Difference between revisions of "Pentachloroanisole"
From Coastal Wiki
(→Notes) |
Dronkers J (talk | contribs) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Definition|title=Pentachloroanisole PCA | {{Definition|title=Pentachloroanisole PCA | ||
| − | |definition= Pentachloroanisole is the main degradation product of [[pentachlorophenol]] (PCP) | + | |definition= Pentachloroanisole is a chlorinated aromatic compound, which is widely distributed at low levels in the environment. It is the main degradation product of [[pentachlorophenol]] (PCP) and pentachloronitrobenzene<ref name="UN">[http://www.unece.org/env/lrtap/TaskForce/popsxg/2009/Track%20A%20PCP%20lead%20reviewer%27s%20summary.pdf UNECE Task Force on Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) 14 April, 2009 Summary of Expert Reviews of Pentachlorophenol (PCP)]</ref>. |
| − | <ref name="UN">[http://www.unece.org/env/lrtap/TaskForce/popsxg/2009/Track%20A%20PCP%20lead%20reviewer%27s%20summary.pdf UNECE Task Force on Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) 14 April, 2009 Summary of Expert Reviews of Pentachlorophenol (PCP)]</ref>}} | + | }} |
== Notes == | == Notes == | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | As pentachloroanisole has a relative stability in the atmosphere | + | As pentachloroanisole is easily evaporated and has a relative stability in the atmosphere, as such it is subject to long range environmental transport and can be found in remote areas such as the Arctic. |
| − | It | + | |
| − | There is | + | It appears to be quite stable in the environment and have a very high (higher than PCP) potential to [[bioaccumulation|bioaccumulate]]. Evidence for [[biomagnification]] still has to be produced. |
| − | <ref name="UN">[http://www.unece.org/env/lrtap/TaskForce/popsxg/2009/Track%20A%20PCP%20lead%20reviewer%27s%20summary.pdf UNECE Task Force on Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) 14 April, 2009 Summary of Expert Reviews of Pentachlorophenol (PCP)]</ref> | + | |
| + | There is no information available on its [[toxic|toxicity]]. However, in [[biota]] PCA can be demethylated back to PCP, which is more easily excreted. Therefore PCA can have a similar toxicity<ref name="UN">[http://www.unece.org/env/lrtap/TaskForce/popsxg/2009/Track%20A%20PCP%20lead%20reviewer%27s%20summary.pdf UNECE Task Force on Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) 14 April, 2009 Summary of Expert Reviews of Pentachlorophenol (PCP)]</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
<P> | <P> | ||
<BR> | <BR> | ||
| Line 35: | Line 37: | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | {{author |
| + | |AuthorID=19826 | ||
| + | |AuthorFullName=Daphnis De Pooter | ||
| + | |AuthorName=Daphnisd}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Toxicity chemicals]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:32, 9 August 2020
Definition of Pentachloroanisole PCA:
Pentachloroanisole is a chlorinated aromatic compound, which is widely distributed at low levels in the environment. It is the main degradation product of pentachlorophenol (PCP) and pentachloronitrobenzene[1].
This is the common definition for Pentachloroanisole PCA, other definitions can be discussed in the article
|
Notes
| Pentachloroanisole |
|---|
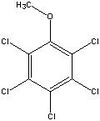
|
| Formula |
| C7H3Cl5O |
As pentachloroanisole is easily evaporated and has a relative stability in the atmosphere, as such it is subject to long range environmental transport and can be found in remote areas such as the Arctic.
It appears to be quite stable in the environment and have a very high (higher than PCP) potential to bioaccumulate. Evidence for biomagnification still has to be produced.
There is no information available on its toxicity. However, in biota PCA can be demethylated back to PCP, which is more easily excreted. Therefore PCA can have a similar toxicity[1].
Environmental standards and legislation
Included in the OSPAR list of substances of priority action
References
Please note that others may also have edited the contents of this article.
|