Difference between revisions of "Mecoprop"
(ref +ref +ref +ref) |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== Notes == | == Notes == | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="toccolours" border="1" style="float: right; clear: right; margin: 0 0 1em 1em; border-collapse: collapse;" | ||
| + | ! bgcolor="#FF8888" | Mecoprop | ||
| + | |- | ||
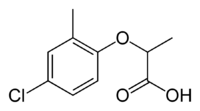
| + | | align="center" bgcolor="#FFFFFF" | [[Image:Mecoprop.png|200px|Mecoprop]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! bgcolor="#8888FF" | Formula | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align="center" | C<sub>10</sub>H<sub>11</sub>ClO<sub>3</sub> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
MCPP is mainly used to control weeds around cereal crops, apples and pears. | MCPP is mainly used to control weeds around cereal crops, apples and pears. | ||
Revision as of 11:52, 25 August 2009
Notes
| Mecoprop |
|---|
|
| Formula |
| C10H11ClO3 |
MCPP is mainly used to control weeds around cereal crops, apples and pears. The release of mecoprop to the environment will be primarily from its application as a herbicide, but also potentially from its manufacture, transport and storage. There are no natural sources of release to the environment.[1]
In water is has a low solubility of 0.734 g/l. It has a low tendency to adsorb to organic matter and soils. In water it takes less than a month to half its concentration. [3]
MCPP has a low potential to bioaccumulate and is therefore not likely to biomagnify. [3]
Mecoprop causes oysters to die at concentrations above 4 mg/l. Most fish species tolerate concentrations up to 10 mg/l and some even concentrations up to 500 mg/l. [4]
Environmental standards and legislation
Included in the water framework list of priority substances