Difference between revisions of "Diuron"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{Definition|title= | + | {{Definition|title=diruon |
|definition=Diuron is used as a herbicide on a variety of both crop and non-crop areas. It is also used as a mildewcide in paints and stains, and as an algaecide in commercial fish production. <ref name="epa">[http://www.epa.gov/oppsrrd1/REDs/diuron_red.pdf EPA US 2003 Reregistration Eligibility Decision (RED) for Diuron] </ref>}} | |definition=Diuron is used as a herbicide on a variety of both crop and non-crop areas. It is also used as a mildewcide in paints and stains, and as an algaecide in commercial fish production. <ref name="epa">[http://www.epa.gov/oppsrrd1/REDs/diuron_red.pdf EPA US 2003 Reregistration Eligibility Decision (RED) for Diuron] </ref>}} | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
{| class="toccolours" border="1" style="float: right; clear: right; margin: 0 0 1em 1em; border-collapse: collapse;" | {| class="toccolours" border="1" style="float: right; clear: right; margin: 0 0 1em 1em; border-collapse: collapse;" | ||
| − | ! bgcolor="#FF8888" | | + | ! bgcolor="#FF8888" | Diuron |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | align="center" bgcolor="#FFFFFF" | [[Image: | + | | align="center" bgcolor="#FFFFFF" | [[Image:Diuron.png|150px|Diuron]] |
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! bgcolor="#8888FF" | Formula | + | ! bgcolor="#8888FF" | Formula |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | align="center" | | + | | align="center" | C<sub>9</sub>H<sub>10</sub>Cl<sub>12</sub>N<sub>2</sub>O |
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 09:43, 17 August 2009
Definition of diruon:
Diuron is used as a herbicide on a variety of both crop and non-crop areas. It is also used as a mildewcide in paints and stains, and as an algaecide in commercial fish production. [1]
This is the common definition for diruon, other definitions can be discussed in the article
|
Notes
| Diuron |
|---|
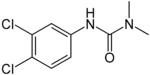
|
| Formula |
| C9H10Cl12N2O |
In the USA diuron has been used since 1967. Durion is mainly used on citrus, berries, asparagus and pineapple. Right-of-way applications (e.g., the area around railroad tracks) are the greatest non-agricultural use of diuron, with approximately 1 million kilograms applied annually.
In water durion has a low tendency to adsorb to particles and organic matter, dispite its has a relatively low water solubility of 42 mg/l. It's a stable molecule in terrestrial systems but can be biodegraded by micro-organisms. It is expected to be much less stable in aquatic systems, where it's concentration might be halved in 30 days (according to lab experiments). Although it has a low potential towards bioaccumulation, it probably doesn't bioaccumulate or biomagnify in wild aquatic populations. [2]
It has a low toxicity for mammals, doses above 3,4 g per kg body weight are needed to induce acute toxicity. There is a higher for aquatic organisms: some fish species die at concentrations above 4,3 mg/l and some marine invertebrate species may die at concentrations above 1 mg/l. [3]. Algae are most vulnerable to the herbicide, it can be toxic for some algae species at concentrations of only 5 µg/l. [4]
Environmental standards and legislation
Included in the water framework list of priority substances