Difference between revisions of "Trichlorobenzene"
(→Notes) |
Dronkers J (talk | contribs) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{tocright}} | |
| − | {{Definition|title=trichlorobenzene | + | {{Definition|title=trichlorobenzene (TCB) |
| − | |definition=Trichlorobenzenes are cyclic aromatic compounds formed by the addition of 3 atoms of chlorine to the benzene ring. There are 3 isomers: 1,2,3-trichlorobenzene (1,2,3-TCB), 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene (1,2,4-TCB) and 1,3,5-trichlorobenzene (1,3,5-TCB) | + | |definition=Trichlorobenzenes are cyclic aromatic compounds formed by the addition of 3 atoms of chlorine to the benzene ring. There are 3 isomers: 1,2,3-trichlorobenzene (1,2,3-TCB), 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene (1,2,4-TCB) and 1,3,5-trichlorobenzene (1,3,5-TCB)<ref name="Ospar">[http://www.ospar.org/documents%5Cdbase%5Cpublications%5Cp00170_BD%20on%20trichlorobenzenes.pdf OSPAR Commission, 2005: OSPAR background document on trichlorobenzenes]</ref>. |
| − | <ref name="Ospar">[http://www.ospar.org/documents%5Cdbase%5Cpublications%5Cp00170_BD%20on%20trichlorobenzenes.pdf OSPAR Commission, 2005: OSPAR background document on trichlorobenzenes]</ref> | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 25: | Line 24: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | The EU production of TCBs | + | The 2003 EU production of TCBs was estimated below 4 000 tonnes, of which a high amount is exported. Today TCBs are be used as intermediate in the production of herbicides and pesticides. However they were historically used as dye carriers, which [[adsorption|adsorb]] into the polyester fibres. During dying a significant amount of TCBs were emitted to waste waters. TCBs have also been used as an additive to [[PCB|PCBs]] for insulating and cooling dielectric fluids<ref name="Ospar">[http://www.ospar.org/documents%5Cdbase%5Cpublications%5Cp00170_BD%20on%20trichlorobenzenes.pdf OSPAR Commission, 2005: OSPAR background document on trichlorobenzenes]</ref>. |
| − | When entered into the marine environment, TCBs will most likely | + | When entered into the marine environment, TCBs will most likely evaporate or adsorb to organic sediments. It's also thought that during transport to the sea, TCBs are adsorbed to the riverine sediments. This results in high concentrations in river sediments, making them "pollution hot spots". They are immobile and very [[persistent]] in these soils. |
| − | + | TCBs are not considered to be carcinogenic. They have been shown to cause acute [[toxic|toxicity]] to algae, crustaceans and [[pollution and pelagic fishes|fish]] at a concentration of 1,4 mg/l, 0,45 mg/l and 21 mg/l respectively. Concentrations in marine waters range from 0,002 µg/l (in open ocean) to 0,03 µg/l (in [[pollution|polluted]] areas). The highest environmental concentrations measured in marine fish range from 0,14 to 2,3 µg/kg [[lipid weight]]. TCBs are also thought to cause reproductive and [[endocrine disrupting compounds|endocrine disrupting]] effects. | |
| − | TCBs | + | TCBs also have a high potential to [[bioaccumulation|bioaccumulate]]<ref name="Ospar">[http://www.ospar.org/documents%5Cdbase%5Cpublications%5Cp00170_BD%20on%20trichlorobenzenes.pdf OSPAR Commission, 2005: OSPAR background document on trichlorobenzenes]</ref>. |
| + | <P> | ||
| + | <BR> | ||
| + | <P> | ||
== Environmental standards and legislation == | == Environmental standards and legislation == | ||
| Line 52: | Line 54: | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | {{author |
| + | |AuthorID=19826 | ||
| + | |AuthorFullName=Daphnis De Pooter | ||
| + | |AuthorName=Daphnisd}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Toxicity chemicals]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:37, 9 August 2020
Definition of trichlorobenzene (TCB):
Trichlorobenzenes are cyclic aromatic compounds formed by the addition of 3 atoms of chlorine to the benzene ring. There are 3 isomers: 1,2,3-trichlorobenzene (1,2,3-TCB), 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene (1,2,4-TCB) and 1,3,5-trichlorobenzene (1,3,5-TCB)[1].
This is the common definition for trichlorobenzene (TCB), other definitions can be discussed in the article
|
Notes
| Trichlorobenzene |
|---|
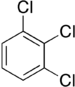
|
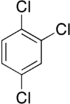
|
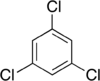
|
| Formula |
| C6H3Cl3 |
The 2003 EU production of TCBs was estimated below 4 000 tonnes, of which a high amount is exported. Today TCBs are be used as intermediate in the production of herbicides and pesticides. However they were historically used as dye carriers, which adsorb into the polyester fibres. During dying a significant amount of TCBs were emitted to waste waters. TCBs have also been used as an additive to PCBs for insulating and cooling dielectric fluids[1].
When entered into the marine environment, TCBs will most likely evaporate or adsorb to organic sediments. It's also thought that during transport to the sea, TCBs are adsorbed to the riverine sediments. This results in high concentrations in river sediments, making them "pollution hot spots". They are immobile and very persistent in these soils.
TCBs are not considered to be carcinogenic. They have been shown to cause acute toxicity to algae, crustaceans and fish at a concentration of 1,4 mg/l, 0,45 mg/l and 21 mg/l respectively. Concentrations in marine waters range from 0,002 µg/l (in open ocean) to 0,03 µg/l (in polluted areas). The highest environmental concentrations measured in marine fish range from 0,14 to 2,3 µg/kg lipid weight. TCBs are also thought to cause reproductive and endocrine disrupting effects.
TCBs also have a high potential to bioaccumulate[1].
Environmental standards and legislation
Included in the OSPAR list of substances of priority action
Included in the water framework list of priority substances
See also
OSPAR background document on trichlorobenzenes
References
Please note that others may also have edited the contents of this article.
|