Difference between revisions of "Dioxins"
(→Notes) |
Dronkers J (talk | contribs) |
||
| (25 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | __TOC__ | ||
| + | |||
{{Definition|title=dioxins | {{Definition|title=dioxins | ||
| − | |definition=Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs) and polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDFs) are two groups of tricyclic, chlorine-substituted, organic compounds. The number of | + | |definition=Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs) and polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDFs) are two groups of tricyclic, [[organochlorine compounds|chlorine-substituted, organic compounds]]. The number of hydrogen atoms on the benzene rings which are replaced by chlorine atoms may range from one to eight. This means that 75 theoretical possible PCDDs and 135 possible PCDFs congeners, can be created. These 210 different molecules are combined in the general term “dioxins”<ref name="Ospar">[http://www.ospar.org/documents%5Cdbase%5Cpublications%5Cp00308_Revised%20BD%20on%20dioxins.pdf OSPAR Commission, 2007: OSPAR background document on dioxins]</ref>. }} |
== Notes == | == Notes == | ||
| − | Dioxins are mainly formed as an unintentional by-product from combustion processes involving organic matter, chlorine compounds and a catalyst, e.g. copper. Formation of trace concentrations of dioxins may take place in any fire or | + | |
| + | {| class="toccolours" border="1" style="float: right; clear: right; margin: 0 0 1em 1em; border-collapse: collapse;" | ||
| + | ! bgcolor="#FF8888" | Dioxins | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align="center" bgcolor="#FFFFFF" | [[Image:Dioxins.jpg|200px|dioxins]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! | 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (above) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="center"| C<sub>12</sub>H<sub>4</sub>Cl<sub>4</sub>O<sub>2</sub> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! | 1,2,3,7,8-Pentachlorodibenzofuran (below) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="center"| C<sub>12</sub>H<sub>3</sub>Cl<sub>5</sub>O | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Dioxins are mainly formed as an unintentional by-product from combustion processes involving organic matter, chlorine compounds and a catalyst, e.g. [[copper]]. Formation of trace concentrations of dioxins may take place in any fire or | ||
combustion process based on natural or man-made organic materials. The presence of chlorinated organic compounds, such as [[trichlorobenzene|chlorobenzenes]] and [[PCB|polychlorinated biphenyls]] (PCBs) may accelerate the dioxin formation. | combustion process based on natural or man-made organic materials. The presence of chlorinated organic compounds, such as [[trichlorobenzene|chlorobenzenes]] and [[PCB|polychlorinated biphenyls]] (PCBs) may accelerate the dioxin formation. | ||
| − | Dioxins are extremely insoluble in water. The solubility depends on the | + | Dioxins are extremely insoluble in water. The solubility depends on the congeners of the dioxin mixture, but a typical solubility is around 20ng/l. In natural waters dioxins are therefore mostly associated organic matter and sediments. Dioxins also have a very low [[volatile|volatility]], thus in the atmosphere dioxins are mostly attached to fine particles. Besides a few industrial point sources, such as old plants producing magnesium, PVC or paper, the most important direct source of dioxins to the aquatic and marine environment are probably dry deposition of airborne particle-bound dioxins<ref name="Ospar">[http://www.ospar.org/documents%5Cdbase%5Cpublications%5Cp00308_Revised%20BD%20on%20dioxins.pdf OSPAR Commission, 2007: OSPAR background document on dioxins]</ref>. |
| + | |||
| + | Dioxins are very stable chemicals. Generally, they are not biodegraded and remain stable at temperatures below 750°C. The biodegradation is slowest for the high-chlorinated congeners. High concentrations can be found in [[coastal area]] sediments; up to 7200 ng/kg ([[dry weight]]) has been found in the Scheldt [[estuary]], while in sediments in off shore areas of the [[North Sea]] dioxin concentrations below 3,2 ng/kg are common. The heavily polluted Norwegian [[fjord|fjords]] can contain up to 60.000 ng/kg of dioxins in their sediments. The sediments are considered to act as a sink for these compounds. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Dioxins have a very high tendency towards [[bioaccumulation]] and [[biomagnification]]. Bioaccumulation appears mainly the result of food intake rather than from direct absorption from the water. Therefore high [[Trophic_level_-_a_marine_example|trophic levels]], like [[pollution and pelagic fishes|fish]] are usually used to monitor dioxin contaminations. Herring from the [[North Sea]] usually contains between 1 and 2ng/kg ([[wet weight]]) of dioxins, which is 5 times less than herring from the heavily [[pollution|polluted]] [[Baltic Sea]]. [[Pollution and marine mammals|Marine mammals]], the top of the North Sea [[food chain]], contain the the highest concentrations of dioxins: In the Baltic Sea, they can contain up to 150 ng/kg [[lipid weight]] in their [[blubber]]. Human fat tissue usually contains between 10 and 50 ng/kg [[lipid weight]] of dioxins. <ref name="Ospar">[http://www.ospar.org/documents%5Cdbase%5Cpublications%5Cp00308_Revised%20BD%20on%20dioxins.pdf OSPAR Commission, 2007: OSPAR background document on dioxins]</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The different forms of dioxins have a different [[toxic|toxicity]]. The most toxic dioxin is 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). The toxicity of the other dioxins are expressed with a number between 0 and 1 which expresses it's relative toxicity compared to TCDD.<P> | ||
| + | The toxicological effects of dioxins have mostly been studied in mammals. They can cause a whole section of health problems including: liver enlargement, liver lesions, cancer and [[endocrine disrupting compounds|endocrine disruption]]<ref name="Ospar">[http://www.ospar.org/documents%5Cdbase%5Cpublications%5Cp00308_Revised%20BD%20on%20dioxins.pdf OSPAR Commission, 2007: OSPAR background document on dioxins]</ref> . | ||
| + | Lethal doses for hamsters are 5 mg per kg body weight<ref>Clark, R,B., 1999. Marine pollution. Oxford University press, Fourth edition, pp 161</ref>. In fish one of the first signs of toxicity is the cessation of food intake, followed by a decreased growth. Other manifestations are minor internal bleedings just below their skin and fins, as well as skeletal deformities and an increased vulnerability to fungal infections<ref>Kennish, M. J. (1996): Practical Handbook of Estuarine and Marine Pollution, CRC Press 524 pp</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <P> | ||
| + | <BR> | ||
| + | <P> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Environmental standards and legislation == | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[OSPAR List of priority substances|Included (as PCDDs and PCDFs) in the OSPAR list of substances of priority action]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[List of priority substances|Included in the water framework list of priority substances]] | ||
| − | + | <BR> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | == See also == | |
| + | [http://www.ospar.org/documents%5Cdbase%5Cpublications%5Cp00308_Revised%20BD%20on%20dioxins.pdf OSPAR background document on dioxins] | ||
| + | <P> | ||
| + | <BR> | ||
| + | <P> | ||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
| + | {{author | ||
| + | |AuthorID=19826 | ||
| + | |AuthorFullName=Daphnis De Pooter | ||
| + | |AuthorName=Daphnisd}} | ||
| − | + | [[Category:Toxicity chemicals]] | |
Latest revision as of 13:09, 9 August 2020
Definition of dioxins:
Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs) and polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDFs) are two groups of tricyclic, chlorine-substituted, organic compounds. The number of hydrogen atoms on the benzene rings which are replaced by chlorine atoms may range from one to eight. This means that 75 theoretical possible PCDDs and 135 possible PCDFs congeners, can be created. These 210 different molecules are combined in the general term “dioxins”[1].
This is the common definition for dioxins, other definitions can be discussed in the article
|
Notes
| Dioxins |
|---|
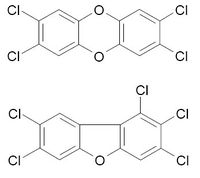
|
| 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (above) |
| C12H4Cl4O2 |
| 1,2,3,7,8-Pentachlorodibenzofuran (below) |
| C12H3Cl5O |
Dioxins are mainly formed as an unintentional by-product from combustion processes involving organic matter, chlorine compounds and a catalyst, e.g. copper. Formation of trace concentrations of dioxins may take place in any fire or combustion process based on natural or man-made organic materials. The presence of chlorinated organic compounds, such as chlorobenzenes and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) may accelerate the dioxin formation.
Dioxins are extremely insoluble in water. The solubility depends on the congeners of the dioxin mixture, but a typical solubility is around 20ng/l. In natural waters dioxins are therefore mostly associated organic matter and sediments. Dioxins also have a very low volatility, thus in the atmosphere dioxins are mostly attached to fine particles. Besides a few industrial point sources, such as old plants producing magnesium, PVC or paper, the most important direct source of dioxins to the aquatic and marine environment are probably dry deposition of airborne particle-bound dioxins[1].
Dioxins are very stable chemicals. Generally, they are not biodegraded and remain stable at temperatures below 750°C. The biodegradation is slowest for the high-chlorinated congeners. High concentrations can be found in coastal area sediments; up to 7200 ng/kg (dry weight) has been found in the Scheldt estuary, while in sediments in off shore areas of the North Sea dioxin concentrations below 3,2 ng/kg are common. The heavily polluted Norwegian fjords can contain up to 60.000 ng/kg of dioxins in their sediments. The sediments are considered to act as a sink for these compounds.
Dioxins have a very high tendency towards bioaccumulation and biomagnification. Bioaccumulation appears mainly the result of food intake rather than from direct absorption from the water. Therefore high trophic levels, like fish are usually used to monitor dioxin contaminations. Herring from the North Sea usually contains between 1 and 2ng/kg (wet weight) of dioxins, which is 5 times less than herring from the heavily polluted Baltic Sea. Marine mammals, the top of the North Sea food chain, contain the the highest concentrations of dioxins: In the Baltic Sea, they can contain up to 150 ng/kg lipid weight in their blubber. Human fat tissue usually contains between 10 and 50 ng/kg lipid weight of dioxins. [1]
The different forms of dioxins have a different toxicity. The most toxic dioxin is 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). The toxicity of the other dioxins are expressed with a number between 0 and 1 which expresses it's relative toxicity compared to TCDD.The toxicological effects of dioxins have mostly been studied in mammals. They can cause a whole section of health problems including: liver enlargement, liver lesions, cancer and endocrine disruption[1] . Lethal doses for hamsters are 5 mg per kg body weight[2]. In fish one of the first signs of toxicity is the cessation of food intake, followed by a decreased growth. Other manifestations are minor internal bleedings just below their skin and fins, as well as skeletal deformities and an increased vulnerability to fungal infections[3].
Environmental standards and legislation
Included (as PCDDs and PCDFs) in the OSPAR list of substances of priority action
Included in the water framework list of priority substances
See also
OSPAR background document on dioxins
References
Please note that others may also have edited the contents of this article.
|