Difference between revisions of "Shore nourishment"
Tasomerville (talk | contribs) m |
Dronkers J (talk | contribs) |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | <div style="border:1px solid #000000; text-align:center; align=center; padding=5px ; margin-right:20px; margin-left:20px"> |
| − | + | The application of coastal nourishments requires insight into the processes that shape the coastal profile. For an introduction to these processes, the reader is referred to the article [[Shoreface profile]] and other articles mentioned herein. | |
| − | + | </div> | |
| − | + | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{Definition|title=Shore nourishment | ||
| + | |definition=Shore nourishments are projects where the coastal system is fed with sediments (sand) from a source (borrow area) at a sufficient distance from the project area so that coastal hydrodynamics remain unaffected. | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Other examples of projects where the coastal system is fed, are large scale land reclamation projects and the construction of an artificial island in the open sea. In these cases often huge volumes of sand are required; typically several hundreds of millions m<sup>3</sup> per project. Shore nourishment projects involve moderate volumes, typically in the order of 1-5 million m<sup>3</sup> (500-2000 m<sup>3</sup>/m) and rarely more than 10 or 20 million m<sup>3</sup> ('sandmotor' nourishment, order 5000 m<sup>3</sup>/m). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Nourishment concept== | ||
| − | + | Shore nourishments can be regarded as a 'natural' way of combating dune erosion and beach erosion as it artificially replaces a deficit in the sediment budget over a certain coastal stretch with a corresponding volume of sand. A structural deficit in the sediment budget is generally due to divergence of longshore sediment transport. Shore nourishment does not eliminate this cause of erosion; erosion will continue, and the nourished sand will be carried away. It is thus inherent in the nourishment concept that the nourished sand is gradually sacrificed. This means that nourishment as a stand-alone method normally requires an ongoing maintenance effort. In general, nourishment is only suited for shoreline sections of substantial length; otherwise, the loss of sand to neighbouring sections will be too large. Regular nourishment requires a permanent well-functioning organisation, which makes nourishment as a stand-alone solution unsuitable for privately owned coastlines. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Image:nourishment methods.gif|thumb|left|300px|<small>Fig. 1. Generally practiced nourishment methods. Pipe discharge on the beach for beach nourishment, over the bow pumping (rainbowing) for nearshore nourishment and split barge for nourishment in the outer part of the upper shoreface. </small>]] | |
| − | [[Image: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | The design of a nourishment scheme depends very much on the grain size of the nourished sand, the so-called borrow material, relative to the grain size of the native sand. As described in [[Shoreface profile]], the characteristics of the sand determine the overall shape of the coastal profile expressed in the equilibrium profile concept. Furthermore, natural hydrodynamic processes tend to sort the sediments in the profile so that the grain size decreases with increasing water depth. Borrow material is generally mined from the seabed sufficiently far offshore to minimize any influence on the hydrodynamics of the coastal zone. Placement in onshore nourishment sites makes use of pipes; for offshore sites, sand is dumped by split barges or by rainbowing (Fig. 1). For small nourishments, land sources are sometimes used. | |
| + | <br clear=all> | ||
| − | + | ==Nourishment applications== | |
| + | In the following, a short introduction is given to various different nourishment methods. | ||
| − | === | + | ====Inner dune nourishment==== |
| − | + | [[File:DuneNourishment.jpg|thumb|right]] | |
| − | + | Inner dune nourishment is the strengthening of the dune belt to prevent breaching by an extreme storm surge; it is not intended to prevent shoreline retreat. This measure can be applied when a single dune row that protects low-lying hinterland from flooding is not strong enough to withstand extreme storm surges. Sand is placed at the landward side of the front dune to increase the dune volume and/or to raise the dune crest. Beach morphodynamic processes are not affected by this measure. The amount of sand needed to achieve the desired protection level can be estimated with the methods described in [[Dune erosion]]. Inner dune nourishment is particularly effective if the dune foot location is stable i.e., no structural retreat due to ongoing erosion. In this case, a one-off intervention is sufficient, so that the additional costs for applying the sand on the land side are also a one-off investment. Recovery of dune vegetation can be promoted by depositing the top layer of the area to be nourished and later applying it as a cover layer over the nourishment. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
====Backshore nourishment==== | ====Backshore nourishment==== | ||
| − | [[Backshore]] nourishment is the strengthening of the upper part of the beach by placing nourishment on the [[backshore]] or at the foot of the dunes. | + | [[File:BackshoreNourishment.jpg|thumb|right]] |
| − | The main objective of [[backshore]] nourishment is to strengthen the [[backshore]]/dune against erosion and [[breaching]] during extreme events. | + | [[Backshore]] nourishment is the strengthening of the upper part of the beach by placing the nourishment on the [[backshore]] or at the foot of the dunes. The material is stockpiled in front of the dunes and acts as a buffer, which is sacrificed during extreme events. |
| + | The main objective of [[backshore]] nourishment is to strengthen the [[backshore]]/dune against erosion and [[breaching]] during extreme events. This kind of nourishment works more by volume than by trying to restore a natural wide beach. The loss is normally large during extreme events, whereby steep scarps are formed. [[Backshore]] nourishment can be characterised as a kind of emergency measure against dune setback/breach; it cannot, therefore, be characterised as a sustainable way of performing nourishment and it does not normally look very natural. | ||
| − | [[Backshore]] nourishment can be performed by hydraulic pumping sand through pipes discharging at the foot of the dunes and later adjusted using a bulldozer. The sand source can be either an offshore supply via a cross-profile pipeline, floating or buried, or it can be supplied along the shore from, for example, a sand [[bypassing]] plant. The sand can also be supplied via land transport by dumpers. | + | [[Backshore]] nourishment can be performed by hydraulic pumping sand through pipes discharging at the foot of the dunes and later adjusted using a bulldozer (Fig. 1). The sand source can be either an offshore supply via a cross-profile pipeline, floating or buried, or it can be supplied along the shore from, for example, a sand [[bypassing]] plant. The sand can also be supplied via land transport by dumpers. |
====Beach nourishment==== | ====Beach nourishment==== | ||
| − | Beach nourishment is the supply of sand to the shore to increase the recreational value and/or to secure the beach against shore erosion by feeding sand on the beach. It is not a | + | [[File:BeachNourishment.jpg|thumb|right]] |
| + | [[Beach nourishment]] is the supply of sand to the shore to increase the recreational value and/or to secure the beach against shore erosion by feeding sand on the beach. It is not a protection measure against flooding, as the beach is normally submerged during extreme events. However, it enhances the protection function of the dune belt or other backshore flood defences. The sand is usually supplied via a cross-profile pipeline and adjusted with bulldozers to the natural beach profile. It is therefore necessary that the borrow sand has grain size similar to the native sand. It may be an advantage to use slightly coarser sand than the natural beach sand, as this will enhance the stability of the resulting slightly steeper profile. Finer sand will very quickly be transferred to deeper water and will thus not contribute directly to a wider beach. However, the fine sand will help building up the outer part of the profile. See also [[Beach nourishment]] and [[Experiences with beach nourishments in Portugal]]. | ||
====Shoreface nourishment==== | ====Shoreface nourishment==== | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[File:OuterBarNourishment.jpg|thumb|right]] |
| − | Shoreface nourishment is the supply of sand to the | + | [[Shoreface nourishment]] (also called profile nourishment) is the supply of sand to the subtidal part of the coastal profile. It will strengthen the coastal profile and add sediment to the littoral budget in general. This type of nourishment is used in areas where coastal protection measures have steepened the coastal profile or in areas with a long-term sediment deficit. Shoreface nourishment is sometimes used in combination with beach nourishment, thus creating a nourished profile close to the equilibrium over the entire [[active coastal zone]]. See [[Shoreface nourishment]] for further details. |
| − | Shoreface nourishment is often performed using split barges. The unloading is fast and the unit price therefore low. Shoreface nourishment can profitably be used in connection with large beach nourishment schemes, in which borrow material, which does not fulfil the requirements for beach nourishment, can be used in the outer part of the profile where it naturally belongs. | + | Shoreface nourishment is often performed using split barges (Fig. 1). The unloading is fast and the unit price therefore low. Shoreface nourishment can profitably be used in connection with large beach nourishment schemes, in which borrow material, which does not fulfil the requirements for beach nourishment, can be used in the outer part of the profile where it naturally belongs. |
====Beach Scraping==== | ====Beach Scraping==== | ||
| + | A [[beach berm]] consisting of coarse sand or gravel is sometimes formed during relatively mild summer wave conditions, which tend to transport seabed material towards the beach. This coarse material can be brought to the upper part of the beach to protect the dune foot or the foot of the cliff against erosion by storm surges. This practice is called beach scraping and is normally performed using front loaders. | ||
| − | + | This method can be used for beaches which are mainly exposed to seasonal erosion, whereas it is probably not suitable for locations exposed to long-term erosion. For other issues, see the page [[Beach scraping]]. | |
| − | |||
| − | ==== | + | ====Creation of a new beach==== |
| − | |||
| − | = | + | [[Image:BeachSlopeGrainSizeData.jpg|thumb|350px|right|<small>Figure 2. Correlation between sediment grainsize and related beach slope from 78 field studies, adapted from Bujan et al. (2019)<ref name=Bu>Bujan, N., Cox, R. and Masselink, G. 2019. From fine sand to boulders: Examining the relationship between beach-face slope and sediment size. Marine Geology 417, 106012</ref>. The violet area indicates the scatter of the data points.</small>]] |
| − | |||
| − | + | In many places (e.g. along the Mediterranean coast) the coast is rocky with few wide sandy beaches. A beach can be created by artificial sand nourishment if this is desired for recreational purposes. There are two main differences with maintenance nourishment of an existing beach: (1) an entire equilibrium beach profile has to be created, up to the [[closure depth]], to minimize sand loss to deep water; (2) the new beach is subject to strong gradients in longshore sand transport that redistribute the nourishment alongshore. Additional measures are necessary to keep the nourished sand in place, such as confining the artificial beach between groynes or breakwaters. However, such structures must be carefully designed to ensure proper functioning, as explained in the articles [[Groynes]] and [[Detached breakwaters]]. The sand volume needed to create a stable beach strongly depends on the grain size. The equilibrium profile of a coarse sandy beach is much steeper than the equilibrium profile of a fine sandy beach (Fig. 2). With coarse sand smaller nourishment volumes are needed and longshore sand losses will be smaller. | |
| − | + | <br clear=all> | |
| − | + | ====Channel wall nourishment==== | |
| − | + | [[File:ChannelWallNourishment.jpg|thumb|right]] | |
| + | At places where the coast is interrupted by tidal inlets, channels of the ebb tidal delta may run some distance along the adjacent shores. The landward migration of these tidal channels can cause erosion of the beaches along these shores. In this case channel wall nourishments can be applied to counteract this landward migration, even when large nourishment volumes are required. However, because lateral channel migration is usually a rather slow process, the lifetime of the nourishment is generally longer than the lifetime of beach or shoreface nourishments. Channel wall nourishments therefore can be a good option to prevent beach erosion by onshore migrating channels. Extensive experience with channel wall nourishments has been gained at tidal inlets along the Dutch coast <ref>Brand, E., Ramaekers, G. and Lodder, Q. 2022. Dutch experience with sand nourishments for dynamic coastline conservation – An operational overview. Ocean and Coastal Management 217, 106008</ref>. | ||
| + | <br clear=all> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[ | + | ==Related articles== |
| + | :[[Beach nourishment]] | ||
| + | :[[Shoreface nourishment]] | ||
| + | :[[Shoreface profile]] | ||
| + | :[[Experiences with beach nourishments in Portugal]] | ||
| + | :[[Dealing with coastal erosion]] | ||
| + | :[[Nearshore sandbars]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==Further reading== |
| − | + | *Mangor, K., Drønen, N. K., Kaergaard, K.H. and Kristensen, N.E. 2017. Shoreline management guidelines. DHI https://www.dhigroup.com/marine-water/ebook-shoreline-management-guidelines | |
| − | * | + | *Reeve, D. E., Chadwick, A. C. and Fleming, C.A. 2018. Coastal Engineering: Processes, Theory and Design Practice. 3rd edition. Boca Raton, Florida, USA: CRC Press (Taylor & Francis Group), 512p. |
| − | + | *CIRIA, 2010. Beach Management Manual, 2nd Edition, Publication no. RP787, London | |
| − | + | *Coastal Engineering Manual 2006. part V Ch. 4 Beach fill design. | |
| − | |||
| − | * | ||
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==References== |
| − | + | <references/> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{4Authors | |
| + | |AuthorID1=13331 | ||
| + | |AuthorFullName1=Mangor, Karsten | ||
| + | |AuthorName1=Karsten | ||
| + | |AuthorID2=11540 | ||
| + | |AuthorName2= Jan van de Graaff | ||
| + | |AuthorFullName2= Jan van de Graaff | ||
| + | |AuthorID3=16611 | ||
| + | |AuthorName3= AnnaKroon | ||
| + | |AuthorFullName3= Anna Kroon | ||
| + | |AuthorID4=120 | ||
| + | |AuthorFullName4=Job Dronkers | ||
| + | |AuthorName4=Dronkers J | ||
| + | }} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Category:Coastal protection]] | |
| − | + | [[Category:Soft coastal interventions]] | |
| − | + | [[Category:Beaches]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[Category: | ||
| − | [[Category: | ||
| − | |||
| − | [[Category: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 15:32, 23 July 2023
The application of coastal nourishments requires insight into the processes that shape the coastal profile. For an introduction to these processes, the reader is referred to the article Shoreface profile and other articles mentioned herein.
Definition of Shore nourishment:
Shore nourishments are projects where the coastal system is fed with sediments (sand) from a source (borrow area) at a sufficient distance from the project area so that coastal hydrodynamics remain unaffected.
This is the common definition for Shore nourishment, other definitions can be discussed in the article
|
Other examples of projects where the coastal system is fed, are large scale land reclamation projects and the construction of an artificial island in the open sea. In these cases often huge volumes of sand are required; typically several hundreds of millions m3 per project. Shore nourishment projects involve moderate volumes, typically in the order of 1-5 million m3 (500-2000 m3/m) and rarely more than 10 or 20 million m3 ('sandmotor' nourishment, order 5000 m3/m).
Contents
[hide]Nourishment concept
Shore nourishments can be regarded as a 'natural' way of combating dune erosion and beach erosion as it artificially replaces a deficit in the sediment budget over a certain coastal stretch with a corresponding volume of sand. A structural deficit in the sediment budget is generally due to divergence of longshore sediment transport. Shore nourishment does not eliminate this cause of erosion; erosion will continue, and the nourished sand will be carried away. It is thus inherent in the nourishment concept that the nourished sand is gradually sacrificed. This means that nourishment as a stand-alone method normally requires an ongoing maintenance effort. In general, nourishment is only suited for shoreline sections of substantial length; otherwise, the loss of sand to neighbouring sections will be too large. Regular nourishment requires a permanent well-functioning organisation, which makes nourishment as a stand-alone solution unsuitable for privately owned coastlines.
The design of a nourishment scheme depends very much on the grain size of the nourished sand, the so-called borrow material, relative to the grain size of the native sand. As described in Shoreface profile, the characteristics of the sand determine the overall shape of the coastal profile expressed in the equilibrium profile concept. Furthermore, natural hydrodynamic processes tend to sort the sediments in the profile so that the grain size decreases with increasing water depth. Borrow material is generally mined from the seabed sufficiently far offshore to minimize any influence on the hydrodynamics of the coastal zone. Placement in onshore nourishment sites makes use of pipes; for offshore sites, sand is dumped by split barges or by rainbowing (Fig. 1). For small nourishments, land sources are sometimes used.
Nourishment applications
In the following, a short introduction is given to various different nourishment methods.
Inner dune nourishment
Inner dune nourishment is the strengthening of the dune belt to prevent breaching by an extreme storm surge; it is not intended to prevent shoreline retreat. This measure can be applied when a single dune row that protects low-lying hinterland from flooding is not strong enough to withstand extreme storm surges. Sand is placed at the landward side of the front dune to increase the dune volume and/or to raise the dune crest. Beach morphodynamic processes are not affected by this measure. The amount of sand needed to achieve the desired protection level can be estimated with the methods described in Dune erosion. Inner dune nourishment is particularly effective if the dune foot location is stable i.e., no structural retreat due to ongoing erosion. In this case, a one-off intervention is sufficient, so that the additional costs for applying the sand on the land side are also a one-off investment. Recovery of dune vegetation can be promoted by depositing the top layer of the area to be nourished and later applying it as a cover layer over the nourishment.
Backshore nourishment
Backshore nourishment is the strengthening of the upper part of the beach by placing the nourishment on the backshore or at the foot of the dunes. The material is stockpiled in front of the dunes and acts as a buffer, which is sacrificed during extreme events. The main objective of backshore nourishment is to strengthen the backshore/dune against erosion and breaching during extreme events. This kind of nourishment works more by volume than by trying to restore a natural wide beach. The loss is normally large during extreme events, whereby steep scarps are formed. Backshore nourishment can be characterised as a kind of emergency measure against dune setback/breach; it cannot, therefore, be characterised as a sustainable way of performing nourishment and it does not normally look very natural.
Backshore nourishment can be performed by hydraulic pumping sand through pipes discharging at the foot of the dunes and later adjusted using a bulldozer (Fig. 1). The sand source can be either an offshore supply via a cross-profile pipeline, floating or buried, or it can be supplied along the shore from, for example, a sand bypassing plant. The sand can also be supplied via land transport by dumpers.
Beach nourishment
Beach nourishment is the supply of sand to the shore to increase the recreational value and/or to secure the beach against shore erosion by feeding sand on the beach. It is not a protection measure against flooding, as the beach is normally submerged during extreme events. However, it enhances the protection function of the dune belt or other backshore flood defences. The sand is usually supplied via a cross-profile pipeline and adjusted with bulldozers to the natural beach profile. It is therefore necessary that the borrow sand has grain size similar to the native sand. It may be an advantage to use slightly coarser sand than the natural beach sand, as this will enhance the stability of the resulting slightly steeper profile. Finer sand will very quickly be transferred to deeper water and will thus not contribute directly to a wider beach. However, the fine sand will help building up the outer part of the profile. See also Beach nourishment and Experiences with beach nourishments in Portugal.
Shoreface nourishment
Shoreface nourishment (also called profile nourishment) is the supply of sand to the subtidal part of the coastal profile. It will strengthen the coastal profile and add sediment to the littoral budget in general. This type of nourishment is used in areas where coastal protection measures have steepened the coastal profile or in areas with a long-term sediment deficit. Shoreface nourishment is sometimes used in combination with beach nourishment, thus creating a nourished profile close to the equilibrium over the entire active coastal zone. See Shoreface nourishment for further details.
Shoreface nourishment is often performed using split barges (Fig. 1). The unloading is fast and the unit price therefore low. Shoreface nourishment can profitably be used in connection with large beach nourishment schemes, in which borrow material, which does not fulfil the requirements for beach nourishment, can be used in the outer part of the profile where it naturally belongs.
Beach Scraping
A beach berm consisting of coarse sand or gravel is sometimes formed during relatively mild summer wave conditions, which tend to transport seabed material towards the beach. This coarse material can be brought to the upper part of the beach to protect the dune foot or the foot of the cliff against erosion by storm surges. This practice is called beach scraping and is normally performed using front loaders.
This method can be used for beaches which are mainly exposed to seasonal erosion, whereas it is probably not suitable for locations exposed to long-term erosion. For other issues, see the page Beach scraping.
Creation of a new beach
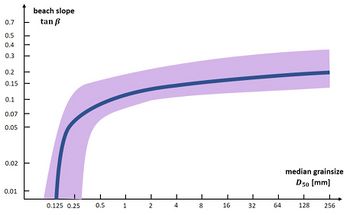
In many places (e.g. along the Mediterranean coast) the coast is rocky with few wide sandy beaches. A beach can be created by artificial sand nourishment if this is desired for recreational purposes. There are two main differences with maintenance nourishment of an existing beach: (1) an entire equilibrium beach profile has to be created, up to the closure depth, to minimize sand loss to deep water; (2) the new beach is subject to strong gradients in longshore sand transport that redistribute the nourishment alongshore. Additional measures are necessary to keep the nourished sand in place, such as confining the artificial beach between groynes or breakwaters. However, such structures must be carefully designed to ensure proper functioning, as explained in the articles Groynes and Detached breakwaters. The sand volume needed to create a stable beach strongly depends on the grain size. The equilibrium profile of a coarse sandy beach is much steeper than the equilibrium profile of a fine sandy beach (Fig. 2). With coarse sand smaller nourishment volumes are needed and longshore sand losses will be smaller.
Channel wall nourishment
At places where the coast is interrupted by tidal inlets, channels of the ebb tidal delta may run some distance along the adjacent shores. The landward migration of these tidal channels can cause erosion of the beaches along these shores. In this case channel wall nourishments can be applied to counteract this landward migration, even when large nourishment volumes are required. However, because lateral channel migration is usually a rather slow process, the lifetime of the nourishment is generally longer than the lifetime of beach or shoreface nourishments. Channel wall nourishments therefore can be a good option to prevent beach erosion by onshore migrating channels. Extensive experience with channel wall nourishments has been gained at tidal inlets along the Dutch coast [2].
Related articles
- Beach nourishment
- Shoreface nourishment
- Shoreface profile
- Experiences with beach nourishments in Portugal
- Dealing with coastal erosion
- Nearshore sandbars
Further reading
- Mangor, K., Drønen, N. K., Kaergaard, K.H. and Kristensen, N.E. 2017. Shoreline management guidelines. DHI https://www.dhigroup.com/marine-water/ebook-shoreline-management-guidelines
- Reeve, D. E., Chadwick, A. C. and Fleming, C.A. 2018. Coastal Engineering: Processes, Theory and Design Practice. 3rd edition. Boca Raton, Florida, USA: CRC Press (Taylor & Francis Group), 512p.
- CIRIA, 2010. Beach Management Manual, 2nd Edition, Publication no. RP787, London
- Coastal Engineering Manual 2006. part V Ch. 4 Beach fill design.
References
- Jump up ↑ Bujan, N., Cox, R. and Masselink, G. 2019. From fine sand to boulders: Examining the relationship between beach-face slope and sediment size. Marine Geology 417, 106012
- Jump up ↑ Brand, E., Ramaekers, G. and Lodder, Q. 2022. Dutch experience with sand nourishments for dynamic coastline conservation – An operational overview. Ocean and Coastal Management 217, 106008
Please note that others may also have edited the contents of this article.
|