Sediment transport formulas for the coastal environment
Contents
Introduction
Calculating nearshore sediment transport is a challenge due to the complexity of the hydrodynamics and the variety of the governing phenomena. Indeed, it is very difficult to estimate sediment fluxes on beaches due to the combination of steady flows (currents) and oscillatory flows (waves). Moreover, many other effects should be integrated such as the variations in mean water level (tide, set-up, set-down), breaking wave effects (turbulence, undertow), and topographic influence (mean slope and bed forms). Furthermore, these parameters induce different types of transport (bed load, suspended load and sheet flow), with very different physical implications for the movement of sand [1] and a probabilistic approach introduced by Einstein [2]. Most of the sediment transport formulas are functions of the bed shear stress and have been developed and calibrated on specific data sets. For example, Bijker [3] and Bailard [4] [5] mainly validated their formula to field data for littoral drift; Van Rijn [6][7][8] or Camenen [9][10] compared their formulas to a large variety of laboratory and field data; Dibajana [11][12] and Ribberink [13][14] compared and fitted their formula to experimental flume data, simulating cross-shore dynamics (current opposite to incoming waves) for sheet-flow conditions especially.
A selection of several sediment transport formulas are presented here to model bedload, suspended load and typical phenomena observed on the nearshore such as phase-lag effects in sheet-flow transport.
Bedload transport under a wave and current interaction
Bijker (1971) formula
One of the first sediment transport formulations that is still often used in engineering applications was proposed by Bijker [3]. It is derived from Frijlink's formula [15] for a current only with a modification of the bottom shear stress using a wave-current model. The direction of sediment fluxes is always that of the current since this formula was proposed to estimate longshore transport rate. Bedload transport [math]q_{sb}[/math] is expressed such as:
[math] q_{sb} = C_b \ d_{50} \ \sqrt{\frac{\mu_c \tau_c}{\rho}} \exp\left( -0.27 \ \frac{(\rho_s-\rho)gd}{\mu_c \tau_{cw}} \right) \qquad (1) [/math]
where [math]d_{50}[/math] is the median grain size diameter, [math]h[/math] the water depth, [math]C_b[/math] a breaking wave parameter, [math]\mu_c[/math] a ripple parameter, [math]\tau_c[/math] the skin shear stress due to current only, [math]\tau_{cw}[/math] the shear stress due to wave-current interaction, and [math]\rho_s[/math], [math]\rho[/math] the sediment and water densities, respectively.
The shear stress due to the wave-current interaction is computed following the method proposed by Bijker [3] introducing waves as a stirring factor:
[math] \tau_{cw} = \left[ 1+0.5 \left(\xi_B \ \frac{U_w}{U_c} \right)^2 \right] \ \tau_{cf} \qquad (2) [/math]
with [math]\xi_B = \sqrt{f_{wt}/f_{ct}}[/math] a parameter due to the wave-current interaction, [math]f_{wt}[/math] the total friction coefficient due to waves (including bedform effects), [math]U_w[/math] the peak value of the wave orbital velocity at the bottom, [math]U_c[/math] the depth-averaged current velocity and [math]\tau_{cf} [/math] the bed shear stress (including form drag).
The ripple parameter introduced by Bijker [3] is defined by the following equation:
[math] \mu_c = \left(f_{ct}/f_c \right)^{3/2} \qquad (3)[/math]
where [math]f_{ct}[/math] is the total friction coefficient due to current (including bedform effects) and [math]f_c[/math] is the skin friction coefficient due to current.
The breaking wave coefficient is defined by:
[math] C_b = 2 , \; H_w/h \lt 0.05 ; \quad C_b = 2 + 3 \ (H_w/h-0.05) , \; 0.05\lt H_w/h\lt 0.4 ; \quad C_b = 5 , \; 0.4\lt H_w/h . \qquad (4) [/math]
where [math]H_w[/math] is the wave height, and [math]h[/math] the water depth.
Bailard and Inman (1981) formula
Bagnold [1] introduced the energetics model in which the main idea is that the sediment flux is proportional to the energy flux [math]\Omega[/math] (local rate of energy dissipation):
[math] \Omega = 0.5 \ \rho \ f_{cw} \ | \overrightarrow{u(t)} |^3 \qquad (5)[/math]
with [math]f_{cw}[/math] the friction coefficient due to the wave-current interaction, [math]\vec{u(t)}[/math] the instantaneous velocity vector, [math]\vec{u(t)} = \vec{U_c} + \vec{u_w(t)}[/math], [math]U_c[/math] the depth-averaged current velocity, and [math]u_w(t)[/math] instantaneous wave velocity over the bed.
The Bailard and Inman formula [5] is derived directly from the Bagnold model. For a horizontal bed, it can ultimately be written as a vector of sediment volume transport:
[math] \overrightarrow{q_{sb}} = \frac{0.5 \ f_{cw}}{g \ (s-1)} \left( \frac{\epsilon_b}{\tan\phi} \lt \mid\vec{u}\mid^2\vec{u}\gt \right) \qquad (6)[/math]
where [math]\epsilon_b[/math] is the bed load efficiency, [math]\phi[/math] the friction angle of the sediment, [math]s[/math] the ratio of sediment and water densities, and [math]\lt \ \gt [/math] yields an average over several periods of the wave.
The bed load efficiency was found slightly different from the one given by Bagnold [16]. Bailard suggested from a calibration with field data that [math]\epsilon_b = 0.1[/math]. One difficulty for this formulation is the estimation of the friction coefficient due to the wave-current interaction as Bailard [5] did not specify any expression for this friction factor.
Van Rijn (1989) formula
The Van Rijn formula [6][8] is expressed in the same way as the Bijker formula, as a bed load formula taking into account the influence of waves as a stirring effect. The direction of sediment fluxes is also that of the current. Bedload transport can be written as follows:
[math] q_{sb} = 0.25 \ d_{50} \ d_*^{-0.3} \ (\tau_{cw}/ \rho)^{0.5} \ \left( \tau_{cw} / \tau_{cr} \ - 1 \right) \qquad (7)[/math]
where [math]d_* = [(s-1)g/\nu^2]^{1/3}d_{50}[/math] the dimensionless sediment diameter, [math]\tau_{cw} = 0.5 f_{cw} U_{cw}[/math] the skin bed shear stress due to current and waves with [math]f_{cw}=\alpha \beta u_c + (1-\alpha) U_w[/math] , [math]\alpha = u_c/(u_c+U_w)[/math], [math]u_c[/math] is the current close to the bottom as defined by Van Rijn [8], [math]\beta[/math] an offset coefficient for bedload, and [math]\tau_{cr}[/math] the critical bed shear stress for inception of movement.
Van Rijn [17] updated his bedload formula. He proposed a new simplified bedload transport formula for steady flow (with or without waves):
[math] q_{sb} = 0.015 \ U_c \ h \ \left(\frac{d_{50}}{h}\right)^{1.2} \ \Psi^{1.5} \qquad (8) [/math]
where [math]\Psi=(U_e-U_{cr})/\sqrt{(s-1)gd_{50}}[/math] is the mobility parameter, [math]U_e=U_c+\gamma U_w[/math] the effective velocity with [math]\gamma=0.4[/math] for irregular waves and [math]\gamma=0.8[/math] for regular waves, [math]U_{cr}[/math] the critical effective velocity for inception of movement.
Ribberink (1998) formula
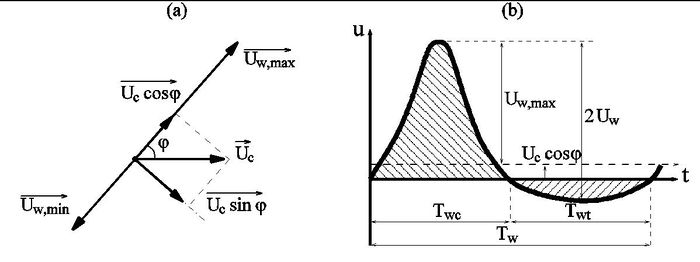
Ribberink [14] proposed a quasi-steady model of bed load transport where the instantaneous solid flux is assumed to be proportional to a function of the difference between the actual time-dependent bed shear stress and the critical bed shear stress (see Fig. 1). This formulation has been calibrated towards several flume data sets including wave-current interaction in a plane regime (suspended load negligible) and field data (unidirectional flows in rivers).
The following expression for the sand transport rate was obtained:
[math] \vec{q_{sb}} = m_{Rib} \ \sqrt{(s-1) \ g \ d_{50}^3} \ \lt \left( |\vec{\theta(t)}|- \theta_{cr} \right)^{n_{Rib}} \frac{\overrightarrow{\theta(t)}}{|\theta(t)|}\gt \qquad (9) [/math]
where [math]\overrightarrow{\theta(t)} = 0.5 \ f_{cw} \ |u(t)|\overrightarrow{u(t)} \ / \ [(s-1) \ g \ d_{50}][/math] is the time-dependent Shields parameter ({\it cf.} figure 1) with the instantaneous velocity [math]\overrightarrow{u(t)} = \vec{U_c} + \overrightarrow{u_w(t)}[/math] and the wave-current friction factor [math]f_{cw}[/math], [math]\theta_{cr}[/math] the critical Shields parameter, [math]\lt \ \gt [/math] yields a time-averaging over several wave periods, and [math]m_{Rib}=11[/math], [math]n_{Rib}=1.65[/math] the adjusted coefficients.
In the same way as the Bailard formula, an equivalent wave-current friction coefficient has to be computed. Ribberink used the Madson and Grant model [18] model for which the friction coefficient [math]f_{cw}[/math] due to the wave and current interaction is defined such as:
[math] f_{cw}=X_v \ f_c +(1-X_v) \ f_w \qquad(10) [/math]
with [math]X_v=|U_c|/(|U_c|+U_w)[/math].
Ribberink also proposed to compute total roughness values as follows:
[math] k_{st} = {\rm max} \left( k_s;d_{50} \ [1+6 \ (\lt |\theta(t)|\gt / \theta_{cr}-1)] \right) \qquad (11)[/math]
where [math]k_s[/math] is skin roughness height.
Formulas with a similar approach have been suggested by Soulsby and Damgaard [19] and Gonzalez and Madsen [20].
Camenen and Larson (2005) formula
Camenen and Larson [9] developed a formula for bed load transport in a similar approach as Ribberink. They introduce an exponential function for the effect of inception of motion following the probabilistic approach introduced by Einstein [2]. The bed load transport [math]q_{sb}[/math] may be expressed as follows:
[math] q_{sbw} = a_w \ \sqrt{(s-1)g \ {d_{50}}^3} \ \sqrt{\theta_{cw,net}} \ \theta_{cw,m} \ \exp\left( -b \frac{\theta_{cr}}{\theta_{cw}} \right) , [/math]
[math] q_{sbn} = a_n \ \sqrt{(s-1)g \ {d_{50}}^3} \ \sqrt{\theta_{cn}} \ \theta_{cw,m} \ \exp\left( -b \frac{\theta_{cr}}{\theta_{cw}} \right) . \qquad (12) [/math]
where the subscripts [math]w[/math] and [math]n[/math] correspond, respectively, to the wave direction and the direction normal to the wave direction and [math]a_w[/math] [math]a_n[/math] and [math]b[/math] are empirical coefficients. [math]\theta_{cw,m}[/math] is the mean Shields parameter and [math]\theta_{cw}[/math] the maximum Shields parameter due to wave-current interaction, and [math]\theta_{cn}=\frac{1}{2} f_c (U_c \sin\varphi)^2 / ((s-1)g d_{50})[/math]. In order to simplify the calculations, the mean and maximum Shields parameter due to wave-current interaction is obtained by straightforward addition:
[math]\theta_{cw,m} = ( {\theta_c}^2 + {\theta_{w,m}}^2 + 2 \theta_{w,m} \theta_c \cos\varphi)^{1/2}[/math]
[math]\theta_{cw} = ( {\theta_c}^2 + {\theta_w}^2 + 2 \theta_w \theta_c \cos\varphi)^{1/2}[/math],
respectively, where [math]\theta_c[/math], [math]\theta_{wm}[/math], and [math]\theta_w[/math] are the current, mean wave, and maximum wave Shields number, and [math]\theta_{w,m}=0.5 \theta_w[/math] for a sinusoidal wave profile.
The net sediment transporting velocity [math]\theta_{cw,net}[/math] in Eq. 12 is given by,
[math] \theta_{cw,net} = \theta_{cw,on}+\theta_{cw,off} \qquad (13) [/math]
where [math]\theta_{cw,on}[/math] and [math]\theta_{cw,off}[/math] are the mean values of the instantaneous shear stress over the two half periods [math]T_{wc}[/math] and [math]T_{wt}[/math] ([math]T_w=T_{wc}+T_{wt}[/math], in which [math]T_w[/math] is the wave period) defined as follows (see Fig. 1),
[math] \theta_{w,onshore} = \frac{1}{2T_{wc}} \int_0^{T_{wc}} \frac{f_{cw} (u_w(t)+U_c\cos\varphi)^2}{(s-1)g d_{50}} dt , [/math]
[math] \theta_{w,offshore} = \frac{1}{2T_{wt}} \int_{T_{wc}}^{T_w} \frac{f_{cw} (u_w(t)+U_c\cos\varphi)^2}{(s-1)g d_{50}} dt \qquad (14) [/math]
where [math]u_w(t)[/math] is the instantaneous wave orbital velocity.
Based on comparison with an extensive data set, the following relationship is proposed for the transport coefficient [math]a_w[/math] [9][21]
[math] a_w = 6 + 6 \ X_t \qquad (15) [/math]
in which [math]X_t = \theta_c/(\theta_c + \theta_w)[/math] , where [math]\theta_c[/math] and [math]\theta_w[/math] are the Shields parameter for current and waves, respectively. The coefficient perpendicular to the waves, where only the current transports sediment, is set to [math]a_n = 12[/math], and the coefficient in the term describing initiation of motion is [math]b = 4.5[/math].
Phase-lag effects in sheet-flow transport
Since the experiments of Dibajnia and Watanabe [11] and Ribberink and Salam [13], one realized that for intense sheet-flow transport, net bedload in the wave direction could be reduced or even be switched to the opposite direction of waves due to the phase-lag between sediment concentrations and fluid velocities [22]. Several authors attempt to model these effects.
Dibajnia and Watanabe (1992) formula
The sediment transport formulation of Dibajnia and Watanabe [11] is the first one to include phase-lag effects. Similar to the Bailard and Ribberink models, it breaks down the sediment transport into two half-cycles due to the presence of waves (see Fig. 2). During the first half-cycle, sediment moves in the direction of the wave, just as it moves in the opposite direction during the second half-cycle. An interesting aspect of the formula is that it takes into account a possible quantity of sand still in suspension after each half-cycle, and hence moving in the other direction. This formula enables transport under a non-linear wave to be described.
The solid volume flux is given by the following equation:
[math] \vec{q_s} = A_{dw} \ W_s \ d \ \frac{\vec{\Gamma}}{\Gamma} \ \Gamma^{B_{dw}} \qquad (16) [/math]
with [math]A_{dw} = 0.001[/math] and [math]B_{dw} = 0.55[/math] the calibration coefficients, and
[math] \vec{\Gamma} = \frac{ T_{wc} \ \vec{u_{wc}} \ ( \Omega_c^{\ 3} + \Omega_t^{'3} ) + T_{wt} \ \vec{u_{wt}} \ ( \Omega_t^{\ 3} + \Omega_c^{'3} )} {(u_{wc} + u_{wt}) \ T_w} \qquad (17) [/math]
where [math]T_w[/math], [math]T_{wc}[/math], [math]T_{wt}[/math] are the period and half-periods of wave taking into account the effect of a current (cf. figure 2); [math]\Omega_c[/math], [math]\Omega_t[/math] are the amount of sand entrained and settled during the half-period [math]T_{wc}[/math] and [math]T_{wt}[/math], respectively; [math]\Omega'_c[/math], [math]\Omega'_t[/math] arecthe amount of suspended sand remaining from the positive and the negative half-cycle respectively. [math]u_{wc}^2[/math] and [math]u_{wt}^2[/math] the average quadratic velocities (wave + current) over each half-period expressed as:
[math] {u_{wj}}^2 = \frac{2}{T_{wj}}\int_t^{t+T_{wj}} u^2(t) \ dt + 2 \ {U_c}^2 \ sin^2\varphi \qquad (18) [/math]
where [math]j[/math] can be [math]c[/math] or [math]t[/math], [math]u(t) = U_c \ \cos\varphi + u_w(t)[/math]. [math]u_w(t)[/math] is the instantaneous wave orbital velocity, and [math]\varphi[/math] the angle between wave direction and current direction.
If [math] \omega_j \leq \omega_{cr}[/math] then [math]\Omega_j = \omega_j \ \frac{2 \ W_s \ T_{wj}}{d} [/math] and [math]\Omega'_j=0, [/math]
If [math] \omega_j \geq \omega_{cr}[/math] then [math] \Omega_j = \frac{2 \ W_s \ T_{wj}}{d}[/math] and [math] \Omega'_j= (\omega_j-1) \ \frac{2 \ W_s \ T_{wj}}{d} , \qquad (19) [/math]
with:
[math] \omega_j = \frac{{u_{wj}}^2}{2 \ (s-1) \ g \ W_s \ T_{wj}} \qquad (20) [/math]
where [math]j[/math] can be [math]c[/math] or [math]t[/math].
[math]\omega_{cr}[/math] is a ripple parameter defined as:
[math] \omega_{cr} = 0.03 \; [/math] if [math] \; \theta_{cw(max)} \leq 0.2 ; [/math]
[math] \omega_{cr} = 1-0.97 \ [1- 6.25 \ (\theta_{cw(max)}-0.2)^2 ]^{0.5} \; [/math] If [math] \; 0.2 \lt \theta_{cw(max)} \lt 0.6 ; [/math]
[math] \omega_{cr} = 1 \; [/math] if [math] \; 0.6 \lt \theta_{cw(max)} \qquad (21) [/math]
where [math]\theta_{cw(max)}[/math] is the maximum Shields parameter due the wave-current interaction (computed following [23], pp.87-95).
Several authors developed a model based on the work of Dibajnia and Watanabe by introducing the effects of acceleration [24] and by introducing the Shields parameter in Eq.17. [25][26]
Camenen and Larson (2006) formula
Following the approach proposed by Dibajnia and Watanabe, Camenen and Larson [27] introduced a parameter in Eq. 13 of the bedload formula to take into account phase-lag effects in bedload transport. This modification was eventually extended to acceleration effects [28][29]. The net sediment transporting velocity [math]\theta_{cw,net}[/math] in Eq. 12 is then given by,
[math] \theta_{cw,net} = (1-\alpha_{pl,b})(1+\alpha_a)\theta_{cw,on}+(1+\alpha_{pl,b})(1-\alpha_a)\theta_{cw,off} \qquad (22) [/math]
in which [math]\alpha_{pl,b} = \alpha_{onshore} - \alpha_{offshore}[/math] and,
[math] \alpha_j = \frac{\nu^{0.25} \ {U_{wj}}^{0.5}}{{W_s} \ {T_j}^{0.75}} \exp\left[ - \left(\frac{U_{w,crsf}}{U_{wj}} \right)^2 \right] \qquad (23) [/math]
where [math]U_{w,crsf}[/math] is the critical velocity for inception of sheet-flow transport [30]}:
[math] U_{w,crsf} = 8.35 \ [(s-1) g \ (d_{50} \ \delta_w)^{1/2}]^{1/2} \ (1 + r_w) \qquad (24) [/math]
where [math]\delta_w = \sqrt{\nu T_w / \pi}[/math] is the Stokes boundary layer thickness [31], and [math]r_w[/math] the wave asymmetry coefficient, [math]r_w = u_{w,max}/U_w-1 ,[/math] with [math]u_{w,max}[/math] being the maximum wave velocity.
Based on the work by Watanabe and Sato [24], the coefficient [math]\alpha_a[/math] is given by [28] (see Fig. 3):
[math] \alpha_a = \frac{1-R_{ac}}{1+R_{ac}}[/math] with [math]R_{ac} = T_{ac}/T_{dc} \qquad (25)[/math]
Suspended-load
Bijker (1971) formula
Bijker [3] related suspended load to bedload as the bed concentration reference value. Suspended load is then estimated using the Einstein integrals:
[math] q_{ss} = 1.83 \ q_{sb} \ \left( I_1\ln \left[ \frac{33 h}{\delta_c} \right] +I_2 \right) \qquad (26) [/math]
where [math]\delta_c=100d/h[/math] is dimensionless thickness of the bed load layer.
The Einstein integrals [math]I_1[/math] and [math]I_2[/math] for the suspended load are given:
[math] I_1 = \int_{\delta}^{1} \left( \frac{1-y}{y} \right)^A dy , [/math]
[math] I_2 = \int_{\delta}^{1} \left( \frac{1-y}{y} \right)^A \ln y \ dy \qquad (27) [/math]
where [math]A=\frac{W_s}{\kappa} (\tau_{cw}/\rho)^{-1/2}[/math] is a function determining the rate of the suspension, [math]\kappa=0.41[/math] is the Von Karman constant, and [math]W_s[/math] the settling velocity.
Bailard (1981) formula
Following the work of Bailard and Inman [5], Bailard developed a total load formula, including a specific term for suspended load [4]:
[math] \vec{q_{sb}} = \frac{0.5 \ f_{cw}}{g \ (s-1)} \left( \frac{\epsilon_s}{W_s} \lt \mid\vec{u}\mid^3\vec{u}\gt \right) \qquad (28) [/math]
where [math]\epsilon_s[/math] is the suspended load efficiency, and [math]\lt \ \gt [/math] yields an average over several periods of the wave.
The suspended load efficiency coefficient is also slightly different from the one given by Bagnold [16]. Bailard suggested from a calibration with field data that [math]\epsilon_s = 0.02[/math].
Van Rijn (1989) formula
The Van Rijn formula [7][8] for suspended load corresponds to a resolution of the equation of concentration over depth:
[math] \frac{dc}{dz} = - \frac{(1-c)^5 \ c \ W_s}{\epsilon_{scw}} \qquad (29)[/math]
where [math]c(z)[/math] is the mean volume concentration (time averaged) at height [math]z[/math], [math](1-c)^5[/math] corresponds to the decrease of the settling velocity due to high concentrations, and [math]\epsilon_{scw}[/math] is the mixing coefficient in case of a wave-current interaction. Then, integrating sediment fluxes over depth:
[math] q_{ss} = \int^h_{z_a} \overline{u(z)} \ c(z) \ dz \qquad (30)[/math]
where [math]h[/math] is the water depth, [math]z_a={\rm max}(k_{sct},k_{swt})[/math] the reference level, [math]k_{sct},k_{swt}[/math] total roughness values due to current and waves, respectively, and [math]\overline{u(z)}[/math] is the mean velocity (time averaged) at height [math]z[/math].
The reference concentration is estimated at the level [math]z_a[/math] based on the Van Rijn bedload formula [8]:
[math] c_a = 0.015 \ \frac{d_{50}}{z_a} \ d_{*}^{-0.3} \ (\tau_{cw} / \tau_{cr} \ -1 )^{1.5} . \qquad (31) [/math]
The sediment diffusion coefficient for a wave and current interaction is given by [7][8] :
[math] \epsilon_{scw}(z) = [\epsilon_{sc}(z)^2+\epsilon_{sw}(z)^2]^{1/2} \qquad (32) [/math]
with:
[math] \epsilon_{sc}(z) = \epsilon_{sc,max} = 0.25 \kappa \beta_s u_* h \;[/math] if [math] \; z \gt h/2[/math] ,
[math] \epsilon_{sc}(z) = \epsilon_{sc,max} \ \left[1-\left(1-2 \frac{z}{h} \right)^2\right] \; [/math] if [math] \; z \leq h/2 \qquad (33) [/math]
where [math]\beta_s={\rm min}(1.5,1+2(W_s/u_*)^2)[/math], and [math]u_*=\sqrt{\tau_{cw}/\rho}[/math] is the shear velocity, and
[math] \epsilon_{sw}(z) = \epsilon_{sw,b} = 0.004 \ a_{br} \ d_* \ \delta_s \ U_w \; [/math] if [math] \; z \leq \delta_s , [/math]
[math] \epsilon_{sw}(z) = \epsilon_{sw,max} = 0.035 \ a_{br} \ h \frac{H_w}{T_w} \; [/math] if [math] \; z \gt h/2 , [/math]
[math] \epsilon_{sw}(z) = \epsilon_{sw,b}+(\epsilon_{sw,max}-\epsilon_{sw,b}) \ \frac{z-\delta_s}{h/2-\delta_s} \; [/math] if [math] \; \delta_s \lt z \leq h/2 \qquad (34) [/math]
with [math]\delta_s=0.3 h (H_w/h)^{0.5}[/math] is the thickness of the boundary layer, and [math]a_{br}={\rm max}(3 H_w/h-0.8,1)[/math], a coefficient. The estimation of the time-averaged velocity is based on the logarithmic velocity profile:
[math] \overline{u(z)} = U_c \ \frac{\log (30 \delta_w/k_a)}{\log(30 h/k_a)-1} \ \frac{\log(30z/k_{sc})}{\log(30\delta_w/k_{sc})-1} \; [/math] if [math] \; z \leq \delta_w , [/math]
[math] \overline{u(z)} = U_c \ \frac{\log(30z/k_a)}{\log(30h/k_a)-1} \; [/math] if [math] \; z \gt \delta_w \qquad (35) [/math]
with [math]\delta_w = 0.072 A_w (A_w/k_{sw})^{-0.25}[/math] the thickness of the wave boundary layer, [math]A_w=U_w T_w/(2\pi)[/math] the wave half-excursion.
Van Rijn updated his suspended-load formula. He proposed a new simplified suspended-load transport formula for steady flow (with or without waves) [32]:
[math] q_{sb} = 0.015 \ U_c \ \frac{d_{50}}{d_*^{0.6}} \ \Psi^{2.0} \qquad (36) [/math].
Camenen and Larson (2008) formula
In determining the suspended load [math]q_{ss}[/math], following the simplified approach by Madsen [33] and Madsen et al. [34], the vertical variation in the horizontal velocity was neglected and an exponential-law profile assumed for the sediment concentration. The suspended sediment load is written (components along the wave direction and perpendicular) [10]:
[math] q_{ssw} = U_{cw,net} \ c_R \frac{\epsilon}{W_s} \left[ 1 - \exp \left( -\frac{W_s h}{\epsilon}\right)\right] , [/math]
[math] q_{ssn} = U_c \sin\varphi \ c_R \frac{\epsilon}{W_s} \left[ 1 - \exp \left( -\frac{W_s h}{\epsilon}\right)\right] \qquad (37) [/math]
where [math]h[/math] is the water depth, [math]U_{cw,net}[/math] is the net mean current after a wave period, [math]c_R[/math] the reference concentration at the bottom, [math]W_s[/math] the sediment fall speed, and [math]\epsilon[/math] the sediment diffusivity. In solving the integral, the ratio [math]W_s h / \epsilon[/math] may often be assumed large, implying that the exponential term is close to zero. However, the assumption that integrating to infinity or to [math]h[/math] produces about the same result, may not be valid when strong mixing due to wave breaking is present.
The bed reference concentration is obtained from
[math] c_R = A_{cR} \ \theta_{cw,m} \ \exp \left( -4.5 \ \frac{\theta_{cr}}{\theta_{cw}}\right) \qquad (38) [/math]
in which the coefficient [math]A_{cR}[/math] is given by
[math] A_{cR} = 1.5 \ 10^{-3} \exp (-0.2 d_*) \qquad (39) [/math]
where [math]d_*=\sqrt[3]{(s-1)g/\nu^2} \ d_{50}[/math] is the dimensionless grain size.
The sediment diffusivity is related to the energy dissipation [35],
[math] \epsilon = h (D /\rho)^{1/3} \qquad (40) [/math]
in which [math]D[/math] is the total effective dissipation expressed as
[math] D = {k_b}^3 \ D_b + {k_c}^3 \ D_c + {k_w}^3 \ D_w \qquad (41) [/math]
where the energy dissipation from wave breaking ([math]D_b[/math]) and from bottom friction due to current ([math]D_c[/math]) and waves ([math]D_w[/math]) were simply added, and [math]k_b[/math], [math]k_c[/math] and [math]k_w[/math] are coefficients. The coefficient [math]k_b[/math] corresponds to an efficiency coefficient ([math]k_b=0.010[/math]), whereas [math]k_c[/math] and [math]k_w[/math] are related to the Schmidt number. Assuming a parabolic profile for the vertical sediment diffusivity, its mean value over the depth (for a steady current or waves, respectively) may be written as follows:
[math] \epsilon_j = h (D_j / \rho)^{1/3} = k_j \ \kappa \ u_{*j} \ h \qquad (42) [/math]
where [math]k_j[/math] is a function of the Schmidt number [math]\sigma_j[/math] or the ratio between the vertical eddy diffusivity of particles and the vertical eddy viscosity of water. [math]u_{*j}[/math] is the shear velocity due to current or waves only, with subscript [math]j[/math] taking on the values [math]c[/math] (current) or [math]w[/math] (waves), respectively. In case of a steady current, [math]k_c =\sigma_c/6 \kappa[/math] whereas for waves [math]k_w =\pi \sigma_w /3 \kappa[/math]. The following expression was developed for the Schmidt number:
[math] \sigma_j = A_1 + A_2 \ \sin^{2} \left( \frac{\pi}{2} \frac{W_s}{u_{*j}} \right) \; [/math] if [math] \; W_s/u_{*j} \leq 1 , [/math]
[math] \sigma_j = 1 + (A_1+A_2-1) \ \sin^{2} \left( \frac{\pi}{2} \frac{u_{*j}}{W_s} \right) \; [/math] if [math] \; W_s/u_{*j} \gt 1 \qquad (43) [/math]
where [math]j[/math] is a subscript equal to [math]c[/math] or [math]w[/math]. [math]A_{c1}=0.4[/math], [math]A_{c2}=3.5[/math], [math]A_{w1}=0.15[/math] and [math]A_{w2}=1.5[/math]. Recent measurements in large rivers showed however that [math]\sigma_c[/math] may be overestimated using Eq. 43 for large water depth [36]. For wave-current interaction, a weighted value is employed for the Schmidt number:
[math] \sigma_{cw}=X_t \ \sigma_c +(1-X_t) \ \sigma_w \qquad (44) . [/math]
The net mean current is defined in a similar way to the net Shields parameter for the bed load in order to take into account a possible sediment transport due to wave asymmetry, as well as a possible phase-lag effects on the suspended concentration,
[math] U_{cw,net} = (1-\alpha_{pl,s})U_{cw,on}+(1+\alpha_{pl,s})U_{cw,off} \qquad (45) [/math]
where [math]\alpha_{pl,s}[/math] is the coefficient describing phase-lag effects on the suspended load, and [math]U_{cw,j}[/math] is the root-mean-square value of the velocity (wave+current) over the half period [math]T_{wj}[/math], where the subscript [math]j[/math] should be replaced either by [math]on[/math] (onshore) or [math]off[/math] (offshore) (see also Fig. 1) according to:
[math] U_{cw,on} = [\frac{1}{T_{wc}} \int_0^{T_{wc}} (u_w(t)+U_c \cos\varphi)^2 dt ]^{1/2} , [/math]
[math] U_{cw,off} = [\frac{1}{T_{wt}} \int_{T_{wc}}^{T_w} (u_w(t)+U_c\cos\varphi)^2 dt]^{1/2} . \qquad (46) [/math]
In case of a steady current [math]U_{cw,net}=U_c[/math].
Related articles
Definitions, processes and models in morphology
Manual Sediment Transport Measurements in Rivers, Estuaries and Coastal Seas
Coastal Hydrodynamics And Transport Processes
Process-based morphological models
Littoral drift and shoreline modelling
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Bagnold, R.A., 1963. An approach of marine sedimentation. In: The Sea. Vol. 3. M. N. Hill, Interscience, New York, pp. 507--528.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Einstein, H.A., 1972. A basic description of sediment transport on beaches. In: Meyer, R.E. (Ed.), Waves on Beaches and Resulting Sediment Transport. Academic Press, pp. 53--93.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Bijker, E.W., 1971. Longshore transport computation. J. Waterways Harbors Division 97, WW4, 687--701.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Bailard, J.A., 1981. An energetic total load sediment transport model for a plane sloping beach. J. Geophysical Res. 86 (C11), 10938-10954.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Bailard, J.A., Inman, D.L., 1981. An energetic bedload model for a plane sloping beach : local transport. J. Geophysical Res. 86(C11), 10938--10954.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 van Rijn, L.C., 1984. Sediment transport, part I: bed load transport. J. Hydraulic Division 110(10), 1431--1456.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 van Rijn, L.C., 1984. Sediment transport, part II: suspended load transport. J. Hydraulic Division 110(11), 1613--1641.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 8.5 van Rijn, L.C., 1989. Handbook sediment transport by currents and waves. Tech. Rep. H461, Delft Hydraulics Lab., The Hague.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Camenen, B., Larson, M., 2005. Bed-load transport under steady and oscillatory flow. In: Proc. Coastal Dynamics'05. ASCE, Barcelona, Spain, pp. 1--8, (CD ROM).
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Camenen, B., Larson, M., 2008. A general formula for noncohesive suspended sediment transport. J. Coastal Res. 24(3), 615--627.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 Dibajnia, M., Watanabe, A., 1992. Sheet flow under nonlinear waves and currents. In: Proc. 23rd Int. Conf. Coastal Eng. ASCE, Venice, Italy, pp. 2015--2029.
- ↑ Dibajnia, M., 1995. Sheet flow transport formula extended and applied to horizontal plane problems. Coastal Eng. J. 38(2), 178--194.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Ribberink, J.S., Al Salem, A.A., 1994. Sediment transport in oscillatory boundary layers in cases of rippled beds and sheet flow. J. Geophysical Res. 99(C6), 707--727.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Ribberink, J.S., 1998. Bed-load transport for steady flows and unsteady oscillatory flows. Coastal Eng. 34, 52--82.
- ↑ Frijlink, H.C., 1952. Discussion des formules de d\'ebit solide de Kalinske, Einstein, et MeyerPeter et M\"uller compte tenue des mesures r\'ecentes de transport dans les rivi\`eres n\'eerlandaises [discussion of bedload movement formulas of Kalinske, Einstein and Meyer-Peter and M\"uller and their application to recent measurements of bedload movement in the rivers of Holland]. In: Comptes rendus 2i\`eme Journée Hydraulique. Grenoble, France, pp. 98--103, (in French).
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Bagnold, R.A., 1966. An approach of sediment transport model from general physics. Tech. Rep. 422-I, US Geol. Survey Prof. Paper.
- ↑ van Rijn, L.C., 2007. Unified view of sediment transport by currents and waves. I: Initiation of motion, bed roughness, and bed-load transport. J. Hydraulic Eng. 133(6), 649—667.
- ↑ Madsen, O.S., Grant, W.D., 1976. Sediment transport in the coastal environment. Tech. Rep. 209, M. I. T., Cambridge, Massassuchetts, USA.
- ↑ Soulsby, R.L., Damgaard, J.S., 2005. Bedload sediment transport in coastal waters. Coastal Eng. 52, 673—689
- ↑ Gonzalez-Rodriguez, D., Madsen, O.S., 2007. Seabed shear stress and bedload transport due to asymmetric and skewed waves. Coastal Eng. 54, 914—929.
- ↑ Camenen, B., Larson, M., 2005. A bedload sediment transport formula for the nearshore. Estuarine, Coastal \& Shelf Science 63, 249--260.
- ↑ Dohmen-Janssen, M., 1999. Grain size influence on sediment transport in oscillatory sheet flow, phase-lags and mobile-bed effects. Ph.D. thesis, Delft Univ. of Technology, The Netherlands, ISBN 90-9012929-4.
- ↑ Soulsby, R.L., 1997. Dynamics of marine sands, a manual for practical applications. Thomas Telford, London, UK, ISBN 0-7277-2584 X.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 Watanabe, A., Sato, S., 2004. A sheet-flow transport rate formula for asymmetric, forward-leaning waves and currents. In: Proc. 29th Int. Conf. Coastal Eng. Lisbon, Portugal, pp. 1703—1714.
- ↑ da Silva, P.A., Temperville, A., Seabra Santos, F., 2006. Sand transport under combined current and wave conditions: A semi-unsteady, practical model. Coastal Eng. 53, 897—913.
- ↑ van der A, D.A., Ribberink, J.S., van der Werf, J.J., O'Donoghue, T., Buijsrogge, R.H., Kranenburg, W.M., 2013. Practical sand transport formula for non-breaking waves and currents. Coastal Eng. 76, 26--42.
- ↑ Camenen, B., Larson, M., 2006. Phase-lag effects in sheet flow transport. Coastal Eng. 53, 531—542,
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 Camenen, B., Larson, M., 2007. A total load formula for the nearshore. In: Proc. Coastal Sediments'07. ASCE, New Orleans, Louisiana, USA, pp. 56--67.
- ↑ Camenen, B., Larson, M., 2010. Discussion of "measurements of sheet flow transport in acceleration-skewed oscillatory flow and comparison with practical formulations" by D.A. van der A, T.O'Donoghue and J.S. Ribberink. Coastal Eng. 58(1), 131--134.
- ↑
- ↑ Chan, K.W., Baird, M. H.I., Round, G.F., 1972. Behaviour of beds of dense particles in a horizontally oscillating liquid. Proc. Royal Society of London A(330), 537—559.
- ↑ van Rijn, L.C., 2007. Unified view of sediment transport by currents and waves. II: Suspended transport. J. Hydraulic Eng. 133(6), 668—689.
- ↑ Madsen, O.S., 1993. Sediment transport outside the surf zone. unpublished technical report, Waterways Experiment Station, U. S. Army Corps of Engineer, Vicksburg, Mississippi, USA.
- ↑ Madsen, O.S., Tajima, Y., Ebersole, B.A., 2003. Longshore sediment transport: a realistic order-of-magnitude estimate. In: Proc. Coastal Sediments'03. ASCE, Clearwater Beach, Florida, USA, pp. 1--8, cDROM.
- ↑ Battjes, J.A., Janssen, J. P. F.M., 1978. Energy loss and set-up due to breaking of random waves. In: Proc. 16th Int. Conf. Coastal Eng. ASCE, pp.569--587.
- ↑ Camenen, B., Le Coz, J., Dramais, G., Peteuil, C., Fretaud, T., Falgon, A., Dussouillez, P., Moore, S.A., 2014. A simple physically-based model for predicting sand transport dynamics in the Lower Mekong River. In: Schleiss, A.J., de Cesare, G., Franca, M.J., Pfister, M. (Eds.), River Flow, Proc. 7th Int. Conf. on Fluvial Hydraulics. Lausanne, Switzerland, pp. 2189--2197.
Please note that others may also have edited the contents of this article.
|

