Difference between revisions of "Tetrasul"
From Coastal Wiki
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
It has a low water solubility 0.03 mg/l and is very lipophylic. It therefore is very likely to [[adsorption|adsorb]] to particles and the sediment and to have a high potential towards [[bioaccumulation]]. | It has a low water solubility 0.03 mg/l and is very lipophylic. It therefore is very likely to [[adsorption|adsorb]] to particles and the sediment and to have a high potential towards [[bioaccumulation]]. | ||
| − | Tetrasul becomes toxic for fishes at concentrations above 11 mg/l. Mammals need to consume more than 3,9 g per | + | Tetrasul becomes toxic for fishes at concentrations above 11 mg/l. Mammals need to consume more than 3,9 g per kilogram of body weight to be affected. <ref name :IC>[http://sitem.herts.ac.uk/aeru/iupac/Reports/1275.htm#none International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Pesticide Properties Database]</ref> |
<P> | <P> | ||
<BR> | <BR> | ||
Revision as of 13:55, 12 August 2009
Definition of Tetrasul:
Tetrasul, also known as diphenylsulphide, is a pesticide which was used against spider mites and aphids. Cite error: Invalid
<ref> tag;
invalid names, e.g. too manyThis is the common definition for Tetrasul, other definitions can be discussed in the article
|
Notes
| Tetrasul |
|---|
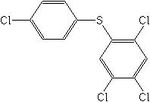
|
| Formula |
| C12H6Cl14S |
Its use has been banned in Europe since 2003. [1]
It has a low water solubility 0.03 mg/l and is very lipophylic. It therefore is very likely to adsorb to particles and the sediment and to have a high potential towards bioaccumulation.
Tetrasul becomes toxic for fishes at concentrations above 11 mg/l. Mammals need to consume more than 3,9 g per kilogram of body weight to be affected. Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag;
invalid names, e.g. too many
Environmental standards and legislation
Included in the OSPAR list of substances of priority action