Difference between revisions of "Template:This weeks featured article"
From Coastal Wiki
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Coastal Hydrodynamics And Transport Processes | '''Coastal Hydrodynamics And Transport Processes | ||
''' | ''' | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:intensity.jpg|thumb|left|500px|'''Figure 4: Main differences between extensive, semi-intensive and intensive mariculture systems in terms of resource use and potential environmental risk (Tacon and Foster, 2003)'''<ref>Tacon AGJ, Forster IP (2003): Aquafeeds and the environment: political implications; Aquaculture 226, p. 181-189</ref>).]] |
| − | + | Generally it is aquaculture in marine environments. | |
| − | + | If one takes a closer look there are different definitions. Some limit mariculture to the raising of marine plants and animals in the ocean itself (EEA, 2008<ref>European Environmental agency; www.glossary.eea.europa.eu/EEAGlossary/M/mariculture, 01/28/08</ref>). | |
| − | < | + | Others also include species from brackish water and include culture methods that take place in salty and brackish water that is not situated in the ocean (CBD, 2004<ref name="CBD">Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity (2004): Solutions for sustainable mariculture-avoiding the adverse effects of mariculture on biological diversity, CBD Technical Series No. 12</ref>, Wecker, 2006<ref name="wecker">Wecker B (2006): Nährstofffluss in einer geschlossenen Kreislaufanlage mit integrierter Prozesswasserklärung über Algenfilter-Modell und Wirklichkeit.; http://e-diss.uni-kiel.de/math-nat.html, 02/15/08</ref>) |
| − | + | . Here this wider definition is referred to... | |
| − | |||
Revision as of 13:23, 2 July 2010
Coastal Hydrodynamics And Transport Processes
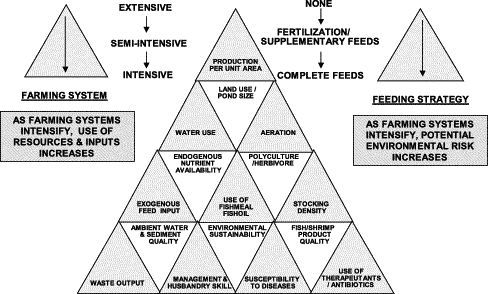
Figure 4: Main differences between extensive, semi-intensive and intensive mariculture systems in terms of resource use and potential environmental risk (Tacon and Foster, 2003)[1]).
Generally it is aquaculture in marine environments. If one takes a closer look there are different definitions. Some limit mariculture to the raising of marine plants and animals in the ocean itself (EEA, 2008[2]). Others also include species from brackish water and include culture methods that take place in salty and brackish water that is not situated in the ocean (CBD, 2004[3], Wecker, 2006[4])
. Here this wider definition is referred to...- ↑ Tacon AGJ, Forster IP (2003): Aquafeeds and the environment: political implications; Aquaculture 226, p. 181-189
- ↑ European Environmental agency; www.glossary.eea.europa.eu/EEAGlossary/M/mariculture, 01/28/08
- ↑ Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity (2004): Solutions for sustainable mariculture-avoiding the adverse effects of mariculture on biological diversity, CBD Technical Series No. 12
- ↑ Wecker B (2006): Nährstofffluss in einer geschlossenen Kreislaufanlage mit integrierter Prozesswasserklärung über Algenfilter-Modell und Wirklichkeit.; http://e-diss.uni-kiel.de/math-nat.html, 02/15/08