Difference between revisions of "Flucythrinate"
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
[[OSPAR List of priority substances|Included in the OSPAR list of substances of priority action]] | [[OSPAR List of priority substances|Included in the OSPAR list of substances of priority action]] | ||
| − | |||
<P> | <P> | ||
<BR> | <BR> | ||
<P> | <P> | ||
| − | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| − | + | {{author | |
| + | |AuthorID=19826 | ||
| + | |AuthorFullName=Daphnis De Pooter | ||
| + | |AuthorName=Daphnisd}} | ||
[[Category:Coastal and marine pollution]] | [[Category:Coastal and marine pollution]] | ||
Revision as of 15:13, 20 March 2013
Definition of flucythrinate:
Flucythrinate is a pesticide belonging to the group of pyrethroids. It is used to control insects in apples, cabbage, field corn, head lettuce, pears and cotton. Flucythrinate is a dark amber, viscous liquid[1].
This is the common definition for flucythrinate, other definitions can be discussed in the article
|
Notes
| Flucythrinate |
|---|
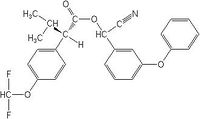
|
| Formula |
| C26H23F2NO4 |
The use of this pesticide has been restricted in the US and banned in the European Union since 2003[2].
Flucythrinate has a low water solubility and a high tendency to adsorb to organic matter and suspended particles. It is therefore mostly associated with soils and sediments. In the soil it is moderately stable, with a half-life of 21 days. It has a low tendency towards bioaccumulate.
Flucythrinate is extremely toxic to fish, which die when exposed to concentrations above 10 ug/l. Marine mammals and sea birds are much more tolerant to the compound, as the are only affected after consumption of several grams per kilogram of body weight. Marine mammals and sea birds also seem to able to excrete flucythrinate more rapidly, which is expected to result in a higher tolerance to chronic exposure[1].
Environmental standards and legislation
Included in the OSPAR list of substances of priority action
References
Please note that others may also have edited the contents of this article.
|