Difference between revisions of "1,5,9 cyclododecatriene"
Dronkers J (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Tocright}} | {{Tocright}} | ||
{{ Definition|title=1,5,9-Cyclododecatriene (CDDT) | {{ Definition|title=1,5,9-Cyclododecatriene (CDDT) | ||
| − | |definition= 1,5,9-Cyclododecatriene is a liquid with a yellow tint and pungent odour<ref name= | + | |definition= 1,5,9-Cyclododecatriene is a liquid with a yellow tint and pungent odour<ref name=p>[https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/trans_trans_cis-1_5_9-Cyclododecatriene pubchem C1,5,9-Cyclododecatriene] </ref>. }} |
== Notes == | == Notes == | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
Aquatic concentrations above 0,2 mg/l cause acute [[toxic|toxicity]] to fish, algae and invertebrates. A dose of 2,5 g/kg body weight is lethal to rats. | Aquatic concentrations above 0,2 mg/l cause acute [[toxic|toxicity]] to fish, algae and invertebrates. A dose of 2,5 g/kg body weight is lethal to rats. | ||
| − | Considering CDDT it is only used as an intermediate in the production of other chemicals, its high volatility and degradability, it has only a minor potential aquatic exposure and thus poses only a minor risk to aquatic organisms<ref name= | + | Considering CDDT it is only used as an intermediate in the production of other chemicals, its high volatility and degradability, it has only a minor potential aquatic exposure and thus poses only a minor risk to aquatic organisms<ref name=p/>. |
<P> | <P> | ||
Revision as of 19:57, 4 August 2020
Definition of 1,5,9-Cyclododecatriene (CDDT):
1,5,9-Cyclododecatriene is a liquid with a yellow tint and pungent odour[1].
This is the common definition for 1,5,9-Cyclododecatriene (CDDT), other definitions can be discussed in the article
|
Notes
| 1,5,9 cyclododecatriene |
|---|
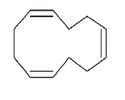
|
| Formula |
| C12H18 |
CDDT is used to produce cyclododecane, which is used in the production of dodecanedioic acid. Dodecanedioic acid can be used in dyes, solvents, adhesives, cleaning agents fertilisers,... .
CDDT has a high volatility, which causes it to have an aquatic half-life (by evaporation) of only 1,3 hours. In the atmosphere it will be degraded rapidly (in less than 30 minutes). As a consequence CDDT will be found mostly in soils, and very little in water, air or sediment. It is not considered to be biodegradable and has a low tendency to bioaccumulate.
Aquatic concentrations above 0,2 mg/l cause acute toxicity to fish, algae and invertebrates. A dose of 2,5 g/kg body weight is lethal to rats.
Considering CDDT it is only used as an intermediate in the production of other chemicals, its high volatility and degradability, it has only a minor potential aquatic exposure and thus poses only a minor risk to aquatic organisms[1].
Environmental standards and legislation
Included in the OSPAR list of substances of priority action
References
Please note that others may also have edited the contents of this article.
|