Difference between revisions of "Bentazon"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Definition|title=bentazon | {{Definition|title=bentazon | ||
| − | |definition=Bentazon is a herbicide used in agriculture for selective post-emergence control of many broad leaf weeds in soybeans, rice, corn, peanut, mint, dry bean, dry peas and succulent lima bean plantations | + | |definition=Bentazon is a herbicide used in agriculture for selective post-emergence control of many broad leaf weeds in soybeans, rice, corn, peanut, mint, dry bean, dry peas and succulent lima bean plantations<ref>[http://www.epa.gov/iris/toxreviews/0134-tr.pdf EPA 1998 TOXICOLOGICAL REVIEW of BENTAZON]</ref>. }} |
Revision as of 12:48, 2 October 2009
Definition of bentazon:
Bentazon is a herbicide used in agriculture for selective post-emergence control of many broad leaf weeds in soybeans, rice, corn, peanut, mint, dry bean, dry peas and succulent lima bean plantations[1].
This is the common definition for bentazon, other definitions can be discussed in the article
|
Notes
| Bentazon |
|---|
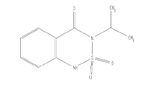
|
| Formula |
| C9H12N203S |
Bentazon is expected to enter surface water by run of from application sites. It has a moderate water solubility of 500 mg/l and a low tendency to adsorb to soils and sediments. In water it can be rapidly broken down by sun light (photodegradation). Its environmental half-life varies between 24 hours and 4 months, depending on the environmental conditions. It can also be biodegraded. [2] [3]
It has a very low a tendency to bioaccumulate.
Bentazon has a low toxicity to most aquatic animals. Concentrations above 100 mg/l are necessary to cause acute toxicity to fishes. Invertebrates are most vulnerable; mussels die at concentrations above 20 mg/l. Concentrations above 5 mg/l might affect phytoplankton. [4]
Environmental standards and legislation
Included in the water framework list of priority substances