Difference between revisions of "AMPA"
From Coastal Wiki
(ref) |
|||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
Currently very little is known about this AMPA. It is formed by biodegradation of the herbicide glyohosate and can be found at lower concentrations in the environment. It adsorbs more strongly to soils than glysphosate and might have a higher tendency towards bioaccumulation. Glysphosate however is not expected to bioaccumulate much because of its high water solubility. AMPA is also more stable than glyphosate. <ref>[http://www.pesticideinfo.org/Detail_Chemical.jsp?Rec_Id=PC37655 www.pesticideinfo.org August 20 2009]</ref> | Currently very little is known about this AMPA. It is formed by biodegradation of the herbicide glyohosate and can be found at lower concentrations in the environment. It adsorbs more strongly to soils than glysphosate and might have a higher tendency towards bioaccumulation. Glysphosate however is not expected to bioaccumulate much because of its high water solubility. AMPA is also more stable than glyphosate. <ref>[http://www.pesticideinfo.org/Detail_Chemical.jsp?Rec_Id=PC37655 www.pesticideinfo.org August 20 2009]</ref> | ||
| − | Measured concentrations of AMPA in surface waters range between 6 and 35 µg/l <ref name= incham>[http://www.inchem.org/documents/ehc/ehc/ehc159.htm | + | Measured concentrations of AMPA in surface waters range between 6 and 35 µg/l <ref name= incham>[http://www.inchem.org/documents/ehc/ehc/ehc159.htm www.inchem.org August 25 2009.]</ref> |
<P> | <P> | ||
Revision as of 10:01, 25 August 2009
Definition of Aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA):
Aminomethylphosphonic acid is mainly produced by environmental biodegradation reactions of the herbicide glyphosate. [1]
This is the common definition for Aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA), other definitions can be discussed in the article
|
Notes
| AMPA |
|---|
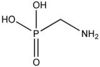
|
| Formula |
| CH6NO3P |
Currently very little is known about this AMPA. It is formed by biodegradation of the herbicide glyohosate and can be found at lower concentrations in the environment. It adsorbs more strongly to soils than glysphosate and might have a higher tendency towards bioaccumulation. Glysphosate however is not expected to bioaccumulate much because of its high water solubility. AMPA is also more stable than glyphosate. [2]
Measured concentrations of AMPA in surface waters range between 6 and 35 µg/l [3]
Environmental standards and legislation
Included in the water framework list of priority substances