Difference between revisions of "Diuron"
() |
Dronkers J (talk | contribs) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{tocright}} | |
{{Definition|title=diruon | {{Definition|title=diruon | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | In the USA diuron has been used since 1967. Durion is mainly used on citrus, berries, asparagus and pineapple. Right-of-way applications (e.g., | + | In the USA diuron has been used since 1967. Durion is mainly used on citrus, berries, asparagus and pineapple. Right-of-way applications (e.g., on rail road tracks) form the greatest non-agricultural use of diuron, with approximately 1 million kilograms applied annually. |
In water durion has a low tendency to [[adsorption|adsorb]] to particles and organic matter, dispite its relatively low water solubility of 42 mg/l. It's a stable molecule in terrestrial systems but can be biodegraded by micro-organisms. It is expected to be much less stable in aquatic systems, with a [[half-life]] of 30 days (according to lab experiments). | In water durion has a low tendency to [[adsorption|adsorb]] to particles and organic matter, dispite its relatively low water solubility of 42 mg/l. It's a stable molecule in terrestrial systems but can be biodegraded by micro-organisms. It is expected to be much less stable in aquatic systems, with a [[half-life]] of 30 days (according to lab experiments). | ||
| − | Although it has a low potential towards [[bioaccumulation]], it probably doesn't bioaccumulate or [[biomagnification|biomagnify]] in wild aquatic populations | + | Although it has a low potential towards [[bioaccumulation]], it probably doesn't bioaccumulate or [[biomagnification|biomagnify]] in wild aquatic populations<ref>[http://www.wsdot.wa.gov/maintenance/pdf/diuron.pdf Washington State Department of Transportation February 2006 Diuron Roadside Vegetation Management Herbicide Fact Sheet]</ref>. |
| − | It has a low toxicity for [[pollution and marine mammals|mammals]], as doses above 3,4 g per kg body weight are needed to induce acute toxicity. Some [[pollution and pelagic fishes|fish]] and marine invertebrate [[species ]] experience acute toxic effects at diuron concentrations above 4,3 mg/l and 1 mg/l respectively | + | It has a low [[toxic|toxicity]] for [[pollution and marine mammals|mammals]], as doses above 3,4 g per kg body weight are needed to induce acute toxicity. Some [[pollution and pelagic fishes|fish]] and marine invertebrate [[species ]] experience acute toxic effects at diuron concentrations above 4,3 mg/l and 1 mg/l respectively<ref>[http://extoxnet.orst.edu/pips/diuron.htm www.extoxnet.orst.edu august 17 2009]</ref>. Algae are most vulnerable to the herbicide, it can be toxic for some algae species at concentrations of only 5 µg/l<ref>[http://www.pesticideinfo.org/List_AquireAcuteSum.jsp?Rec_Id=PC33293&Taxa_Group=Phytoplankton www.pesticideinfo.org august 17 2009]</ref>. |
<P> | <P> | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| + | {{author | ||
| + | |AuthorID=19826 | ||
| + | |AuthorFullName=Daphnis De Pooter | ||
| + | |AuthorName=Daphnisd}} | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Toxicity chemicals]] |
Latest revision as of 13:10, 9 August 2020
Definition of diruon:
Diuron is used as a herbicide on a variety of both crop and non-crop areas. It is also used as a mildewcide in paints and stains, and as an algaecide in commercial fish production[1].
This is the common definition for diruon, other definitions can be discussed in the article
|
Notes
| Diuron |
|---|
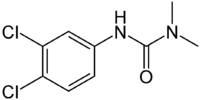
|
| Formula |
| C9H10Cl12N2O |
In the USA diuron has been used since 1967. Durion is mainly used on citrus, berries, asparagus and pineapple. Right-of-way applications (e.g., on rail road tracks) form the greatest non-agricultural use of diuron, with approximately 1 million kilograms applied annually.
In water durion has a low tendency to adsorb to particles and organic matter, dispite its relatively low water solubility of 42 mg/l. It's a stable molecule in terrestrial systems but can be biodegraded by micro-organisms. It is expected to be much less stable in aquatic systems, with a half-life of 30 days (according to lab experiments). Although it has a low potential towards bioaccumulation, it probably doesn't bioaccumulate or biomagnify in wild aquatic populations[2].
It has a low toxicity for mammals, as doses above 3,4 g per kg body weight are needed to induce acute toxicity. Some fish and marine invertebrate species experience acute toxic effects at diuron concentrations above 4,3 mg/l and 1 mg/l respectively[3]. Algae are most vulnerable to the herbicide, it can be toxic for some algae species at concentrations of only 5 µg/l[4].
Environmental standards and legislation
Included in the water framework list of priority substances
See also
Diuron on the ED North Database
References
Please note that others may also have edited the contents of this article.
|