Difference between revisions of "AMPA"
From Coastal Wiki
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{Tocright}} | ||
{{Definition|title=Aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) | {{Definition|title=Aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) | ||
| Line 33: | Line 34: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| − | + | {{author | |
| + | |AuthorID=19826 | ||
| + | |AuthorFullName=Daphnis De Pooter | ||
| + | |AuthorName=Daphnisd}} | ||
[[Category:Coastal and marine pollution]] | [[Category:Coastal and marine pollution]] | ||
Revision as of 16:27, 19 March 2013
Definition of Aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA):
Aminomethylphosphonic acid is mainly produced by environmental biodegradation reactions of the herbicide glyphosate[1].
This is the common definition for Aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA), other definitions can be discussed in the article
|
Notes

|
| AMPA |
|---|
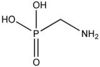
|
| Formula |
| CH6NO3P |
Currently very little is known about AMPA. It is formed by biodegradation of the herbicide glyohosate. Compared to glyohosate; present at lower concentrations in the environment, although it's more stable, it adsorbs more strongly to soils and might have a higher tendency towards bioaccumulation. Glysphosate itself however is not expected to bioaccumulate much because of its higher water solubility[2].
Measured concentrations of AMPA in surface waters range between 6 and 35 µg/l [3].
Environmental standards and legislation
Included in the water framework list of priority substances
References
Please note that others may also have edited the contents of this article.
|