Difference between revisions of "Lindane"
Dronkers J (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (21 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{tocright}} | |
{{Definition|title= lindane | {{Definition|title= lindane | ||
| − | |definition=Lindane is the common name for the γ-isomer of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) and is used as an insecticide. | + | |definition=Lindane is the common name for the γ-isomer of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) and is used as an insecticide. Like all isomers of HCH, lindane belongs to the greater group of [[organochlorine compounds]]<ref name = OECD>[http://www.ospar.org/documents%5Cdbase%5Cpublications%5Cp00153_Background%20document%20on%20lindane%20updated.pdf OSPAR Commission, 2006: OSPAR background document on lindane]</ref>. |
| − | <ref name = OECD>[http://www.ospar.org/documents%5Cdbase%5Cpublications%5Cp00153_Background%20document%20on%20lindane%20updated.pdf | + | }} |
== Notes == | == Notes == | ||
| − | + | {| class="toccolours" border="1" style="float: right; clear: right; margin: 0 0 1em 1em; border-collapse: collapse;" | |
| + | ! bgcolor="#FF8888" | γ-hexachlorocyclohexane | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align="center" bgcolor="#FFFFFF" | [[Image:Lindane.jpg|150px|Lindane]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! bgcolor="#8888FF" | Formula | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align="center" | C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>6</sub>Cl<sub>6</sub> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | The | + | The use of HCH mixtures is prohibited in Western Europe and North America since 1979. The use of its main constituent, lindane has been phased out in Europe since 2002. Lindane is an insecticide which had a widespread use in agriculture and forestry, for seed treatment, in household biocidal products, as a textile preservative and as a wood preservative. Lindane has been intensively used for many years since 1949 but has been replaced in most applications. Its use decreased from an estimated use of nearly 7900 tonnes in 1970 in Europe, to about 2300 tonnes in 1996<ref name = OECD>[http://www.ospar.org/documents%5Cdbase%5Cpublications%5Cp00153_Background%20document%20on%20lindane%20updated.pdf OSPAR Commission, 2006: OSPAR background document on lindane]</ref>. |
| + | Lindane is a relatively [[volatile]] substance, therefore high amounts (hundreds of tonnes each year) entered the atmosphere. This atmospheric load gets partly deposited in the ocean. Another major input of lindane to the marine environment is riverine transport from the application areas. Lindane is more water soluble than most other organochlorine compounds and is less [[adsorption|adsorbed]] to particles. | ||
| + | Lindane is very stable in water, it is mainly removed by adsorption to sediments and uptake by [[biota]], where some biodegradation may take place. Its [[half-life]] in sea water is between 20 and 200 days. Although lindane is less lipophilic than other organochlorine compounds it also has a tendency towards [[bioaccumulation]]. It also has some potential to [[biomagnification|biomagnify]]. It might pose a greater threat to [[pollution and marine mammals|marine mammals]] than to [[pollution and pelagic fishes|predatory fishes]] because marine mammals seem to be less efficient in eliminating it from their bodies. Fish appear to be able to eliminate lindane through their gills. | ||
| + | The global marine background concentration of lindane has been estimated to be 0,6 ng/l. It occurs world wide and is present in all compartments and [[trophic level|trophic levels]] of the arctic. Concentrations in the [[North Sea]] range from 0,3 to 8 ng/l (in the Dutch Wadden Sea). Concentrations of lindane in [[biota]] are thought to be decreasing. They have been as high as a few µg/kg [[wet weight]] in [[pollution and zoobenthos|mussels]], 152 µg/kg wet weight in fish, and 2-4 mg/kg [[lipid weight]] in the [[blubber ]] of marine mammals. | ||
| + | Water concentrations between 0,5 µg/l and 2,5 µg/l have proved lethal for fish, shrimp and crabs. Zooplankton such as [http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=148370 ''Daphnia''] appear to be able to tolerate concentrations up to 1600 µg/l<ref name = OECD>[http://www.ospar.org/documents%5Cdbase%5Cpublications%5Cp00153_Background%20document%20on%20lindane%20updated.pdf OSPAR Commission, 2006: OSPAR background document on lindane]</ref>. | ||
| + | <P> | ||
| + | <BR> | ||
| + | <P> | ||
| − | + | == Environmental standards and legislation == | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | [[OSPAR List of priority substances|Included in the OSPAR list of substances of priority action (as hexachlorocyclohexane)]] | |
| − | + | <P> | |
| − | + | <BR> | |
| − | + | <P> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | == See also == | |
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.vliz.be/projects/endis/EDnorth.php?showchemprop=true&showeffects=true&chemeffects=true&chemid=250 Lindane on the ED North Database] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.vliz.be/vmdcdata/ecotox/ecotox.php?action=DispChem&ChemID=127 Lindane on the Ecotox Database] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.ospar.org/documents%5Cdbase%5Cpublications%5Cp00153_Background%20document%20on%20lindane%20updated.pdf OSPAR background document on lindane] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <P> | ||
| + | <BR> | ||
| + | <P> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
| + | {{author | ||
| + | |AuthorID=19826 | ||
| + | |AuthorFullName=Daphnis De Pooter | ||
| + | |AuthorName=Daphnisd}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Toxicity chemicals]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:23, 9 August 2020
Definition of lindane:
Lindane is the common name for the γ-isomer of hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH) and is used as an insecticide. Like all isomers of HCH, lindane belongs to the greater group of organochlorine compounds[1].
This is the common definition for lindane, other definitions can be discussed in the article
|
Notes
| γ-hexachlorocyclohexane |
|---|
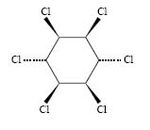
|
| Formula |
| C6H6Cl6 |
The use of HCH mixtures is prohibited in Western Europe and North America since 1979. The use of its main constituent, lindane has been phased out in Europe since 2002. Lindane is an insecticide which had a widespread use in agriculture and forestry, for seed treatment, in household biocidal products, as a textile preservative and as a wood preservative. Lindane has been intensively used for many years since 1949 but has been replaced in most applications. Its use decreased from an estimated use of nearly 7900 tonnes in 1970 in Europe, to about 2300 tonnes in 1996[1].
Lindane is a relatively volatile substance, therefore high amounts (hundreds of tonnes each year) entered the atmosphere. This atmospheric load gets partly deposited in the ocean. Another major input of lindane to the marine environment is riverine transport from the application areas. Lindane is more water soluble than most other organochlorine compounds and is less adsorbed to particles. Lindane is very stable in water, it is mainly removed by adsorption to sediments and uptake by biota, where some biodegradation may take place. Its half-life in sea water is between 20 and 200 days. Although lindane is less lipophilic than other organochlorine compounds it also has a tendency towards bioaccumulation. It also has some potential to biomagnify. It might pose a greater threat to marine mammals than to predatory fishes because marine mammals seem to be less efficient in eliminating it from their bodies. Fish appear to be able to eliminate lindane through their gills.
The global marine background concentration of lindane has been estimated to be 0,6 ng/l. It occurs world wide and is present in all compartments and trophic levels of the arctic. Concentrations in the North Sea range from 0,3 to 8 ng/l (in the Dutch Wadden Sea). Concentrations of lindane in biota are thought to be decreasing. They have been as high as a few µg/kg wet weight in mussels, 152 µg/kg wet weight in fish, and 2-4 mg/kg lipid weight in the blubber of marine mammals.
Water concentrations between 0,5 µg/l and 2,5 µg/l have proved lethal for fish, shrimp and crabs. Zooplankton such as Daphnia appear to be able to tolerate concentrations up to 1600 µg/l[1].
Environmental standards and legislation
Included in the OSPAR list of substances of priority action (as hexachlorocyclohexane)
See also
Lindane on the ED North Database
Lindane on the Ecotox Database
OSPAR background document on lindane
References
Please note that others may also have edited the contents of this article.
|