Difference between revisions of "DDT"
Dronkers J (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{tocright}} | |
{{Definition|title= dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane | {{Definition|title= dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane | ||
| − | |definition= Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) is a | + | |definition= Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT) is a [[persistent]] [[organochlorine pesticides|organochlorine pesticide]]<ref>Lawrence E (ed.), 2000. Henderson’s Dictionary of Biological Terms. 12th edition. Prentice Hall, Pearson Education Limited. Harlow, Great Britain.</ref>. }} |
== Notes == | == Notes == | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
|} | |} | ||
DDT, like other organochlorine pesticides enter the marine environment mainly through inputs from water and air, as a result of their use in agriculture. Although the use of DDT in Western countries has been forbidden since the 1970's, they are still detected in the marine environment due to it's extreme stability ([[half-life]] of 15 years), to illegal use or to use elsewhere (third world countries). | DDT, like other organochlorine pesticides enter the marine environment mainly through inputs from water and air, as a result of their use in agriculture. Although the use of DDT in Western countries has been forbidden since the 1970's, they are still detected in the marine environment due to it's extreme stability ([[half-life]] of 15 years), to illegal use or to use elsewhere (third world countries). | ||
| − | DDT is metabolised into dichlorodiphenyldichloroethylene (DDE) which is equally toxic. Therefore, to asses the risk of DDT exposure, the sum both contaminants needs to be taken into account. This also means that when you encounter a high | + | DDT is metabolised into dichlorodiphenyldichloroethylene (DDE) which is equally toxic. Therefore, to asses the risk of DDT exposure, the sum both contaminants needs to be taken into account. This also means that when you encounter a high DDT/DDE ratio, the contamination must be a recent one<ref>OSPAR Commission 2000. Quality Status Report 2000, OSPAR Commission, London</ref>. |
| − | DDT affects the central nervous system of insects and other animals. This results in hyperactivity, paralysis and death. | + | DDT affects the central nervous system of insects and other animals. This results in hyperactivity, paralysis and death. DDT also affects eggshell production in birds and the [[endocrine system]] of most animals<ref>Kennish, M. J. (1996): Practical Handbook of Estuarine and Marine Pollution, CRC Press 524 pp</ref>. |
| − | DDT also affects eggshell production in birds and the [[endocrine system]] of most animals | + | <P> |
| − | + | DDT has a very high tenancy towards [[biomagnification]]. When in a simple ecosystem the background concentration is equal to 1, then zooplankton can accumulate concentrations of 13.000, small fish species concentrations of 170.000, large fishes up to 670.000 and finally birds will accumulate concentrations up to 8.300.000<ref name="pub">Janssen, C. (2008). Wat is giftig en wat niet, de zee onder de loep. Het Laboratorium voor Milieutoxicologie en Aquatische Ecologie, in: Goffin, A. et al. (Ed.) (2008). UGent aan Zee. pp. 54-61</ref>. DDT has been found in all marine ecosystems, including the Antarctic and the deep sea. It can be found in all components of the marine [[food web]]. | |
| − | <P>DDT has a very high tenancy towards [[biomagnification]]. When in a simple ecosystem the background concentration is equal to 1, then zooplankton can accumulate concentrations of 13.000, small fish species concentrations of 170.000, large fishes up to 670.000 and finally birds will accumulate concentrations up to 8.300.000 | ||
<P> | <P> | ||
<BR> | <BR> | ||
<P> | <P> | ||
| + | |||
== Case studies == | == Case studies == | ||
[[PCBs and organochlorine pesticides in Antarctic algae]]<P> | [[PCBs and organochlorine pesticides in Antarctic algae]]<P> | ||
[[PCBs and organochlorine pesticides in shrimp from the Belgian North Sea]]<P> | [[PCBs and organochlorine pesticides in shrimp from the Belgian North Sea]]<P> | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[Organohalogenated contaminants in harbour porpoises|Organochlorine pesticides in Harbour porpoises]] |
<P> | <P> | ||
<BR> | <BR> | ||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| + | {{author | ||
| + | |AuthorID=19826 | ||
| + | |AuthorFullName=Daphnis De Pooter | ||
| + | |AuthorName=Daphnisd}} | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Toxicity chemicals]] |
Latest revision as of 13:06, 9 August 2020
Contents |
Definition of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane:
This is the common definition for dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane, other definitions can be discussed in the article
|
Notes
| DDT |
|---|
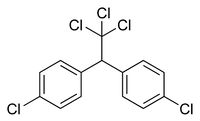
|
| Formula |
| C14H9C15 |
DDT, like other organochlorine pesticides enter the marine environment mainly through inputs from water and air, as a result of their use in agriculture. Although the use of DDT in Western countries has been forbidden since the 1970's, they are still detected in the marine environment due to it's extreme stability (half-life of 15 years), to illegal use or to use elsewhere (third world countries). DDT is metabolised into dichlorodiphenyldichloroethylene (DDE) which is equally toxic. Therefore, to asses the risk of DDT exposure, the sum both contaminants needs to be taken into account. This also means that when you encounter a high DDT/DDE ratio, the contamination must be a recent one[2].
DDT affects the central nervous system of insects and other animals. This results in hyperactivity, paralysis and death. DDT also affects eggshell production in birds and the endocrine system of most animals[3].
DDT has a very high tenancy towards biomagnification. When in a simple ecosystem the background concentration is equal to 1, then zooplankton can accumulate concentrations of 13.000, small fish species concentrations of 170.000, large fishes up to 670.000 and finally birds will accumulate concentrations up to 8.300.000[4]. DDT has been found in all marine ecosystems, including the Antarctic and the deep sea. It can be found in all components of the marine food web.
Case studies
PCBs and organochlorine pesticides in Antarctic algaePCBs and organochlorine pesticides in shrimp from the Belgian North Sea
Organochlorine pesticides in Harbour porpoises
See also
References
- ↑ Lawrence E (ed.), 2000. Henderson’s Dictionary of Biological Terms. 12th edition. Prentice Hall, Pearson Education Limited. Harlow, Great Britain.
- ↑ OSPAR Commission 2000. Quality Status Report 2000, OSPAR Commission, London
- ↑ Kennish, M. J. (1996): Practical Handbook of Estuarine and Marine Pollution, CRC Press 524 pp
- ↑ Janssen, C. (2008). Wat is giftig en wat niet, de zee onder de loep. Het Laboratorium voor Milieutoxicologie en Aquatische Ecologie, in: Goffin, A. et al. (Ed.) (2008). UGent aan Zee. pp. 54-61
Please note that others may also have edited the contents of this article.
|