Difference between revisions of "Geographical Information System"
From Coastal Wiki
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
;Simple definition : A Geographic Information System organizes large volumes of raw data into a map form for easy comprehension. | ;Simple definition : A Geographic Information System organizes large volumes of raw data into a map form for easy comprehension. | ||
:GIS divides raw data into layers so it can give you a better understanding for the whole world. | :GIS divides raw data into layers so it can give you a better understanding for the whole world. | ||
| + | |||
| Line 23: | Line 24: | ||
**Information referenced by its location in space | **Information referenced by its location in space | ||
[[Image:Spatialinfo.jpg|400px|centre]] | [[Image:Spatialinfo.jpg|400px|centre]] | ||
| + | |||
==GIS functions== | ==GIS functions== | ||
| Line 30: | Line 32: | ||
*Analysis | *Analysis | ||
*Output | *Output | ||
| + | |||
===Storing data using Geodatabase=== | ===Storing data using Geodatabase=== | ||
| Line 38: | Line 41: | ||
[[Image:Geodatabase.jpg|400px]] | [[Image:Geodatabase.jpg|400px]] | ||
| + | |||
==CZM and GIS== | ==CZM and GIS== | ||
| Line 50: | Line 54: | ||
[[Image:GISCZM3.jpg|400px|centre|Coastal Zone management: GIS perspective]] | [[Image:GISCZM3.jpg|400px|centre|Coastal Zone management: GIS perspective]] | ||
| + | |||
==Data types== | ==Data types== | ||
Revision as of 13:24, 8 January 2007
Geographical Information System (GIS) is a tool for analysis and presentation of spatial data. It is a collection of computer hardware, software and geographic data for capturing, managing, analyzing and displaying all forms of geographically references information.
Contents
What is GIS?
- Simple definition
- A Geographic Information System organizes large volumes of raw data into a map form for easy comprehension.
- GIS divides raw data into layers so it can give you a better understanding for the whole world.
Why is GIS unique?
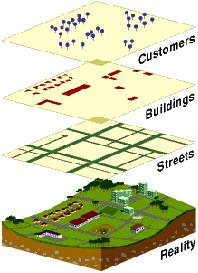
- GIS handles SPATIAL information
- Information referenced by its location in space
GIS functions
- Data input
- Storage
- Management
- Analysis
- Output
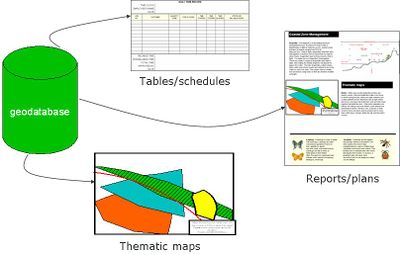
Storing data using Geodatabase
- Geodatabase is a container for spatial and non- spatial data that can be organized in a certain structure.
- Advantages:
- provide a single, consolidated data storage for field measurements and all types of data used.
- Controlling data entry by applying validation rule on the attributes.
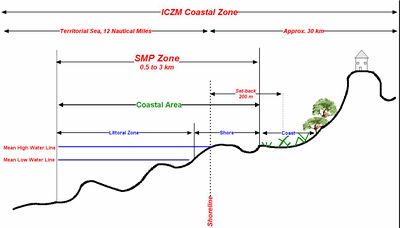
CZM and GIS
- GIS stores all data relevant for the CZM
- GIS handles data on all spatial scales (North Egypt coast vs. a single harbour)
- GIS is a powerful analysis tool.
- Comparison of measurements from different years
- Overlay analysis of measurements and modelling results
Data types
- DFS2 Data MIKE 21
- Dfs1 Data MIKE 21
- XYZ Data
- Wave time series & Rose
- Scanned Maps
- CAD drawing
Additional Data
- Land use
- Sediment classification
- Satellite images
- Geographical maps
- Reports (design, licenses, Site investigation)
- ….etc.
External links
GIS WWWW resource list of servers likely to be of interest to the GIS community
8th January, Ulrik Lumborg and Caitlin Pilkington (caitlin.pilkington@gmail.com), DHI.