Difference between revisions of "Geographical Information System"
(→Data types) |
(→What is GIS?) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
:GIS divides raw data into layers so it can give you a better understanding for the whole world. | :GIS divides raw data into layers so it can give you a better understanding for the whole world. | ||
| + | A GIS is designed for the collection, storage, and analysis of objects and phenomena where geographic location is an important characteristic or critical to the analysis - this definition is broad and applies to a wide variety of methods for storing, accessing, and manipulating geographic information; it does not limit GIS to the computer environment<ref>Cox, A., Gifford, F. An overview to geographic information systems. The Journal of Academic Librarianship, Volume 23, Issue 6, November 1997, Pages 449-461</ref> . | ||
| + | ===Characteristics of a GIS=== | ||
| + | GIS stores: | ||
| + | *geographic coordinate data (spatial data) | ||
| + | *attribute data | ||
| + | '''Spatial data:''' | ||
| + | *represent features having known locations on earth | ||
| + | *one of: points (0D), lines (1D) or areas (2D) | ||
| + | '''Attribute data:''' | ||
| + | *non-graphic information linked to the geographical features (spatial data) describing features eg type of road, name, history. | ||
| + | ===Data layers and objects=== | ||
| + | *map data separated and stored in layers usually based on common geographical themes or data type | ||
| + | *alternative: objected-oriented GIS: geographical and all other information regarding a feature stored as an object | ||
| + | ==Formats== | ||
| + | Two basic formats for storing and processing coordinate data: Vector and Raster | ||
| + | '''Vector:''' | ||
| + | *uses point locations (X,Y coordinate) | ||
| + | *advantage: less storage space | ||
| + | *disadvantage: may be more difficult to perform certain overlay functions | ||
| − | + | '''Raster:''' | |
| − | + | *data stored as a matrix of pixels, representing points. | |
| − | + | *to analyse or overlay multiple data layers, the layers must share a common projection and coordinate system, and layers must have topology established | |
| − | + | *Disadvantage: it is necessary to store the entire matrix | |
| − | + | *Advantage: can perform neighbourhood analysis easily | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Why is GIS unique?== | ==Why is GIS unique?== | ||
Revision as of 14:52, 11 January 2007
Geographical Information System (GIS) is a tool for analysis and presentation of spatial data. It is a collection of computer hardware, software and geographic data for capturing, managing, analysing and displaying all forms of geographically referenced information.
Contents
What is GIS?
- Simple definition
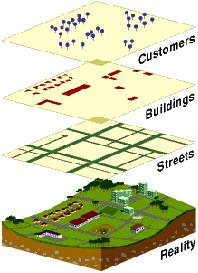
- A Geographic Information System organizes large volumes of raw data into a map form for easy comprehension.
- GIS divides raw data into layers so it can give you a better understanding for the whole world.
A GIS is designed for the collection, storage, and analysis of objects and phenomena where geographic location is an important characteristic or critical to the analysis - this definition is broad and applies to a wide variety of methods for storing, accessing, and manipulating geographic information; it does not limit GIS to the computer environment[1] .
Characteristics of a GIS
GIS stores:
- geographic coordinate data (spatial data)
- attribute data
Spatial data:
- represent features having known locations on earth
- one of: points (0D), lines (1D) or areas (2D)
Attribute data:
- non-graphic information linked to the geographical features (spatial data) describing features eg type of road, name, history.
Data layers and objects
- map data separated and stored in layers usually based on common geographical themes or data type
- alternative: objected-oriented GIS: geographical and all other information regarding a feature stored as an object
Formats
Two basic formats for storing and processing coordinate data: Vector and Raster
Vector:
- uses point locations (X,Y coordinate)
- advantage: less storage space
- disadvantage: may be more difficult to perform certain overlay functions
Raster:
- data stored as a matrix of pixels, representing points.
- to analyse or overlay multiple data layers, the layers must share a common projection and coordinate system, and layers must have topology established
- Disadvantage: it is necessary to store the entire matrix
- Advantage: can perform neighbourhood analysis easily
Why is GIS unique?
- GIS handles SPATIAL information
- Information referenced by its location in space
GIS functions
- Data input
- Storage
- Management
- Analysis
- Output
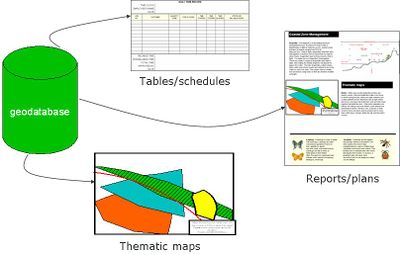
Storing data using Geodatabase
- Geodatabase is a container for spatial and non- spatial data that can be organized in a certain structure.
- Advantages:
- provide a single, consolidated data storage for field measurements and all types of data used.
- Controlling data entry by applying validation rule on the attributes.
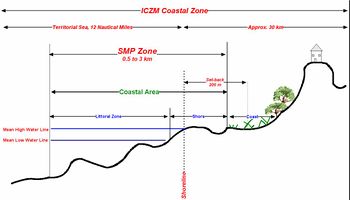
CZM and GIS
- GIS stores all data relevant for the CZM
- GIS handles data on all spatial scales (North Egypt coast vs. a single harbour)
- GIS is a powerful analysis tool.
- Comparison of measurements from different years
- Overlay analysis of measurements and modelling results
Data types
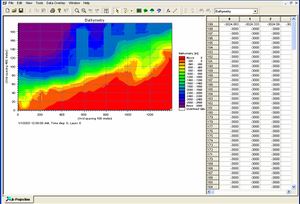
- DFS2 Data MIKE 21
- Dfs1 Data MIKE 21
- XYZ Data
- Wave time series & Rose
- Scanned Maps
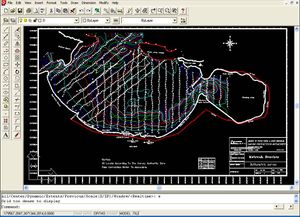
- CAD drawing
Additional Data
- Land use
- Sediment classification
- Satellite images
- Geographical maps
- Reports (design, licenses, Site investigation)
- ….etc.
External links
GIS WWWW resource list of servers likely to be of interest to the GIS community
8th January, Ulrik Lumborg and Caitlin Pilkington (caitlin.pilkington@gmail.com), DHI.- ↑ Cox, A., Gifford, F. An overview to geographic information systems. The Journal of Academic Librarianship, Volume 23, Issue 6, November 1997, Pages 449-461