Difference between revisions of "Tetrasul"
From Coastal Wiki
(→Notes) |
|||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
Tetrasul has a low water solubility (0.03 mg/l) and is very hydrophobic. It therefore is very likely to [[adsorption|adsorb]] to particles and the sediment and to have a high potential towards [[bioaccumulation]]. | Tetrasul has a low water solubility (0.03 mg/l) and is very hydrophobic. It therefore is very likely to [[adsorption|adsorb]] to particles and the sediment and to have a high potential towards [[bioaccumulation]]. | ||
| − | Tetrasul becomes [[toxic]] for [[pollution and pelagic fishes|fishes]] at concentrations above 11 mg/l. As a substance witch bioaccumulates and possibly also [[biomagnification|biomagnifies]] there may be risks to [[pollution and marine mammals|marine mammals]] by secondary poisoning. Mammals which consume more than 3,9 g per kilogram of body weight might be affected. Chronic exposure might cause effects at lower doses<ref name | + | Tetrasul becomes [[toxic]] for [[pollution and pelagic fishes|fishes]] at concentrations above 11 mg/l. As a substance witch bioaccumulates and possibly also [[biomagnification|biomagnifies]] there may be risks to [[pollution and marine mammals|marine mammals]] by secondary poisoning. Mammals which consume more than 3,9 g per kilogram of body weight might be affected. Chronic exposure might cause effects at lower doses<ref name="IC"/>. |
<P> | <P> | ||
<BR> | <BR> | ||
Revision as of 15:39, 20 March 2013
Notes

|
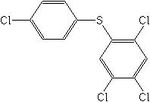
| Tetrasul |
|---|
|
| Formula |
| C12H6Cl14S |
The use of tetrasul has been banned in Europe since 2003[2].
Tetrasul has a low water solubility (0.03 mg/l) and is very hydrophobic. It therefore is very likely to adsorb to particles and the sediment and to have a high potential towards bioaccumulation.
Tetrasul becomes toxic for fishes at concentrations above 11 mg/l. As a substance witch bioaccumulates and possibly also biomagnifies there may be risks to marine mammals by secondary poisoning. Mammals which consume more than 3,9 g per kilogram of body weight might be affected. Chronic exposure might cause effects at lower doses[1].
Environmental standards and legislation
Included in the OSPAR list of substances of priority action
References
Please note that others may also have edited the contents of this article.
|