Difference between revisions of "Glyphosate"
() |
(→Notes) |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
The glyphosate is used as a herbicide to control a number of broadleaf weeds and grasses. The principal food use sites | The glyphosate is used as a herbicide to control a number of broadleaf weeds and grasses. The principal food use sites | ||
| − | include corn, wheat, sorghum, citrus and stone fruits, potatoes and onions, asparagus, coffee, peanuts, and pineapples. There are also a number of non-food use sites including ornamental, turf, forestry, and industrial rights-of-way (rail road tracks) | + | include corn, wheat, sorghum, citrus and stone fruits, potatoes and onions, asparagus, coffee, peanuts, and pineapples. There are also a number of non-food use sites including ornamental, turf, forestry, and industrial rights-of-way (rail road tracks)<ref name="Epa">[http://www.epa.gov/oppsrrd1/REDs/old_reds/glyphosate.pdf EPA 1993 Registration Eligibility Decision for Glyphosate ]</ref>. |
| − | Although it is rather soluble in water (11,6 g/l), in application sites, glyphosate [[adsorption|adsorbs]] to soils and should stay in the top 15 cm. This reduces its exposure to surface waters and the marine environment. Glyphosate is a rather unstable molecule that can be biodegraded. In most environments, its [[half-life]] is less than 30 days, although in some cases it takes up to 174 days to half its environmental concentration. Glyphosate is usually biodegraded to [[AMPA]] | + | Although it is rather soluble in water (11,6 g/l), in application sites, glyphosate [[adsorption|adsorbs]] to soils and should stay in the top 15 cm. This reduces its exposure to surface waters and the marine environment. Glyphosate is a rather unstable molecule that can be biodegraded. In most environments, its [[half-life]] is less than 30 days, although in some cases it takes up to 174 days to half its environmental concentration. Glyphosate is usually biodegraded to [[AMPA]]<ref name="Epa">[http://www.epa.gov/oppsrrd1/REDs/old_reds/glyphosate.pdf EPA 1993 Registration Eligibility Decision for Glyphosate ]</ref> . |
| − | Glyphosate doesn't have a tendency to [[bioaccumulation|bioaccumulate]] or [[biomagnification|biomagnify]] | + | Glyphosate doesn't have a tendency to [[bioaccumulation|bioaccumulate]] or [[biomagnification|biomagnify]]<ref name="Epa">[http://www.epa.gov/oppsrrd1/REDs/old_reds/glyphosate.pdf EPA 1993 Registration Eligibility Decision for Glyphosate ]</ref>. |
| − | Concentrations of 10µg/l might cause acute toxicity in one water flea [[species]], while other [[pollution and zooplankton|zooplankton]] can tolerate short exposure to glyphosate concentrations of 25 mg/l. Concentrations which cause acute toxicity in [[pollution and benthic fishes|fish]] range from 5 mg/l to 19 g/l, depending on the species | + | Concentrations of 10µg/l might cause acute [[toxic|toxicity]] in one water flea [[species]], while other [[pollution and zooplankton|zooplankton]] can tolerate short exposure to glyphosate concentrations of 25 mg/l. Concentrations which cause acute toxicity in [[pollution and benthic fishes|fish]] range from 5 mg/l to 19 g/l, depending on the species<ref>[http://www.pesticideinfo.org/Detail_Chemical.jsp?Rec_Id=PC33138 www.pesticideinfo.org 25 August 2009]</ref>. |
| − | Concentrations in fresh surface water range between 0.5 and 1700 µg/l | + | Concentrations in fresh surface water range between 0.5 and 1700 µg/l<ref>[http://www.inchem.org/documents/ehc/ehc/ehc159 www.inchem.org 25 August 2009]</ref>. |
<P> | <P> | ||
<BR> | <BR> | ||
<P> | <P> | ||
| + | |||
== Environmental standards and legislation == | == Environmental standards and legislation == | ||
Revision as of 08:40, 5 October 2009
Definition of glyphosate:
Glyphosate was first used as a herbicide in 1973. It's one of the world's most widely used herbicides and is used in 130 countries for the weed control of more than 100 crops[1]. It occurs as a white crystalline solid[2].
This is the common definition for glyphosate, other definitions can be discussed in the article
|
Notes
| Glyphosate |
|---|
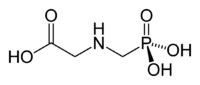
|
| Formula |
| C3H8NO5P |
The glyphosate is used as a herbicide to control a number of broadleaf weeds and grasses. The principal food use sites include corn, wheat, sorghum, citrus and stone fruits, potatoes and onions, asparagus, coffee, peanuts, and pineapples. There are also a number of non-food use sites including ornamental, turf, forestry, and industrial rights-of-way (rail road tracks)[2].
Although it is rather soluble in water (11,6 g/l), in application sites, glyphosate adsorbs to soils and should stay in the top 15 cm. This reduces its exposure to surface waters and the marine environment. Glyphosate is a rather unstable molecule that can be biodegraded. In most environments, its half-life is less than 30 days, although in some cases it takes up to 174 days to half its environmental concentration. Glyphosate is usually biodegraded to AMPA[2] .
Glyphosate doesn't have a tendency to bioaccumulate or biomagnify[2].
Concentrations of 10µg/l might cause acute toxicity in one water flea species, while other zooplankton can tolerate short exposure to glyphosate concentrations of 25 mg/l. Concentrations which cause acute toxicity in fish range from 5 mg/l to 19 g/l, depending on the species[3].
Concentrations in fresh surface water range between 0.5 and 1700 µg/l[4].
Environmental standards and legislation
Included in the water framework list of priority substances
See also
Glyphosate on ED North Database