Difference between revisions of "Dam break flow"
Dronkers J (talk | contribs) |
Dronkers J (talk | contribs) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | This article discusses the often catastrophic flows that result from the sudden collapse of high dams that protect low-lying land. The mechanisms causing dam breaks are not dealt with; for this the reader is referred to the extensive literature existing on this subject, see for example Zhang et al. (2016) <ref>Zhang, L., Peng, M., Chang, D. and Xu, Y. 2016. Dam failure and Risk Assessment. John Wiley and Sons, Singapore</ref> and Almog et al. (2011) <ref>Almog, E., Kelham, P and King, R. 2011. Modes of dam failure and monitoring and measuring techniques. Environmental Agency,UK https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/290819/scho0811buaw-e-e.pdf</ref> and to the article [[Stability of rubble mound breakwaters and shore revetments]]. | + | This article discusses the often-catastrophic flows that result from the sudden collapse of high dams that protect low-lying land. The mechanisms causing dam breaks are not dealt with; for this the reader is referred to the extensive literature existing on this subject, see for example Zhang et al. (2016) <ref>Zhang, L., Peng, M., Chang, D. and Xu, Y. 2016. Dam failure and Risk Assessment. John Wiley and Sons, Singapore</ref> and Almog et al. (2011) <ref>Almog, E., Kelham, P and King, R. 2011. Modes of dam failure and monitoring and measuring techniques. Environmental Agency,UK https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/290819/scho0811buaw-e-e.pdf</ref> and to the article [[Stability of rubble mound breakwaters and shore revetments]]. |
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
| − | Dam failure can lead to disastrous situations. Most dam-break tragedies are related to the collapse of reservoir dams in mountain rivers. The failure of sea dikes can also cause major disasters, although the level difference in this case is not as large. A dramatic example is the failure of more than hundred sea dikes in the Netherlands during the extreme storm surge of 1953, see Fig. 1. Many of these dikes protected polders lying a few meters below the average sea level, while the storm surge level in the tidal inlets reached up to five meters. Rapid flooding killed almost two thousand people who were unable to flee in time to safe places <ref>Gerritsen, H. 2005. What happened in 1953? The Big Flood in the Netherlands in retrospect. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 363: 1271–1291</ref>. The most common | + | Dam failure can lead to disastrous situations. Most dam-break tragedies are related to the collapse of reservoir dams in mountain rivers. The failure of sea dikes can also cause major disasters, although the level difference in this case is not as large. A dramatic example is the failure of more than hundred sea dikes in the Netherlands during the extreme storm surge of 1953, see Fig. 1. Many of these dikes protected polders lying a few meters below the average sea level, while the storm surge level in the tidal inlets reached up to five meters. Rapid flooding killed almost two thousand people who were unable to flee in time to safe places <ref>Gerritsen, H. 2005. What happened in 1953? The Big Flood in the Netherlands in retrospect. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 363: 1271–1291</ref>. The most common failure mechanisms of earth dams are related to overtopping and seepage (also called piping or internal erosion)<ref>Richards, K.S. and Reddy, K.R. 2007. Critical appraisal of piping phenomena in earth dams. |
| + | Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 66: 381–402</ref><ref>Jiang, X., Woerman, A., Chen, P., Huang, Q. and Chen, H. 2020. Mechanism of the progressive failure of non-cohesive natural dam slopes. Geomorphology 363, 107198</ref>. In the case of the 1953 storm surge, overtopping and subsequent scour of the interior dike slope was the most important dike failure mechanism (see [[Overtopping resistant dikes]]). | ||
| Line 26: | Line 27: | ||
==Frictionless dam-break flow: analytical solution== | ==Frictionless dam-break flow: analytical solution== | ||
| − | Analytical solutions relate to idealized situations as depicted in Fig. 2. The initial situation consists of an infinite reservoir with a water level that is <math> h_0 </math> higher than the horizontal ground level downstream of the dam. Dam break is simulated by instantaneous removal of the dam. This causes a positive surge in the positive <math> x </math>-direction and a negative surge in the negative <math> x </math>-direction. | + | Analytical solutions relate to idealized situations as depicted in Fig. 2. The initial situation consists of an infinite reservoir with a water level that is <math> h_0 </math> higher than the horizontal ground level downstream of the dam. Dam break is simulated by instantaneous removal of the dam. This causes a positive surge in the positive <math> x </math>-direction and a negative surge in the negative <math> x </math>-direction. Here we consider the case of a horizontal dry floor in front of the positive surge (water level <math>h = 0</math>). The upstream water body behind the negative surge is undisturbed (water level <math>h = h_0 </math> and current speed <math> u = 0 </math>). |
| + | |||
[[image:SouthForkDamFailure1889.jpg|thumb|left|300px|Fig. 3. The earth-filled South Fork Dam on Lake Conemaugh (Pennsylvania, US) collapsed in 1889, killing 2,209 people in downstream villages.]] | [[image:SouthForkDamFailure1889.jpg|thumb|left|300px|Fig. 3. The earth-filled South Fork Dam on Lake Conemaugh (Pennsylvania, US) collapsed in 1889, killing 2,209 people in downstream villages.]] | ||
| Line 34: | Line 36: | ||
| − | The study of dam break | + | The study of dam-break flow was triggered by several dam failures in the 19th century, in particular the breach of the South Fork Dam in Pennsylvania (USA) in 1889, Fig. 3. Three years later Ritter <ref> Ritter, A. 1892. Die Fortpflanzung der Wasserwellen. Zeitschrift des Vereines Deutscher Ingenieure 36: 947-954 </ref> published an exact analytical solution for dam-break flow by assuming that frictional effects can be ignored. The derivation is given in box 1. According to this solution, the tip of the positive surge advances at high speed (supercritical flow) given by <math> u_s= 2 c_0</math>, where <math>c_0 = \sqrt {gh_0}</math> and <math> g </math> is the gravitational acceleration. The shape of the positive and negative surge is a concave-up parabola, |
| Line 55: | Line 57: | ||
| − | Figure 4 also shows the shape of the dam break wave that was observed in laboratory experiments. For small values of <math> x /(c_0 t) </math>, the frictionless solution corresponds fairly well with the observations. However, the front zone is different: the shape is a bull nose, rather than a sharp edge. The front also advances more slowly; the speed of the front decreases with time | + | Figure 4 also shows the shape of the dam-break wave that was observed in laboratory experiments. For small values of <math> x /(c_0 t) </math>, the frictionless solution corresponds fairly well with the observations. However, the front zone is different: the shape is a bull nose, rather than a sharp edge. The front also advances more slowly; the speed of the front rapidly decreases with time from a value close to <math> u_s = 2 c_0 </math> to a value close to <math> u_s = c_0 </math><ref name=Y22>Yang, S., Yang, W., Zhang, C., Qin, S., Wei, K. and Zhang, J. 2022. Experimental and numerical study on the evolution of wave front profile of dam-break waves. Ocean Engineering 247, 110681</ref>. The reason for this difference is the neglect of frictional effects that are important in the thin fluid layer near the front. |
| − | [[image:DamBreakFlowDerivation.jpg|thumb|center|900px|Box 1. Derivation of the solution for frictionless dam break flow.]] | + | [[image:DamBreakFlowDerivation.jpg|thumb|center|900px|Box 1. Derivation of the solution for frictionless dam-break flow.]] |
| Line 71: | Line 73: | ||
<math>h(s) \propto s^a , \quad a = 1/3 – 1/2 \; ,</math> | <math>h(s) \propto s^a , \quad a = 1/3 – 1/2 \; ,</math> | ||
| − | where <math>s</math> is the distance measured from the wave front, and where it has been assumed that the flow velocity in the tip region does not (strongly) depend on <math>s</math><ref>Dressler, R.F. 1952. Hydraulic resistance effect upon the dambreak functions. J. Res. Natl. Bureau of Standards, 49(3): 217–225</ref><ref name=W>Whitham, G.B. 1955. The effects of hydraulic resistance in the dam-break problem. Proc. Roy. Soc. of London, Serie A, 227: 399–407</ref><ref>Hogg, A.J. and Pritchard, D. 2004. The effects of hydraulic resistance on dam-break and other shallow inertial flows. J. Fluid Mech. 501: 179–212</ref><ref name=C09>Chanson, H. 2009. Application of the method of characteristics to the dam break wave problem. Journal of Hydraulic Research 47: 41–49</ref><ref name=DLL>Deng, H., Liu, H. and Lu, S. 2018. Analytical Study of Dam-Break Wave Tip Region. J. Hydraul. Eng. 144: 4018015</ref>. This shape is similar to what is observed in flume experiments (Fig. 4)<ref name=S/>. At the bore front, the flow has a strong downward component and it is highly turbulent. Field observations of very high suspended sediment | + | where <math>s</math> is the distance measured from the wave front, and where it has been assumed that the flow velocity in the tip region does not (strongly) depend on <math>s</math><ref>Dressler, R.F. 1952. Hydraulic resistance effect upon the dambreak functions. J. Res. Natl. Bureau of Standards, 49(3): 217–225</ref><ref name=W>Whitham, G.B. 1955. The effects of hydraulic resistance in the dam-break problem. Proc. Roy. Soc. of London, Serie A, 227: 399–407</ref><ref>Hogg, A.J. and Pritchard, D. 2004. The effects of hydraulic resistance on dam-break and other shallow inertial flows. J. Fluid Mech. 501: 179–212</ref><ref name=C09>Chanson, H. 2009. Application of the method of characteristics to the dam-break wave problem. Journal of Hydraulic Research 47: 41–49</ref><ref name=DLL>Deng, H., Liu, H. and Lu, S. 2018. Analytical Study of Dam-Break Wave Tip Region. J. Hydraul. Eng. 144: 4018015</ref>. This shape is similar to what is observed in flume experiments (Fig. 4)<ref name=S/>. At the bore front, the flow has a strong downward component and it is highly turbulent. Field observations of very high suspended sediment concentrations just behind the bore front demonstrate the strong erosion capacity of dam-break flows<ref>Khezri, N. and Chanson, H. 2012. Inception of bed load motion beneath a bore. Geomorphology 153: 39–47</ref> (see also the article [[Tidal bore dynamics]]). |
| − | The bore front speed <math> | + | The bore front speed <math>u_s</math> decreases with time. At small times <math>t<<t_{\infty}</math>, the bore front speed varies approximately as <ref name=W/> |
| − | <math> | + | <math>u_s \approx c_0 \, (2 – 3.45 \sqrt{t / t_{\infty}}) \; , \qquad (4) </math> |
where <math> t_{\infty} = \sqrt{(h_0/g)}/ c_D </math> and <math>c_D</math> is the friction coefficient (usual values in the range <math>\approx (2-10)\, 10^{-3}</math>). | where <math> t_{\infty} = \sqrt{(h_0/g)}/ c_D </math> and <math>c_D</math> is the friction coefficient (usual values in the range <math>\approx (2-10)\, 10^{-3}</math>). | ||
| − | At large times <math>t \ge t_{\infty}</math> the bore front speed varies approximately as <ref name=C09 | + | At large times <math>t \ge t_{\infty}</math> the bore front speed varies approximately as <ref name=C09/><ref name=DLL/> |
| − | <math> | + | <math>u_s \approx c_0 \sqrt{ t_{\infty} / 3 t} \; . \qquad (5)</math> |
| + | |||
| + | See the appendix for a derivation. It should be emphasized that these approximate formulas have been derived for very large (infinite) reservoirs in which the backward wave is not reflected. | ||
| − | |||
==Field observations== | ==Field observations== | ||
| − | Data of dam break discharges can be derived from the rate at which the reservoir level is falling. Complementary field data can be retrieved from analyzing the | + | Data of dam-break discharges can be derived from the rate at which the reservoir level is falling. Complementary field data can be retrieved from analyzing the morphological impact of the dam break. Detailed experimental data of dam-break events only exist for laboratory settings. |
| − | Data from numerous reservoir dam breaks in the past have provided empirical formulas for the maximum discharge <math>Q_{max}</math> through the breach <ref>Froehlich, D.C. 2016. Predicting Peak Discharge from Gradually Breached Embankment Dam. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, ASCE 04016041</ref><ref name=W> Wang, B., Chen, Y., Wu, C., Peng, Y., Song, J., Liu, W. and Liu, X. 2018. Empirical and semi-analytical models for predicting peak outflows caused by embankment dam failures. Journal of Hydrology 562: 692–702</ref>. From this data it was deduced that the width of the breach is often a function of the water volume <math>V</math> in the reservoir (volume above breach level). A rough estimate of the width is given by <ref name=F8></ref> <math> B \approx 0.3 V ^ {1/3} </math>. Empirical formulas for the maximum dam break discharge then yield <ref>Webby, M. G. 1996. Discussion of ‘Peak outflow from breached embankment dam.’ by D. C. Froehlich. J. Water Resour. Plann. Management 122:4(316), 316–317</ref> <ref name=W></ref> | + | Data from numerous reservoir dam breaks in the past have provided empirical formulas for the maximum discharge <math>Q_{max}</math> through the breach <ref>Froehlich, D.C. 2016. Predicting Peak Discharge from Gradually Breached Embankment Dam. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, ASCE 04016041</ref><ref name=W>Wang, B., Chen, Y., Wu, C., Peng, Y., Song, J., Liu, W. and Liu, X. 2018. Empirical and semi-analytical models for predicting peak outflows caused by embankment dam failures. Journal of Hydrology 562: 692–702</ref>. From this data it was deduced that the width of the breach is often a function of the water volume <math>V</math> in the reservoir (volume above breach level). A rough estimate of the width is given by<ref name=F8>Froehlich, D.C. 2008. Embankment Dam Breach Parameters and Their Uncertainties. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, ASCE 134: 1708-1721</ref> <math> B \approx 0.3 V ^ {1/3} </math>. Empirical formulas for the maximum dam-break discharge then yield <ref>Webby, M. G. 1996. Discussion of ‘Peak outflow from breached embankment dam.’ by D. C. Froehlich. J. Water Resour. Plann. Management 122:4(316), 316–317</ref> <ref name=W></ref> |
<math>Q_{max} \approx 0.04 \sqrt{g} \, V^{0.37} h_0^{1.4} \approx 0.15 h_0 \, B \, \sqrt{g h_0} \, V^{0.04} h_0^{-0.1} . \qquad (6)</math> | <math>Q_{max} \approx 0.04 \sqrt{g} \, V^{0.37} h_0^{1.4} \approx 0.15 h_0 \, B \, \sqrt{g h_0} \, V^{0.04} h_0^{-0.1} . \qquad (6)</math> | ||
| Line 95: | Line 98: | ||
From this follows an empirical estimate for the order of magnitude of the maximum discharge per unit width, | From this follows an empirical estimate for the order of magnitude of the maximum discharge per unit width, | ||
| − | <math> q_{max} \approx 0. | + | <math> q_{max} \approx 0.2 h_0 \, \sqrt{g h_0} , \qquad (7)</math> |
| + | |||
| + | where we have considered a large reservoir volume (<math>V \approx 10^7 m^3</math>) and a water depth <math>h_0 \approx 15 m</math>. The empirical estimate (7) is about 70% of the estimate (3) given by the frictionless flow solution. When comparing real dam failures with the idealized frictionless model, differences are not only due to the neglect of friction but also to the non-instantaneous nature of real dam-break events. Besides, the assumption of a dry channel bed in front of the dam often does not hold in practice - see next section. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Dam-break flow into a wetted channel== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:DamBreakWettedChannel.jpg|thumb|right|450px|Fig. 5. Schematic representation of dam-break flow into a wetted channel of small relative depth (<math>(h_0-h_2)/h_2 >10</math>). Blue pale: Dam-break wave. Blue: Channel water. The interface is not sharp but diffuse due to strong mixing.]] | ||
| − | + | An analytical solution of frictionless dam-break flow into a wetted channel was given by Stoker (1957<ref>Stoker, J.J., 1957. Water Waves; the Mathematical Theory and Applications. Wily-Interscience</ref>). Flume experiments show that Stoker’s solution does not correctly predict the profile of the wave front, but it accurately predicts the wave front celerity and the wave height behind the wave front<ref name=Y22/>. The experiments of Yang et al. (2022<ref name=Y22/>) reveal significant differences between dam-break waves over dry and wet beds, both in flow pattern and wave front profile. Specifically, dam-break wave over a dry bed exhibits continuously increasing water depth behind a thin wave front characterized with little or no air entrainment. In contrast, a dam-break wave over a wet bed exhibits a highly turbulent broken wave front for cases with relatively shallow initial downstream water depth, see Fig. 5. For cases with relatively large initial downstream water depth (<math>(h_0-h_2)/h_2 < 10</math>), the dam-break wave exhibits a broken or undulating unbroken wave front<ref name=Y22/>. Theoretical analysis indicates that dam-break waves over a wet bed are very sensitive to the shallow downstream water depth <math>h_2</math>, and even a slight change in <math>h_2</math> will lead to a significant variation in wave height and wave front celerity. For the case of shallow downstream water depth, the wave front advance is mainly driven by the mutual drag between the upstream wave in the upper layer and the downstream water in the lower layer. Vortices along the interface extending into the downstream water result in mixing between the upper layer and the middle layer of the downstream water. For cases with great downstream water depth, the advance of wave front is influenced by the push of the upstream water to the downstream water, and the interface gradually lags behind the wave front. The mixing at the interface is significantly decreased and a smooth interface is observed, with no mix happening between the different layers of the downstream water<ref name=Y22/>. | |
==Numerical models== | ==Numerical models== | ||
| − | The analytical methods for describing dam-break flow provide a qualitative picture and some first-order estimates for the bore profile and surge speed. Major assumptions underlying the simplifications are, (1) hydrostatic pressure throughout the dam break flow, (2) uniform flow velocity throughout the bore tip region, and (3) the reservoir and outflow region can be represented by an unbounded prismatic channel. For actual field situations, the dam-break flow must be modeled numerically. A correct simulation of the backward surge requires models of the Boussinesq type that take into account vertical fluid accelerations<ref>Castro-Orgaz, O. and Chanson, H. 2017. Ritter’s dry-bed dam-break flows: positive and negative wave dynamics. Environ Fluid Mech (2017) 17:665–694</ref>. Practical situations are generally characterized by the complex geometry of a highly irregular river bed that evolves during the dam-break event. Current numerical models cannot easily meet the requirements for performing accurate simulations of such real events. | + | The analytical methods for describing dam-break flow provide a qualitative picture and some first-order estimates for the bore profile and surge speed. Major assumptions underlying the simplifications are, (1) hydrostatic pressure throughout the dam-break flow, (2) uniform flow velocity throughout the bore tip region, and (3) the reservoir and outflow region can be represented by an unbounded prismatic channel. For actual field situations, the dam-break flow must be modeled numerically. A correct simulation of the backward surge requires models of the Boussinesq type that take into account vertical fluid accelerations<ref name=CC>Castro-Orgaz, O. and Chanson, H. 2017. Ritter’s dry-bed dam-break flows: positive and negative wave dynamics. Environ Fluid Mech (2017) 17:665–694</ref>. Practical situations are generally characterized by the complex geometry of a highly irregular river bed that evolves during the dam-break event. Current numerical models cannot easily meet the requirements for performing accurate simulations of such real events. |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Appendix: Analytical expression frictional dam-break flow== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:DamBreakFrictionScheme.jpg|thumb|400px|right|Fig. A1. Schematic representation of frictional dam-break flow according to the model of Chanson (2009<ref name=C09/>). Blue pale: The wave shape following the frictionless solution of Ritter; Blue: The wave shape in the frictional tip region. ]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Here we follow the derivation proposed by Chanson (2009<ref name=C09/>), which gives an analytical expression of the frictional dam-break flow over a horizontal dry channel bed that matches closely the results of more elaborate analytical models<ref name=DLL/>, the results of flume experiments<ref name=Y22/>, and the results of numerical models<ref name=CC/>. The main assumptions are the following: (1) frictional effects are only substantial in the tip region of the dam-break wave and negligible elsewhere, (2) the flow velocity <math>u_f</math> in the tip region is spatially uniform (<math>u_f=u_s</math>), (3) frictional effects dominate the momentum balance in this tip region, and (4) the shallow-water equations hold for the whole dam-break wave. These assumptions are based on observations of dam-break flow in laboratory experiments. | ||
| + | Non-dimensionless hydrodynamic parameters are defined as follows: <math>h \rightarrow h/h_0, \; x \rightarrow x/h_0, \; u \rightarrow u/c_0, \; t \rightarrow t \sqrt{g/h_0}</math>. The shallow-water equations then read | ||
| + | <math>\Large\frac{\partial h}{\partial t}\normalsize +\Large\frac{\partial hu}{\partial x}\normalsize = 0, \quad \Large\frac{\partial u}{\partial t}\normalsize + u\Large\frac{\partial u}{\partial x}\normalsize + \Large\frac{\partial h}{\partial x}\normalsize + c_D \Large\frac{u^2}{h}\normalsize =0 ,\qquad (A1)</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | where <math>c_D</math> is the friction coefficient. The flow is frictionless (<math>c_D=0</math>) upstream of the tip region <math>x \le x_1</math>, where <math>x_1</math> is the location of the transition between frictionless and friction-dominated flow, see Fig.A1. In this zone the dam-break flow is given by | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>h_{nf} = \frac{1}{9} (2-\frac{x}{t})^2 , \quad u_{nf} =\frac{2}{3} (1+\frac{x}{t}) . \qquad(A2) </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the tip region the momentum balance is approximated by <math>\quad \Large\frac{\partial h}{\partial x}\normalsize + c_D \Large\frac{u^2}{h}\normalsize =0 ,\qquad (A3)</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:DamBreakFrictionCelerity.jpg|thumb|300px|left|Fig. A2. The dimensionless celerity of the dam-break wave front as a function of dimensionless time. Blue: The frictionless Ritter solution. Red: The frictional model of Chanson (2009<ref name=C09/>) with <math>c_D=0.002</math>.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The shape of the tip region is given by integration: <math>h_f=\sqrt{2 c_D u_f^2 (x_s – x)} , \qquad (A4)</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | where <math>x_s</math> is the location of the tip of the dam-break wave. The transition location <math>x_1</math> can be derived from the mass balance requirement expressing the fact that the water volume in the frictional tip region must be the same as the water volume that would be present if the flow in the tip region were frictionless: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\int_{x_1}^{x_s} h_f(x)dx = \int_{x_1}^{2t} h_{nf}(x)dx \; \rightarrow \; \sqrt{2 c_D u_f^2} \int_{x_1}^{x_s} \sqrt{x_s-x} dx = \frac{1}{9} \int_{x_1}^{2t} (2-\frac{x}{t})^2 dx . \qquad (A5) </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The location <math>x_s</math> and the celerity <math>u_f</math> of the tip of the dam-break wave is found by evaluating this condition together with the boundary conditions <math>h_f(x_1)=h_{nf}(x_1), \; u_f=u_{nf}(x_1) . \qquad (A6)</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | This yields the expressions | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>x_s = (\frac{3}{2} u_f -1)\, t + \Large\frac{(2-u_f)^4}{32 c_D u_f^2} \normalsize , \qquad | ||
| + | (2-u_f)^3 = 24 c_D u_f^2 t . \qquad (A7)</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The time evolution of the celerity <math>u_f</math> of the tip of the dam-break wave is shown in Fig. A2. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==Related articles== | ==Related articles== | ||
:[[Tidal bore dynamics]] | :[[Tidal bore dynamics]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:41, 10 August 2022
This article discusses the often-catastrophic flows that result from the sudden collapse of high dams that protect low-lying land. The mechanisms causing dam breaks are not dealt with; for this the reader is referred to the extensive literature existing on this subject, see for example Zhang et al. (2016) [1] and Almog et al. (2011) [2] and to the article Stability of rubble mound breakwaters and shore revetments.
Contents
Introduction
Dam failure can lead to disastrous situations. Most dam-break tragedies are related to the collapse of reservoir dams in mountain rivers. The failure of sea dikes can also cause major disasters, although the level difference in this case is not as large. A dramatic example is the failure of more than hundred sea dikes in the Netherlands during the extreme storm surge of 1953, see Fig. 1. Many of these dikes protected polders lying a few meters below the average sea level, while the storm surge level in the tidal inlets reached up to five meters. Rapid flooding killed almost two thousand people who were unable to flee in time to safe places [3]. The most common failure mechanisms of earth dams are related to overtopping and seepage (also called piping or internal erosion)[4][5]. In the case of the 1953 storm surge, overtopping and subsequent scour of the interior dike slope was the most important dike failure mechanism (see Overtopping resistant dikes).
The consequences of dam failure have been studied for more than a century. It nevertheless remains a challenging topic due to the high non-linearity of the flood wave propagation. The problem can be tackled with numerical models, but rough estimates and insight into the tidal wave dynamics can be obtained with analytical solution methods.
Frictionless dam-break flow: analytical solution
Analytical solutions relate to idealized situations as depicted in Fig. 2. The initial situation consists of an infinite reservoir with a water level that is [math] h_0 [/math] higher than the horizontal ground level downstream of the dam. Dam break is simulated by instantaneous removal of the dam. This causes a positive surge in the positive [math] x [/math]-direction and a negative surge in the negative [math] x [/math]-direction. Here we consider the case of a horizontal dry floor in front of the positive surge (water level [math]h = 0[/math]). The upstream water body behind the negative surge is undisturbed (water level [math]h = h_0 [/math] and current speed [math] u = 0 [/math]).
The study of dam-break flow was triggered by several dam failures in the 19th century, in particular the breach of the South Fork Dam in Pennsylvania (USA) in 1889, Fig. 3. Three years later Ritter [6] published an exact analytical solution for dam-break flow by assuming that frictional effects can be ignored. The derivation is given in box 1. According to this solution, the tip of the positive surge advances at high speed (supercritical flow) given by [math] u_s= 2 c_0[/math], where [math]c_0 = \sqrt {gh_0}[/math] and [math] g [/math] is the gravitational acceleration. The shape of the positive and negative surge is a concave-up parabola,
[math]
h(x,t) =
\begin{cases}
h_0 , \qquad x \lt -c_0 t \\
\Large\frac{h_0}{9}\normalsize \; (2 - \Large\frac{x}{c_0 t}\normalsize)^2 , \quad -c_0 t\lt x\lt 2c_0 t \qquad (1) \\
0 , \qquad x \gt 2 c_0 t
\end{cases}
[/math]
[math]u(x,t) = \Large\frac{2 c_0}{3}\normalsize \, (1 + \Large\frac{x}{c_0 t}\normalsize) , \quad -c_0 t \lt x \lt 2 c_0 t \; . \qquad (2)[/math]
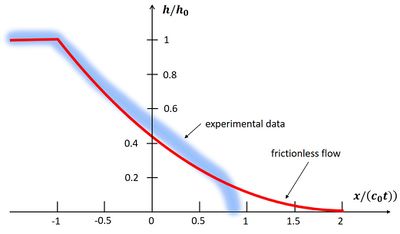
This solution is shown in Fig. 4. According to Eqs. (1, 2), the discharge through the breach per unit width is given by
[math]q = \frac{8}{27} h_0 \sqrt{g h_0}. \qquad (3) [/math]
Figure 4 also shows the shape of the dam-break wave that was observed in laboratory experiments. For small values of [math] x /(c_0 t) [/math], the frictionless solution corresponds fairly well with the observations. However, the front zone is different: the shape is a bull nose, rather than a sharp edge. The front also advances more slowly; the speed of the front rapidly decreases with time from a value close to [math] u_s = 2 c_0 [/math] to a value close to [math] u_s = c_0 [/math][7]. The reason for this difference is the neglect of frictional effects that are important in the thin fluid layer near the front.
Dam-break flow with friction
When friction terms are included in the flow equations, there is no exact analytical solution. It is generally assumed that the frictionless flow equations are approximately valid in a short period after dam break and for small values of [math]x / (c_0 t) [/math]. In the front zone, where the water depth is small, the momentum balance is dominated by frictional momentum dissipation. If the inertia terms [math]\partial u / \partial t + u \partial u / \partial x [/math] in the momentum equation are ignored, then the current in the front region is mainly determined by the balance of gravitational acceleration [math] g \partial h / \partial x [/math] and shear stress [math]\tau[/math], the latter term being proportional to the square of the flow velocity. With such models the shape of the bore in the friction-dominated zone is given by[11]
[math]h(s) \propto s^a , \quad a = 1/3 – 1/2 \; ,[/math]
where [math]s[/math] is the distance measured from the wave front, and where it has been assumed that the flow velocity in the tip region does not (strongly) depend on [math]s[/math][12][13][14][15][16]. This shape is similar to what is observed in flume experiments (Fig. 4)[9]. At the bore front, the flow has a strong downward component and it is highly turbulent. Field observations of very high suspended sediment concentrations just behind the bore front demonstrate the strong erosion capacity of dam-break flows[17] (see also the article Tidal bore dynamics).
The bore front speed [math]u_s[/math] decreases with time. At small times [math]t\lt \lt t_{\infty}[/math], the bore front speed varies approximately as [13]
[math]u_s \approx c_0 \, (2 – 3.45 \sqrt{t / t_{\infty}}) \; , \qquad (4) [/math]
where [math] t_{\infty} = \sqrt{(h_0/g)}/ c_D [/math] and [math]c_D[/math] is the friction coefficient (usual values in the range [math]\approx (2-10)\, 10^{-3}[/math]).
At large times [math]t \ge t_{\infty}[/math] the bore front speed varies approximately as [15][16]
[math]u_s \approx c_0 \sqrt{ t_{\infty} / 3 t} \; . \qquad (5)[/math]
See the appendix for a derivation. It should be emphasized that these approximate formulas have been derived for very large (infinite) reservoirs in which the backward wave is not reflected.
Field observations
Data of dam-break discharges can be derived from the rate at which the reservoir level is falling. Complementary field data can be retrieved from analyzing the morphological impact of the dam break. Detailed experimental data of dam-break events only exist for laboratory settings.
Data from numerous reservoir dam breaks in the past have provided empirical formulas for the maximum discharge [math]Q_{max}[/math] through the breach [18][13]. From this data it was deduced that the width of the breach is often a function of the water volume [math]V[/math] in the reservoir (volume above breach level). A rough estimate of the width is given by[19] [math] B \approx 0.3 V ^ {1/3} [/math]. Empirical formulas for the maximum dam-break discharge then yield [20] [13]
[math]Q_{max} \approx 0.04 \sqrt{g} \, V^{0.37} h_0^{1.4} \approx 0.15 h_0 \, B \, \sqrt{g h_0} \, V^{0.04} h_0^{-0.1} . \qquad (6)[/math]
From this follows an empirical estimate for the order of magnitude of the maximum discharge per unit width,
[math] q_{max} \approx 0.2 h_0 \, \sqrt{g h_0} , \qquad (7)[/math]
where we have considered a large reservoir volume ([math]V \approx 10^7 m^3[/math]) and a water depth [math]h_0 \approx 15 m[/math]. The empirical estimate (7) is about 70% of the estimate (3) given by the frictionless flow solution. When comparing real dam failures with the idealized frictionless model, differences are not only due to the neglect of friction but also to the non-instantaneous nature of real dam-break events. Besides, the assumption of a dry channel bed in front of the dam often does not hold in practice - see next section.
Dam-break flow into a wetted channel
An analytical solution of frictionless dam-break flow into a wetted channel was given by Stoker (1957[21]). Flume experiments show that Stoker’s solution does not correctly predict the profile of the wave front, but it accurately predicts the wave front celerity and the wave height behind the wave front[7]. The experiments of Yang et al. (2022[7]) reveal significant differences between dam-break waves over dry and wet beds, both in flow pattern and wave front profile. Specifically, dam-break wave over a dry bed exhibits continuously increasing water depth behind a thin wave front characterized with little or no air entrainment. In contrast, a dam-break wave over a wet bed exhibits a highly turbulent broken wave front for cases with relatively shallow initial downstream water depth, see Fig. 5. For cases with relatively large initial downstream water depth ([math](h_0-h_2)/h_2 \lt 10[/math]), the dam-break wave exhibits a broken or undulating unbroken wave front[7]. Theoretical analysis indicates that dam-break waves over a wet bed are very sensitive to the shallow downstream water depth [math]h_2[/math], and even a slight change in [math]h_2[/math] will lead to a significant variation in wave height and wave front celerity. For the case of shallow downstream water depth, the wave front advance is mainly driven by the mutual drag between the upstream wave in the upper layer and the downstream water in the lower layer. Vortices along the interface extending into the downstream water result in mixing between the upper layer and the middle layer of the downstream water. For cases with great downstream water depth, the advance of wave front is influenced by the push of the upstream water to the downstream water, and the interface gradually lags behind the wave front. The mixing at the interface is significantly decreased and a smooth interface is observed, with no mix happening between the different layers of the downstream water[7].
Numerical models
The analytical methods for describing dam-break flow provide a qualitative picture and some first-order estimates for the bore profile and surge speed. Major assumptions underlying the simplifications are, (1) hydrostatic pressure throughout the dam-break flow, (2) uniform flow velocity throughout the bore tip region, and (3) the reservoir and outflow region can be represented by an unbounded prismatic channel. For actual field situations, the dam-break flow must be modeled numerically. A correct simulation of the backward surge requires models of the Boussinesq type that take into account vertical fluid accelerations[22]. Practical situations are generally characterized by the complex geometry of a highly irregular river bed that evolves during the dam-break event. Current numerical models cannot easily meet the requirements for performing accurate simulations of such real events.
Appendix: Analytical expression frictional dam-break flow

Here we follow the derivation proposed by Chanson (2009[15]), which gives an analytical expression of the frictional dam-break flow over a horizontal dry channel bed that matches closely the results of more elaborate analytical models[16], the results of flume experiments[7], and the results of numerical models[22]. The main assumptions are the following: (1) frictional effects are only substantial in the tip region of the dam-break wave and negligible elsewhere, (2) the flow velocity [math]u_f[/math] in the tip region is spatially uniform ([math]u_f=u_s[/math]), (3) frictional effects dominate the momentum balance in this tip region, and (4) the shallow-water equations hold for the whole dam-break wave. These assumptions are based on observations of dam-break flow in laboratory experiments.
Non-dimensionless hydrodynamic parameters are defined as follows: [math]h \rightarrow h/h_0, \; x \rightarrow x/h_0, \; u \rightarrow u/c_0, \; t \rightarrow t \sqrt{g/h_0}[/math]. The shallow-water equations then read
[math]\Large\frac{\partial h}{\partial t}\normalsize +\Large\frac{\partial hu}{\partial x}\normalsize = 0, \quad \Large\frac{\partial u}{\partial t}\normalsize + u\Large\frac{\partial u}{\partial x}\normalsize + \Large\frac{\partial h}{\partial x}\normalsize + c_D \Large\frac{u^2}{h}\normalsize =0 ,\qquad (A1)[/math]
where [math]c_D[/math] is the friction coefficient. The flow is frictionless ([math]c_D=0[/math]) upstream of the tip region [math]x \le x_1[/math], where [math]x_1[/math] is the location of the transition between frictionless and friction-dominated flow, see Fig.A1. In this zone the dam-break flow is given by
[math]h_{nf} = \frac{1}{9} (2-\frac{x}{t})^2 , \quad u_{nf} =\frac{2}{3} (1+\frac{x}{t}) . \qquad(A2) [/math]
In the tip region the momentum balance is approximated by [math]\quad \Large\frac{\partial h}{\partial x}\normalsize + c_D \Large\frac{u^2}{h}\normalsize =0 ,\qquad (A3)[/math]

The shape of the tip region is given by integration: [math]h_f=\sqrt{2 c_D u_f^2 (x_s – x)} , \qquad (A4)[/math]
where [math]x_s[/math] is the location of the tip of the dam-break wave. The transition location [math]x_1[/math] can be derived from the mass balance requirement expressing the fact that the water volume in the frictional tip region must be the same as the water volume that would be present if the flow in the tip region were frictionless:
[math]\int_{x_1}^{x_s} h_f(x)dx = \int_{x_1}^{2t} h_{nf}(x)dx \; \rightarrow \; \sqrt{2 c_D u_f^2} \int_{x_1}^{x_s} \sqrt{x_s-x} dx = \frac{1}{9} \int_{x_1}^{2t} (2-\frac{x}{t})^2 dx . \qquad (A5) [/math]
The location [math]x_s[/math] and the celerity [math]u_f[/math] of the tip of the dam-break wave is found by evaluating this condition together with the boundary conditions [math]h_f(x_1)=h_{nf}(x_1), \; u_f=u_{nf}(x_1) . \qquad (A6)[/math]
This yields the expressions
[math]x_s = (\frac{3}{2} u_f -1)\, t + \Large\frac{(2-u_f)^4}{32 c_D u_f^2} \normalsize , \qquad (2-u_f)^3 = 24 c_D u_f^2 t . \qquad (A7)[/math]
The time evolution of the celerity [math]u_f[/math] of the tip of the dam-break wave is shown in Fig. A2.
Related articles
References
- ↑ Zhang, L., Peng, M., Chang, D. and Xu, Y. 2016. Dam failure and Risk Assessment. John Wiley and Sons, Singapore
- ↑ Almog, E., Kelham, P and King, R. 2011. Modes of dam failure and monitoring and measuring techniques. Environmental Agency,UK https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/290819/scho0811buaw-e-e.pdf
- ↑ Gerritsen, H. 2005. What happened in 1953? The Big Flood in the Netherlands in retrospect. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 363: 1271–1291
- ↑ Richards, K.S. and Reddy, K.R. 2007. Critical appraisal of piping phenomena in earth dams. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 66: 381–402
- ↑ Jiang, X., Woerman, A., Chen, P., Huang, Q. and Chen, H. 2020. Mechanism of the progressive failure of non-cohesive natural dam slopes. Geomorphology 363, 107198
- ↑ Ritter, A. 1892. Die Fortpflanzung der Wasserwellen. Zeitschrift des Vereines Deutscher Ingenieure 36: 947-954
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 Yang, S., Yang, W., Zhang, C., Qin, S., Wei, K. and Zhang, J. 2022. Experimental and numerical study on the evolution of wave front profile of dam-break waves. Ocean Engineering 247, 110681
- ↑ Dressler, R. 1954. Comparison of theories and experiments for the hydraulic dam-break wave. Proc. Int. Assoc. Scientific Hydrology Assemblée Générale, Rome, Italy 3 (38)M 319–328
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Schoklitsch, A. 1917. Über Dambruchwellen. Kaiserliche Akademie der Wissenschaften, Wien, Mathematisch-Naturwissenschaftliche Klasse, Sitzungberichte IIa, 126: 1489–1514
- ↑ Cavaillé,Y. 1965. Contribution à l’étude de l’écoulement variable accompagnant la vidange brusque d’une retenue. Publ. Scient. et Techn. du Ministère de l’Air, 410, Paris, France, 165
- ↑ Baldock T.E. and Torres-Freyermuth, A. 2020. Numerical study of the flow structure at a swash tip propagating over a rough bed. Coastal Engineering 161, 103729
- ↑ Dressler, R.F. 1952. Hydraulic resistance effect upon the dambreak functions. J. Res. Natl. Bureau of Standards, 49(3): 217–225
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 Whitham, G.B. 1955. The effects of hydraulic resistance in the dam-break problem. Proc. Roy. Soc. of London, Serie A, 227: 399–407 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "W" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ Hogg, A.J. and Pritchard, D. 2004. The effects of hydraulic resistance on dam-break and other shallow inertial flows. J. Fluid Mech. 501: 179–212
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 15.3 15.4 Chanson, H. 2009. Application of the method of characteristics to the dam-break wave problem. Journal of Hydraulic Research 47: 41–49
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 Deng, H., Liu, H. and Lu, S. 2018. Analytical Study of Dam-Break Wave Tip Region. J. Hydraul. Eng. 144: 4018015
- ↑ Khezri, N. and Chanson, H. 2012. Inception of bed load motion beneath a bore. Geomorphology 153: 39–47
- ↑ Froehlich, D.C. 2016. Predicting Peak Discharge from Gradually Breached Embankment Dam. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, ASCE 04016041
- ↑ Froehlich, D.C. 2008. Embankment Dam Breach Parameters and Their Uncertainties. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, ASCE 134: 1708-1721
- ↑ Webby, M. G. 1996. Discussion of ‘Peak outflow from breached embankment dam.’ by D. C. Froehlich. J. Water Resour. Plann. Management 122:4(316), 316–317
- ↑ Stoker, J.J., 1957. Water Waves; the Mathematical Theory and Applications. Wily-Interscience
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 Castro-Orgaz, O. and Chanson, H. 2017. Ritter’s dry-bed dam-break flows: positive and negative wave dynamics. Environ Fluid Mech (2017) 17:665–694
Please note that others may also have edited the contents of this article.
|




