Difference between revisions of "Musk xylene"
(→Notes) |
Dronkers J (talk | contribs) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
Musk xylene is primarily used in detergents and soaps. Therefore the main source of musk xylene to the marine environment is the widespread use of musk xylene in these products. Negative publicity has lead to a reduction in the use of musk xylene (European use declined from 170 tonnes in 1992 to 67 tonnes in 2000), which also resulted in downward trends in concentrations in the environment. | Musk xylene is primarily used in detergents and soaps. Therefore the main source of musk xylene to the marine environment is the widespread use of musk xylene in these products. Negative publicity has lead to a reduction in the use of musk xylene (European use declined from 170 tonnes in 1992 to 67 tonnes in 2000), which also resulted in downward trends in concentrations in the environment. | ||
| − | Musk xylene is a substance with a low vapor pressure, therefore only very low concentrations of it can be found in the atmosphere. It has a low water solubility (0,15 mg/l) and a high tendency to adsorb to soils. | + | Musk xylene is a substance with a low vapor pressure, therefore only very low concentrations of it can be found in the atmosphere. It has a low water solubility (0,15 mg/l) and a high tendency to adsorb to soils. In the soil it can be easily degraded (concentration is halved in less then 60 days). In water however it is very stable (it takes more than 150 days to half the musk xylene concentration. It has a high tendency to [[bioaccumulation|bioacumulate]] in many organisms, it is unclear whether it [[biomagnification|biomagnifies]]. The substance has effects the reproduction of zooplankton at concentrations above 0,056 mg/l. <ref>[http://echa.europa.eu/doc/candidate_list/svhc_supdoc_muskxylene_publication.pdf European Chemicals Agency 8 October 2008: Support Document for Identification of 5-tert-Butyl-2,4,6-trinitro-m-xylene as a Substance of Very High Concern]</ref> |
In the North Sea concentrations up to 0,17 ng/l have been found. In the liver of fish concentrations up to 0,008 mg/kg [[wet weight]] were measured.<ref name = OECD>[http://www.ospar.org/documents%5Cdbase%5Cpublications%5Cp00200_BD%20on%20musk%20xylene.pdf OSPAR Commission, 2004: OSPAR background document on Musk xylene]</ref> | In the North Sea concentrations up to 0,17 ng/l have been found. In the liver of fish concentrations up to 0,008 mg/kg [[wet weight]] were measured.<ref name = OECD>[http://www.ospar.org/documents%5Cdbase%5Cpublications%5Cp00200_BD%20on%20musk%20xylene.pdf OSPAR Commission, 2004: OSPAR background document on Musk xylene]</ref> | ||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | {{author |
| + | |AuthorID=19826 | ||
| + | |AuthorFullName=Daphnis De Pooter | ||
| + | |AuthorName=Daphnisd}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Toxicity chemicals]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:26, 9 August 2020
Definition of musk xylene:
Musk ingredients are substances with a typical musky scent, used by the fragrance industry in wide range of consumer products including; cosmetics, detergents, soaps, fabric softeners and cleaning products. Synthetic musks are generally divided into three groups of substances with similar properties but different chemical structures: nitromusks, polycyclic musks and macrocyclic musks. The main nitromusks are musk xylene and musk ketone. [1]
This is the common definition for musk xylene, other definitions can be discussed in the article
|
Notes
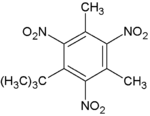
| Musk xylene |
|---|
|
| Formula C12H15N3O6 |
| C12H15N3O6 |
Musk xylene is primarily used in detergents and soaps. Therefore the main source of musk xylene to the marine environment is the widespread use of musk xylene in these products. Negative publicity has lead to a reduction in the use of musk xylene (European use declined from 170 tonnes in 1992 to 67 tonnes in 2000), which also resulted in downward trends in concentrations in the environment.
Musk xylene is a substance with a low vapor pressure, therefore only very low concentrations of it can be found in the atmosphere. It has a low water solubility (0,15 mg/l) and a high tendency to adsorb to soils. In the soil it can be easily degraded (concentration is halved in less then 60 days). In water however it is very stable (it takes more than 150 days to half the musk xylene concentration. It has a high tendency to bioacumulate in many organisms, it is unclear whether it biomagnifies. The substance has effects the reproduction of zooplankton at concentrations above 0,056 mg/l. [2]
In the North Sea concentrations up to 0,17 ng/l have been found. In the liver of fish concentrations up to 0,008 mg/kg wet weight were measured.[1]
Environmental standards and legislation
Included in the OSPAR list of substances of priority action
Included in the water framework list of priority substances
See also
OSPAR background document on lindane
References
Please note that others may also have edited the contents of this article.
|