Difference between revisions of "Bisphenol-A"
(ref +ref) |
(ref) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | Bisphenol-A is also known as 4,4’-Isopropylidenediphenol, at room temperature it occurs as a white powder or in flakes. | + | {{Definition|title=Bisphenol-A |
| + | |||
| + | |definition=Bisphenol-A is also known as 4,4’-Isopropylidenediphenol, at room temperature it occurs as a white powder or in flakes. <ref name="en">[http://ecb.jrc.it/documents/Existing-Chemicals/RISK_ASSESSMENT/ADDENDUM/bisphenola_add_325.pdf February 2008 Updated European Risk Assessment Report 4,4’-ISOPROPYLIDENEDIPHENOL (BISPHENOL-A)]</ref>}} | ||
== Notes == | == Notes == | ||
| + | {| class="toccolours" border="1" style="float: right; clear: right; margin: 0 0 1em 1em; border-collapse: collapse;" | ||
| + | ! bgcolor="#FF8888" | Bisphenol-A | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align="center" bgcolor="#FFFFFF" | [[Image:Bisphenol A.png|200px|Bisphenol-A ]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! bgcolor="#8888FF" | Formula | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align="center" | C<sub>15</sub>H<sub>16</sub>O<sub>2</sub> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
The total amount of bisphenol-A manufactured within the EU, based upon submissions to CEFIC by the manufacturers, of 2005 was estimated at approximately 1,150,000 tonnes/year | The total amount of bisphenol-A manufactured within the EU, based upon submissions to CEFIC by the manufacturers, of 2005 was estimated at approximately 1,150,000 tonnes/year | ||
mainly produced to manufacture polycarbonate, witch is widely used plastic.<ref name="echa">[http://echa.europa.eu/doc/trd_substances/4_4_isopropylidene_diphenol_bisphenol_a/ann_xv_trd/trd_uk_bisphenol_a.pdf ECHA 2008 ANNEX XV RESTRICTION REPORT Bisphenol-A]</ref> | mainly produced to manufacture polycarbonate, witch is widely used plastic.<ref name="echa">[http://echa.europa.eu/doc/trd_substances/4_4_isopropylidene_diphenol_bisphenol_a/ann_xv_trd/trd_uk_bisphenol_a.pdf ECHA 2008 ANNEX XV RESTRICTION REPORT Bisphenol-A]</ref> | ||
| − | In water bisphenol A is moderately soluble, 300 mg/l, and considered to have a moderate tendency to [[adsorption|adsorb]] to suspended particles and sediments. It has a very low tendency to evaporate into the atmosphere where most of it will be degraded in less than a day. In water and soils it is rather stable, althoug it can readily be biodegraded. It only takes 3 to 8 days to half it's environmental concentrations by biodegradation. 100% removal of environmental contamination can occur within 17 days. | + | In water bisphenol A is moderately soluble, 300 mg/l, and considered to have a moderate tendency to [[adsorption|adsorb]] to suspended particles and sediments. It has a very low tendency to evaporate into the atmosphere where most of it will be degraded in less than a day. In water and soils it is rather stable, althoug it can readily be biodegraded. It only takes 3 to 8 days to half it's environmental concentrations by biodegradation. 100% removal of environmental contamination can occur within 17 days. <ref name="en">[http://ecb.jrc.it/documents/Existing-Chemicals/RISK_ASSESSMENT/ADDENDUM/bisphenola_add_325.pdf February 2008 Updated European Risk Assessment Report 4,4’-ISOPROPYLIDENEDIPHENOL (BISPHENOL-A)]</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | Bisphenol A has a low tendency to [[bioaccumulation|bioaccumulate]]. Therefore in poses a low toxicity threat by biomagnification towards marine mammals. Acute toxicity is only obtained when mammals consume more than 33 mg of bisphenol A per kg body weigh each day.<ref name="en">[http://ecb.jrc.it/documents/Existing-Chemicals/RISK_ASSESSMENT/ADDENDUM/bisphenola_add_325.pdf February 2008 Updated European Risk Assessment Report 4,4’-ISOPROPYLIDENEDIPHENOL (BISPHENOL-A)]</ref> | ||
| − | |||
| + | Bisphenol a has been shown to exhibit [[endocrine disrupting compounds|endocrine disrupting effects]]. In [http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=101 gastropods] concentrations bellow 100 µg/l has been shown cause reduced penis sizes in males and enhanced oocyte production in females. The latter results in an increased embryo production at low bisphenol A concentrations. This effect has even been demonstrated in some gastropod species at concentrations of only 100 ng/l. <ref name="echa">[http://echa.europa.eu/doc/trd_substances/4_4_isopropylidene_diphenol_bisphenol_a/ann_xv_trd/trd_uk_bisphenol_a.pdf ECHA 2008 ANNEX XV RESTRICTION REPORT Bisphenol-A]</ref> It demonstrates a moderate acute toxicity towards aquatic species. Most species start dying at concentrations above 1 mg/l. <ref name="pe">[http://www.pesticideinfo.org/Detail_Chemical.jsp?Rec_Id=PC33756#Related_Chems www.pesticideinfo.org august 24]</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <P> | ||
| + | <BR> | ||
| + | <P> | ||
| + | == Environmental standards and legislation == | ||
| + | [[List of priority substances|Included in the water framework list of priority substances]] | ||
| + | <P> | ||
| + | <BR> | ||
| + | <P> | ||
| + | == See also == | ||
| + | [http://www.vliz.be/projects/endis/EDnorth.php?showchemprop=true&showeffects=true&chemeffects=true&chemid=157 Bisphenol-A on ED North Database] | ||
| + | <P> | ||
| + | <BR> | ||
| + | <P> | ||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
| − | + | [[Category:Coastal and marine pollution]] | |
Revision as of 10:27, 24 August 2009
Definition of Bisphenol-A:
Bisphenol-A is also known as 4,4’-Isopropylidenediphenol, at room temperature it occurs as a white powder or in flakes. [1]
This is the common definition for Bisphenol-A, other definitions can be discussed in the article
|
Notes
| Bisphenol-A |
|---|
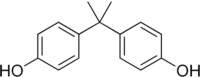
|
| Formula |
| C15H16O2 |
The total amount of bisphenol-A manufactured within the EU, based upon submissions to CEFIC by the manufacturers, of 2005 was estimated at approximately 1,150,000 tonnes/year mainly produced to manufacture polycarbonate, witch is widely used plastic.[2]
In water bisphenol A is moderately soluble, 300 mg/l, and considered to have a moderate tendency to adsorb to suspended particles and sediments. It has a very low tendency to evaporate into the atmosphere where most of it will be degraded in less than a day. In water and soils it is rather stable, althoug it can readily be biodegraded. It only takes 3 to 8 days to half it's environmental concentrations by biodegradation. 100% removal of environmental contamination can occur within 17 days. [1]
Bisphenol A has a low tendency to bioaccumulate. Therefore in poses a low toxicity threat by biomagnification towards marine mammals. Acute toxicity is only obtained when mammals consume more than 33 mg of bisphenol A per kg body weigh each day.[1]
Bisphenol a has been shown to exhibit endocrine disrupting effects. In gastropods concentrations bellow 100 µg/l has been shown cause reduced penis sizes in males and enhanced oocyte production in females. The latter results in an increased embryo production at low bisphenol A concentrations. This effect has even been demonstrated in some gastropod species at concentrations of only 100 ng/l. [2] It demonstrates a moderate acute toxicity towards aquatic species. Most species start dying at concentrations above 1 mg/l. [3]
Environmental standards and legislation
Included in the water framework list of priority substances
See also
Bisphenol-A on ED North Database