Difference between revisions of "PBDE"
(→Notes) |
|||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDE) are part of the wider group of brominated flame retardants. PBDEs are the most widely utilized group of these flame retardants and can make up 5 to 30% of the weight of plastics. They are mixed into the plastic polymers but are not chemically bound to the plastic, which makes it easy for them to leach into the environment. The number of broom atoms and their positions can vary. This leads to a total of 209 different forms of PBDEs. The form which poses the highest environmental | + | Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDE) are part of the wider group of brominated flame retardants. PBDEs are the most widely utilized group of these flame retardants and can make up 5 to 30% of the weight of plastics. They are mixed into the plastic polymers but are not chemically bound to the plastic, which makes it easy for them to leach into the environment. The number of broom atoms and their positions can vary. This leads to a total of 209 different forms of PBDEs. The form which poses the highest environmental threat is '''pentabromodiphenyl ether'''. |
| − | ''' | + | |
They are widespread in the environment, persistent and have been detected in tissues of animals from all marine environments. Like PCBs, PBDEs are strongly hydrophobic and therefore [[adsorption|adsorb]] to particles and lipids causing them to [[biomagnification|biomagnify]], even more than PCBs. Therefore, the highest concentrations of PBDEs have been measured in [[pollution and marine mammals|marine mammals]], [[pollution and pelagic fishes|fish]] and [[pollution and sea birds|sea birds]], making them the most vulnerable species for PBDE poisoning. PBDEs are suspected to cause reproductive failures by causing estrogenic effects, as well as cause liver toxicity, thyroid toxicity, and neurodevelopmental toxicity. <ref name = pub>http://www.epa.gov/oppt/pbde/</ref> <ref>Michael Martin, Paul K. S. Lam, Bruce J. Richardson, 2004, An Asian quandary: where have all of the PBDEs gone? Marine Pollution Bulletin, 49, 5-6, 375-382</ref> | They are widespread in the environment, persistent and have been detected in tissues of animals from all marine environments. Like PCBs, PBDEs are strongly hydrophobic and therefore [[adsorption|adsorb]] to particles and lipids causing them to [[biomagnification|biomagnify]], even more than PCBs. Therefore, the highest concentrations of PBDEs have been measured in [[pollution and marine mammals|marine mammals]], [[pollution and pelagic fishes|fish]] and [[pollution and sea birds|sea birds]], making them the most vulnerable species for PBDE poisoning. PBDEs are suspected to cause reproductive failures by causing estrogenic effects, as well as cause liver toxicity, thyroid toxicity, and neurodevelopmental toxicity. <ref name = pub>http://www.epa.gov/oppt/pbde/</ref> <ref>Michael Martin, Paul K. S. Lam, Bruce J. Richardson, 2004, An Asian quandary: where have all of the PBDEs gone? Marine Pollution Bulletin, 49, 5-6, 375-382</ref> | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
<BR> | <BR> | ||
<P> | <P> | ||
| + | |||
== Case studies == | == Case studies == | ||
Revision as of 09:46, 31 August 2009
Definition of polybrominated diphenyl ether:
Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) are a particular class of flame retardant chemicals. These chemicals are often used as flame retardants in plastics for TV cabinets, consumer electronics, wire insulation, personal computers and small appliances. The benefit of these chemicals is their ability to slow the ignition and the rate of fire growth. As a result, they increase the available time to escape in the event of a fire.
[1]
This is the common definition for polybrominated diphenyl ether, other definitions can be discussed in the article
|
Notes
| Polybrominated diphenyl ether |
|---|
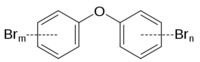
|
| Formula |
| C10H10-XBXO |
Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDE) are part of the wider group of brominated flame retardants. PBDEs are the most widely utilized group of these flame retardants and can make up 5 to 30% of the weight of plastics. They are mixed into the plastic polymers but are not chemically bound to the plastic, which makes it easy for them to leach into the environment. The number of broom atoms and their positions can vary. This leads to a total of 209 different forms of PBDEs. The form which poses the highest environmental threat is pentabromodiphenyl ether.
They are widespread in the environment, persistent and have been detected in tissues of animals from all marine environments. Like PCBs, PBDEs are strongly hydrophobic and therefore adsorb to particles and lipids causing them to biomagnify, even more than PCBs. Therefore, the highest concentrations of PBDEs have been measured in marine mammals, fish and sea birds, making them the most vulnerable species for PBDE poisoning. PBDEs are suspected to cause reproductive failures by causing estrogenic effects, as well as cause liver toxicity, thyroid toxicity, and neurodevelopmental toxicity. [1] [2]
In Western countries there is a ban on the manufacturing of these products since 2005. [3] [4]
Case studies
Pesticides in harbour porpoises
Possible causes for breading failure in common terns
Flame retardants organotin compounds and surfactants in opossum shrimps of the Scheldt estuary.
PBDE through the entire North Sea food web
Environmental standards and legislation
Included in the OSPAR list of substances of priority action
Included in the water framework list of priority substances
See also
OSPAR background document on brominated flame retardants
Octabroomdifenylether (a PBDE) on the ED North Database
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 http://www.epa.gov/oppt/pbde/
- ↑ Michael Martin, Paul K. S. Lam, Bruce J. Richardson, 2004, An Asian quandary: where have all of the PBDEs gone? Marine Pollution Bulletin, 49, 5-6, 375-382
- ↑ http://www.epa.gov/oppt/pbde/
- ↑ http://www.leas.ca/Europe-takes-lead-in-banning-PBDEs.htm