Difference between revisions of "Neodecanoic acid, ethenyl ester"
Dronkers J (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (9 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Definition|title=neodecanoic acid, ethenyl ester | {{Definition|title=neodecanoic acid, ethenyl ester | ||
| − | |definition= Neodecanoic acid, ethenyl ester is an [[anthropogenic]] chemical used exclusively in polymerization to make | + | |definition= Neodecanoic acid, ethenyl ester is an [[anthropogenic]] chemical used exclusively in polymerization to make products more hydrolytically and UV-stable. The primary uses include polymers used in paints and coatings (65%), and adhesives i.e. re-dispersible powders (35%)<ref name = OECD>[http://www.oecd.org/LongAbstract/0,3425,en_2649_34379_41825008_1_1_1_37407,00.html OECD Initial hazard assessment of Neodecanoic acid, ethenyl ester; CAS 5100-05-23; SIDS Initial Assessment Report For SIAM 24 Paris, France, 17 – 20 April 2007]</ref>. |
| − | <ref name = OECD>OECD Initial hazard assessment of Neodecanoic acid, ethenyl ester; CAS 5100-05-23; SIDS Initial Assessment Report For SIAM 24 Paris, France, 17 – 20 April 2007</ref> }} | + | }} |
| + | == Notes == | ||
| − | == | + | {| class="toccolours" border="1" style="float: right; clear: right; margin: 0 0 1em 1em; border-collapse: collapse;" |
| + | ! bgcolor="#FF8888" | Neodecanoic acid, ethenyl ester | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align="center" bgcolor="#FFFFFF" | [[Image:Decanoic acid.gif|200px| ]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! bgcolor="#8888FF" | Formula | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align="center" | C<sub>12</sub>H<sub>22</sub>O<sub>2</sub> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
Neodecanoic acid, ethenyl ester has a low risk of entering the environment. The production is carried out in a closed circuit with minimal releases to the environment. Only a very small amount (0,006%) of the neodecanoic acid, ethenyl ester used in paints and coatings can expected to be lost into the environment. | Neodecanoic acid, ethenyl ester has a low risk of entering the environment. The production is carried out in a closed circuit with minimal releases to the environment. Only a very small amount (0,006%) of the neodecanoic acid, ethenyl ester used in paints and coatings can expected to be lost into the environment. | ||
| − | Its total global production volume ranges from 46,000 to 230,000 tonnes/yr. | + | Its total global production volume ranges from 46,000 to 230,000 tonnes/yr<ref name = OECD>[http://www.oecd.org/LongAbstract/0,3425,en_2649_34379_41825008_1_1_1_37407,00.html OECD Initial hazard assessment of Neodecanoic acid, ethenyl ester; CAS 5100-05-23; SIDS Initial Assessment Report For SIAM 24 Paris, France, 17 – 20 April 2007]</ref>. |
| − | Neodecanoic acid ethenyl ester is a light viscous liquid and is moderately volatile | + | Neodecanoic acid ethenyl ester is a light viscous liquid and is moderately [[volatile]]. Due to its low water solubility, it is suspected that in the environment it would be mostly associated with sediments. Only small amounts would be found in water and the atmosphere. |
| − | It doesn't dissolve much in water and has a high affinity towards organic matter. | + | It doesn't dissolve much in water and has a high affinity towards organic matter. However, it has only a moderate tendency towards [[bioaccumulation]]. There doesn't appear to be a risk for [[biomagnification]]. [[Pollution and pelagic fishes|Fish]] for example are able to eliminate neodecanoic acid ethenyl ester quite efficiently from their tissues (95% in 14 days)<ref name = OECD>[http://www.oecd.org/LongAbstract/0,3425,en_2649_34379_41825008_1_1_1_37407,00.html OECD Initial hazard assessment of Neodecanoic acid, ethenyl ester; CAS 5100-05-23; SIDS Initial Assessment Report For SIAM 24 Paris, France, 17 – 20 April 2007]</ref> . |
| − | Neodecanoic acid ethenyl ester appears to be a very stable monomer that is not biodegradable, at least not by rats in vitro. It shows an high acute toxicity for fish and zooplankton and a lower one for algae: 0.84 mg/l, 0.3 mg/l and 3.4 mg/l respectively. | + | Neodecanoic acid, ethenyl ester appears to be a very stable monomer that is not biodegradable, at least not by rats in vitro. It shows an high acute [[toxic|toxicity]] for fish and zooplankton and a lower one for algae: 0.84 mg/l, 0.3 mg/l and 3.4 mg/l respectively. Presently no studies have been conducted on chronic toxicity or sublethal effects. |
In rats it has a low toxicity when inhaled, eaten or touched. It can also cause (minimal) irritation to their eyes and skin. | In rats it has a low toxicity when inhaled, eaten or touched. It can also cause (minimal) irritation to their eyes and skin. | ||
| − | The substance is considered to be of low risk towards human health, but might cause environmental problems (especially for fish and marine invertebrates) if released into the environment. | + | The substance is considered to be of low risk towards human health, but might cause environmental problems (especially for fish and marine invertebrates) if released into the environment<ref name = OECD>[http://www.oecd.org/LongAbstract/0,3425,en_2649_34379_41825008_1_1_1_37407,00.html OECD Initial hazard assessment of Neodecanoic acid, ethenyl ester; CAS 5100-05-23; SIDS Initial Assessment Report For SIAM 24 Paris, France, 17 – 20 April 2007]</ref> . |
<P> | <P> | ||
<BR> | <BR> | ||
<P> | <P> | ||
| + | |||
== Environmental standards and legislation == | == Environmental standards and legislation == | ||
[[OSPAR List of priority substances|Included in the OSPAR list of substances of priority action]] | [[OSPAR List of priority substances|Included in the OSPAR list of substances of priority action]] | ||
| + | <P> | ||
| + | <BR> | ||
| + | <P> | ||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
| + | {{author | ||
| + | |AuthorID=19826 | ||
| + | |AuthorFullName=Daphnis De Pooter | ||
| + | |AuthorName=Daphnisd}} | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Toxicity chemicals]] |
Latest revision as of 13:27, 9 August 2020
Definition of neodecanoic acid, ethenyl ester:
Neodecanoic acid, ethenyl ester is an anthropogenic chemical used exclusively in polymerization to make products more hydrolytically and UV-stable. The primary uses include polymers used in paints and coatings (65%), and adhesives i.e. re-dispersible powders (35%)[1].
This is the common definition for neodecanoic acid, ethenyl ester, other definitions can be discussed in the article
|
Notes
| Neodecanoic acid, ethenyl ester |
|---|
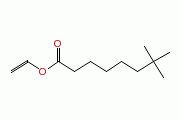
|
| Formula |
| C12H22O2 |
Neodecanoic acid, ethenyl ester has a low risk of entering the environment. The production is carried out in a closed circuit with minimal releases to the environment. Only a very small amount (0,006%) of the neodecanoic acid, ethenyl ester used in paints and coatings can expected to be lost into the environment. Its total global production volume ranges from 46,000 to 230,000 tonnes/yr[1].
Neodecanoic acid ethenyl ester is a light viscous liquid and is moderately volatile. Due to its low water solubility, it is suspected that in the environment it would be mostly associated with sediments. Only small amounts would be found in water and the atmosphere.
It doesn't dissolve much in water and has a high affinity towards organic matter. However, it has only a moderate tendency towards bioaccumulation. There doesn't appear to be a risk for biomagnification. Fish for example are able to eliminate neodecanoic acid ethenyl ester quite efficiently from their tissues (95% in 14 days)[1] .
Neodecanoic acid, ethenyl ester appears to be a very stable monomer that is not biodegradable, at least not by rats in vitro. It shows an high acute toxicity for fish and zooplankton and a lower one for algae: 0.84 mg/l, 0.3 mg/l and 3.4 mg/l respectively. Presently no studies have been conducted on chronic toxicity or sublethal effects. In rats it has a low toxicity when inhaled, eaten or touched. It can also cause (minimal) irritation to their eyes and skin.
The substance is considered to be of low risk towards human health, but might cause environmental problems (especially for fish and marine invertebrates) if released into the environment[1] .
Environmental standards and legislation
Included in the OSPAR list of substances of priority action
References
Please note that others may also have edited the contents of this article.
|