- ↑ Burson, A., Stomp, M., Greenwell, E., Grosse, J. and Huisman, J. 2018. Competition for nutrients and light: testing advances in resource competition with a natural phytoplankton community. Ecology 99: 1108–1118
- ↑ Cloern, J.E. 2018. Why large cells dominate estuarine phytoplankton. Limnology and Oceanography 63: 392-409
- ↑ Redfield, A.C. 1958. The Biological Control of Chemical Factors in the Environment. American Scientist 46: 205-221
- ↑ Field, C. B., Behrenfeld, M. J., Randerson, J. T. and Falkowski, P. 1998. Primary production of the biosphere: integrating terrestrial and oceanic components. Science 281: 237–240
- ↑ Flynn, K.J., Stoecker, D.K., Mitra, A., Raven, J.A., Glibert, P.M., Hansen, P.J., Graneli, E. and Burkholder, J.M., 2013. Misuse of the phytoplankton-zooplankton dichotomy: the need to assign organisms as mixotrophs within plankton functional types. J. Plankton Res. 35: 3–11
- ↑ , D., Gower, J.F.R., Dekker, A.G., Phinn, S.R. and Brando, V.E. 2014. A review of ocean color remote sensing methods and statistical techniques for the detection, mapping and analysis of phytoplankton blooms in coastal and open oceans. Progress in Oceanography 123: 123–144
- ↑ Davidson, K., Gowen, R.J., Tett, P., Bresnan, E., Harrison, P.J., McKinney, A., Milligan, S., Mills, D.K., Silke, J. and Crooks, A.M. 2012. Harmful plankton blooms: How strong is the evidence that nutrient ratios and forms influence their occurrence? Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 115: 399–413
- ↑ Bissinger, J. E., Montagnes, D. J. S., Sharples, J., and Atkinson, D. 2008. Predicting marine phytoplankton maximum growth rates from temperature: improving on the Eppley curve using quantile regression. Limnol. Oceanogr. 53: 487–493. doi: 10.4319/lo.2008.53.2.0487
- ↑ Boyd, P.W., Rynearson, T.A,. Armstrong, E.A., Fu, F., Hayashi, K., et al., 2013. Marine Phytoplankton Temperature versus Growth Responses from Polar to Tropical Waters – Outcome of a Scientific Community-Wide Study. PLoS ONE 8(5): e63091. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0063091
- ↑ Wagner-Cremer, F., Steur, F. van Wezel, R., Verweij, G. and Kouwets, F. 2018. Wat momentopnamen van fytoplankton ons kunnen vertellen over de geschiedenis van de kust. H2O-Online / 19 januari 2018
- ↑ Taylor, J. R. and Ferrari, R. 2011. Shutdown of turbulent convection as a new criterion for the onset of spring phytoplankton blooms. Limnology and Oceanography 56: 2293–2307
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Berdalet, E.,McManus, M.A., Ross, O.N., Burchard, H., Chavez, F.P., Jaffe, J.S., Jenkinson, I.R., Kudela, R., Lips, I., Lips, U., Lucas, A., Rivas, D., Ruiz-delaTorre, M.C., Ryan, J., Sullivan, J.M.k and Yamazakim H. 2014. Understanding harmful algae in stratified systems: Review of progress and future directions. Deep-Sea Research II 101: 4–20
- ↑ Sigman, D. M. and Hain, M. P. 2012. The Biological Productivity of the Ocean. Nature Education Knowledge 3: 21 https://www.nature.com/scitable/knowledge/library/the-biological-productivity-of-the-ocean-70631104/
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 17.3 Glibert, P.M. 2020. Harmful algae at the complex nexus of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae 91, 101583 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "Gli" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ Van de Poll, W.H., Kulk, G., Timmermans, K.R., Brussaard, C.P.D., van der Woerd, H.J., Kehoe, M.J., Mojica, K.D.A., Visser, R.J.W., Rozema, P.D. and Buma, A.G.J., 2013. Phytoplankton chlorophyll a biomass, composition, and productivity along a temperature and stratification gradient in the Northeast Atlantic Ocean. Biogeosciences 10: 4227–4240
- ↑ Hutchinson, G.E. 1961. The paradox of the plankton. American Naturalist 95:137–147
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Philippart, C.J.M., Beukema, J.J., Cadée, G.C., Dekker, R., Goedhart, P.W., van Iperen, J.M., Leopold, M.F. and Herman, P.M.J. 2007. Impacts of nutrient reduction on coastal communities. Ecosystems 10: 95-118
- ↑ Bharathia, M.D., Sarmaa, V.V.S.S. and Ramaneswaric, K. 2018. Intra-annual variations in phytoplankton biomass and its composition in the tropical estuary: Influence of river discharge. Marine Pollution Bulletin 129: 14–25
- ↑ Anderson, N.J. 2000. Diatoms, temperature and climate change. Eur. J. Phycol. 35: 307–314
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 Glibert, P.M. 2016. Margalef revisited: A new phytoplankton mandala incorporating twelve dimensions, including nutritional physiology. Harmful Algae 55: 25–30
- ↑ Margalef, R. 1978. Life-forms of phytoplankton as survival alternatives in an unstable environment. Oceanologica Acta 1: 493-508
- ↑ Klausmeier, C.A. and Litchman, E. 2001. Plankton games: The vertical distribution of phytoplankton in poorly mixed water columns. Limnol. Oceanogr. 46: 1998–2007
- ↑ Los, F.J. and Wijsman, J.M.W. 2007. Application of a validated primary production model (BLOOM) as a screening tool for marine, coastal and transitional waters. Journal of Marine Systems 64: 201-215
- ↑ Pahlow, M. 2005. Linking chlorophyll-nutrient dynamics to the Redfield N:C ratio with a model of optimal phytoplankton growth. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 287: 33−43
- ↑ Harvey, E.L. and Menden-Deuer, S. 2012. Predator-Induced Fleeing Behaviors in Phytoplankton: A New Mechanism for Harmful Plankton Bloom Formation? PLoS ONE 7(9): e46438. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0046438
- ↑ Branco,P., Egas, M., Hall, S.R. and Huisman, J. 2020. Why Do Phytoplankton Evolve Large Size in Response to Grazing? The American Naturalist vol. 195 , no. 1
- ↑ Baudoux, A-C. 2007. The role of viruses in marine phytoplankton mortality. Thesis Groningen University, 148 pp
- ↑ Mojica, K.D.A., Huisman, J., Wilhelm, S.W. and Brussaard, C.P.D. 2016. Latitudinal variation in virus-induced mortality of phytoplankton across the North Atlantic Ocean. The ISME Journal 10: 500–513; doi:10.1038/ismej.2015.130
- ↑ Llort, J., Langlais, C., Matear, R., Moreau, S., Lenton, A. and Strutton, P. G. 2018. Evaluating Southern Ocean Carbon Eddy-Pump From Biogeochemical-Argo Floats. Journal of Geophysical Research Oceans 123: 971–984
- ↑ DeVries, T., Le Querec, C., Andrew, O., Berthet, S., Hauck, J., Ilyina, T., Landschutzer, P., Lenton, A., Lima, A.D., Nowicki, M., Schwinger, J. and Seferian, R. 2019. Decadal trends in the ocean carbon sink. PNAS 116: 11646–11651
- ↑ Nixon, S. W. 1988. Physical energy inputs and the comparative ecology of lake and marine ecosystems. Limnol. Oceanogr. 33: 1005–1025
- ↑ Nixon, S.W. and Buckley, B. A. 2002. “A strikingly rich zone” – Nutrient enrichment and secondary production in coastal marine ecosystems. Estuaries 25: 782–796
- ↑ Smayda T.J. 1997. Harmful plankton blooms: their ecophysiology and general relevance to phytoplankton blooms in the sea. Limnology and Oceanography 42: 1137–1153
- ↑ Zingone, A., Wyatt, T. 2004. Harmful plankton blooms: keys to the understanding of the phytoplankton ecology. In: Robinson, A.R., McCarthy, J. and Rothschild, B.J. (eds.) The Sea. Harvard University Press, Harvard, pp 867-926
- ↑ Hallegraeff, G. M. 1993. A review of harmful plankton blooms and their apparent global increase. Phycologia 32: 79–99
- ↑ Anderson, D. 2012. HABs in a changing world: a perspective on harmful plankton blooms, their impacts, and research and management in a dynamic era of climactic and environmental change. Harmful Algae 2012 (2012). 2014 ; 2012: 3–17 PMID: 26640829; PMCID: PMC4667985
- ↑ Berdalet, E., Fleming, L.E., Gowen, R., Davidson, K., Hess, P., Backer, L.C., Moore, S.K., Hoagland, P. and Enevoldsen, H. 2016. Marine harmful plankton blooms, human health and wellbeing: challenges and opportunities in the 21st century. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U.K. 96: 61–91
- ↑ Wells, M.L., Karlson, B., Wulff, A., Kudela, R., Trick, C., Asnaghi, V., Berdalet, E., Cochlan, W.,. Davidson, K., De Rijcke, M., Dutkiewicz, S., Hallegraeff, G., Flynn, K.J., Legrand, C., Paerl, H., Slke, J., Suikkanen, S., Thompson, P. and Trainer, V.L. 2020. Future HAB science: Directions and challenges in a changing climate. Harmful Algae 91, 101632
- ↑ Westberry, T.K., Solsbe, G.M. and Behrenfeld, M.J. 2023. Gross and net primary production in the global ocean: An ocean color remote sensing perspective. Earth-Science Reviews 237, 104322
- ↑ Howarth, R.W. 1988. Nutrient limitation of net primary production in marine ecosystems, Annual Rev. Ecol. Syst. 19: 89–110
- ↑ Cloern, J.E., Foster, S.Q. and Kleckner, A.E. 2014. Phytoplankton primary production in the world's estuarine -coastal ecosystems. Biogeosciences 11: 2477–2501
- ↑ Liu, B., de Swart, H. E. and de Jonge, V. N. 2018. Phytoplankton bloom dynamics in turbid, well-mixed estuaries: a model study. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science. 211: 137-151
- ↑ McSweeney, J. M., Chant, R. J., Wilkin, J. L. and Sommerfield, C. K. 2016. Suspended sediment impacts on light-limited productivity in the Delaware estuary. Estuaries and Coasts 40: 977–993
- ↑ De Jonge, V. N. and van Beusekom, J. E. E., 1992. Contribution of resuspended microphytobenthos to total phytoplankton in the Ems estuary and its possible role for grazers. Netherlands Journal of Sea Research 30: 91–105
- ↑ Caffrey, J. M. 2004. Factors controlling net ecosystem metabolism in US estuaries. Estuaries 27: 90–101
- ↑ Gattuso, J.-P., Frankignoulle, M., and Wollast, R. 1998. Carbon and carbonate metabolism in coastal aquatic ecosystems. Annual Rev. Ecol. Syst. 29: 405–433
- ↑ 50.0 50.1 50.2 50.3 Huppert, A., Blasius, B. and Stone, L. 2002. A Model of Phytoplankton Blooms. The American Naturalist 159: 156-171
- ↑ Huppert, A., Blasius, B., Olinky, R. and Stone, L. 2005. A Model for Seasonal Phytoplankton Blooms. Journal of Theoretical Biology 236: 276–290
Please note that others may also have edited the contents of this article.
|