Difference between revisions of "Portal:Eutrophication"
From Coastal Wiki
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div style="width:34%; float:right;"> | <div style="width:34%; float:right;"> | ||
| − | {{/box-header|Learn more about eutrophication|{{FULLPAGENAME}}/ | + | {{/box-header|Learn more about eutrophication|{{FULLPAGENAME}}/Eutrophication|}} |
| − | {{{{FULLPAGENAME}}/ | + | {{{{FULLPAGENAME}}/Eutrophication}} |
{{/box-footer|}} | {{/box-footer|}} | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 13:57, 17 February 2014
edit
Eutrophication
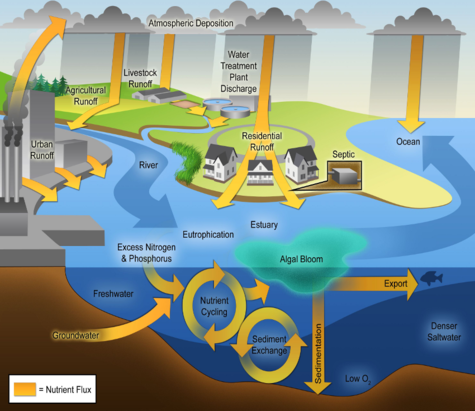
Eutrophication ('eu' = true or well; 'trophy' = food) is a leading threat to water quality around the world. In the North Sea and English Channel, the phenomenon is related to two major activities: agriculture and industry. This gives an excess of nutrients (nitrates, phosphates,...) in the water. This enrichment promotes the growth of algae. A small increase in algal biomass does not have any adverse effect on the ecosystem and can even result in an increase in certain fish populations. An over-stimulation of the growth of algae (an algal bloom), however, can lead to turbidity of the water. When the algae die, the water may be temporarily low in oxygen (hypoxia) what can result in the death of many fish.
edit
Concept drawing
edit
Learn more about eutrophication
European legislations regarding eutrophication
Eutrophication causes and consequences
Monitoring
Modelling
Eutrophication in the news
Dictionary
What are Portals? | List of portals